

As described in Chapter 2, the Transportation Improvement Program (TIP) development and project prioritization and funding process consists of numerous phases and is supported by several different funding sources. This appendix includes information about transportation projects that the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) considered for funding through the Highway Discretionary (Regional Target) Program in the federal fiscal years (FFYs) 2023–27 TIP.
To be considered for funding by the MPO, a project must fulfill certain basic criteria. Projects evaluated through the MPO’s Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections, Complete Streets, Intersection Improvements, and Major Infrastructure investment programs must meet these criteria:
For projects evaluated through the MPO’s Community Connections Program, the following criteria apply:
If a project meets the above criteria, it is presented to the MPO board in the Universe of Projects (Table A-1) to be considered for funding. This project list is presented to the MPO board in November and provides a snapshot of information available on projects at that stage in the TIP development. Some projects that get evaluated for funding may not appear in the Universe, as more project information may become available following the compilation of the Universe. In addition, some projects that appear on the Universe list may not be evaluated in a given year if these projects are not actively being advanced by municipal or state planners or if they are not at the minimum required level of design for evaluation. Community Connections projects are not included in the Universe because proponents of those projects apply for funding through a discrete application process, the submission deadline for which is after the presentation of the Universe to the MPO board.
Once a proponent provides sufficient design documentation for a project in the Universe and the municipality or state is actively prioritizing the project for funding, the project can be evaluated by MPO staff. The evaluation criteria used to score projects are based on the MPO’s goals and objectives. After the projects are evaluated, the scores are shared with project proponents, posted on the MPO’s website, and presented to the MPO board for review and discussion. The scores for projects evaluated during development of the FFYs 2023–27 TIP for programming in the MPO’s Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections, Complete Streets, Intersection Improvements, and Major Infrastructure investment programs are summarized in Table A-3. Scores for projects that applied for funding through the MPO’s Community Connections Program during the FFYs 2023–27 TIP cycle are summarized in Table A-4.
As has been mentioned throughout this document, the MPO board approved a suite of changes to the TIP project selection criteria in October 2020. One of the central goals was to create distinct criteria for each investment program to allow for evaluations to be conducted in ways that better reflect the nuances of different types of transportation projects. For this reason, the project selection criteria for each investment program are shown in separate tables in this appendix as follows: Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections (Table A-5); Community Connections (Table A-6); Complete Streets (Table A-7); Intersection Improvements (Table A-8); and Major Infrastructure (Table A-9). Archived project evaluation criteria for all investment programs, which were discontinued in October 2020 after the FFYs 2021–25 TIP cycle, are shown in Tables A-10 and A-11.
In addition to project scores, several other factors are taken into consideration by the MPO when selecting projects for funding. Table A-2 describes many of these elements, including the relationships between the MPO’s FFYs 2023–27 Regional Target projects and the MPO’s Long-Range Transportation Plan (LRTP), studies and technical assistance conducted by MPO staff through the Unified Planning Work Program (UPWP), the federally required performance measures discussed in Chapter 4, and Massachusetts’ modal plans. These projects are listed by MPO investment program. More details about each of these projects are available in the funding tables and project descriptions included in Chapter 3. Performance-related information for the FFYs 2023–27 Regional Target projects is included in Chapter 4, and information about greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions for these projects is available in Appendix B.
Table A-1
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Universe of Projects
| Key | ||||||||||
| Evaluated for FFYs 2022-26 TIP | ||||||||||
| New project in TIP universe for FFYs 2023-27 TIP | ||||||||||
| In 2022-26 universe, not evaluated | ||||||||||
| Municipality | Project Proponent | Project Name | PROJIS | Design Status (as of 11/12/21) | Year Added to Universe | Cost Estimate | Highway District | Notes | Previous Evaluation Score | Score for FFYs 2023-27 TIP? |
| Inner Core | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Boston | Boston | Reconstruction of Albany Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 6 | Pursuing 2022 PRC approval. | N/A | |
| Boston | MassDOT | Reconstruction on Gallivan Boulevard (Route 203), from Neponset Circle to East of Morton Street Intersection | 606896 | PRC approved (2012) | 2018 | $11,500,000 | 6 | Resulted from FFY 2012 Addressing Priority Corridors MPO Study | N/A | |
| Boston | MassDOT | Improvements on Morton Street (Route 203), from West of Gallivan Boulevard to Shea Circle | 606897 | PRC approved (2012) | 2018 | $11,500,000 | 6 | Resulted from FFY 2012 Addressing Priority Corridors MPO Study | N/A | |
| Boston | Boston | Roadway Improvements along Commonwealth Avenue (Route 30), from Alcorn Street to Warren/Kelton Streets (Phase 3 & Phase 4) | 608449 | 25% submitted (9/28/2017) |
2017 or earlier | $31,036,006 | 6 | Last scored for FFYs 2020-24 TIP. | 56 | |
| Boston | MassDOT | Gallivan Boulevard (Route 203) Safety Improvements, from Washington Street to Granite Avenue | 610650 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $5,750,000 | 6 | Priority for District 6. Road safety audit being initiated. | N/A | |
| Brookline | Brookline | Rehabilitation of Washington Street | 610932 | PRC approved (2020) | 2020 | $25,888,631 | 6 | 56.9 | Yes | |
| Chelsea | Chelsea | Reconstruction of Spruce Street, from Everett Avenue to Williams Street | 610675 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $5,408,475 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Chelsea | Chelsea | Reconstruction of Everett Avenue and 3rd Street, from Broadway to Ash Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 6 | N/A | ||
| Chelsea | Chelsea | Park Street & Pearl Street Reconstruction | 611983 | PRC approved (2021) | 2020 | $10,451,525 | 6 | 68.9 | Yes | |
| Chelsea | Chelsea | Reconstruction of Marginal Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2019 | N/A | 6 | N/A | ||
| Lynn | Lynn | Reconstruction of Western Avenue (Route 107) | 609246 | PRC approved (2018) | 2018 | $36,205,000 | 4 | Project programmed in LRTP (FFYs 2025-29) but no longer considered Major Infrastructure by MPO. | 71.4 | Yes |
| Lynn, Salem | MassDOT | Reconstruction of Route 107 | 608927 | PRC approved (2017) | 2020 | $38,155,000 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Melrose | Melrose | Reconstruction of Lebanon Street, from Lynde Street to Malden City Line | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Newton | Newton | Reconstruction of Washington Street, from Church Street to Chestnut Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 6 | N/A | ||
| Revere | Revere | Reconstruction of Ocean Ave, Revere Street, and Revere Beach Boulevard | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Winthrop | Winthrop | Reconstruction & Improvements on Route 145 | 609446 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $7,565,512 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Boston, Brookline | Boston, Brookline | Mountfort St. & Commonwealth Ave. Connection | 608956 | PRC approved (2017) | 2018 | $916,883 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Cambridge | DCR | Intersection Improvements at Fresh Pond Parkway/Gerry's Landing Road, from Brattle Street to Memorial Drive | 609290 | PRC approved (2018) | 2019 | $7,000,000 | 6 | Short-term improvements being initiated. Project may be candidate for funding in future year. | N/A | |
| Everett | MassDOT | Intersection Improvements on Route 16 | 611969 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $15,300,000 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Medford | Medford | Intersection Improvements at Main Street and South Street | 611974 | PRC approved (2021) | 2019 | $8,498,000 | 4 | Project location studied by CTPS. Priority for municipality. | N/A | |
| Newton | MassDOT | Traffic Signal and Safety Improvements at Interchange 127 (Newton Corner) | 609288 | PRC approved (2018) | 2019 | $14,000,000 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Quincy | MassDOT | Intersection Improvements at Route 3A (Southern Artery) and Broad Street | 608569 | PRC approved (2016) | 2020 | $2,900,000 | 6 | Priority for District 6. | N/A | |
| Quincy | Quincy | Intersection Improvements at Willard Street and Ricciuti Drive | 610823 | PRC approved (2020) | 2020 | $1,544,650 | 6 | Project at conceptual stage. 25% design advancing. | N/A | |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Belmont | Belmont | Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) | 609204 | 25% submitted (11/3/2021) | 2018 | $16,703,600 | 4 | 59 | Yes | |
| Boston | Boston | Fenway Multi-Use Path Phase III | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 6 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Everett, Somerville | DCR | Mystic River Bicycle and Pedestrian Crossing | 612004 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $38,218,334 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Lynn, Nahant | Lynn, Nahant | Northern Strand Extension | 610919 | DPH (11/17/2021) | 2020 | $9,363,750 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Medford | Medford | Shared Use Path Connection at the Route 28/ Wellington Underpass | 611982 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $3,625,000 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Boston | Boston | Bridge Replacement, Meridian Street Over Chelsea Creek (Andrew P. McArdle Bridge) | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 6 | Project not programmed in LRTP (likely to meet MPO definition for Major Infrastructure based on cost) | N/A | |
| Revere, Malden | MassDOT | Improvements on Route 1 (NB) Add-A-Lane | 610543 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $7,210,000 | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| Revere, Saugus | Revere, Saugus | Roadway Widening on Route 1 North (Phase 2) | 611999 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $2,397,600 | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| Somerville | Somerville | McGrath Boulevard Project | 607981 | PRC approved (2014) | 2017 or earlier | $88,250,000 | 4 | LRTP project (FFYs 2025-29) | 66.2 | Yes |
| Minuteman Advisory Group on Interlocal Coordination | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Lexington | Lexington | Route 4/225 (Bedford Street) and Hartwell Avenue | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2019 | $30,557,000 | 4 | Project programmed in LRTP (FFYs 2030-34) but no longer considered Major Infrastructure by MPO. | N/A | |
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Littleton | Littleton | Intersection Improvements at Route 119/Beaver Brook Road | 610702 | PRC approved (2020) | 2020 | $3,120,110 | 3 | MassDOT agreed to fund design after 25% design approved. | N/A | |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Concord | Concord | Assabet River Pedestrian Bridge | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | $2,000,000-$3,600,000 | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Acton | MassDOT | Intersection Improvements at Route 2 and Route 27 Ramps | 610553 | PRC approved (2019) | 2020 | $3,480,000 | 3 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). Priority for District 3 and Town of Acton. | N/A | |
| Concord | Concord | Reconstruction & Widening on Route 2, from Sandy Pond Road to Bridge over MBTA/B&M Railroad | 608015 | PRC approved (2014) | 2019 | $8,000,000 | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| MetroWest Regional Collaborative | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Weston | Weston | Reconstruction on Route 30 | 608954 | 25% submitted (10/19/2020) | 2018 | $15,203,814 | 6 | Design Public Hearing targeted for January/February 2022. | 49.2 | Yes |
| Holliston | Holliston | Reconstruction of Concord Street (Route 126) | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Added through subregional outreach. Project is municipal priority, as it's tied to necessary below-grade sewer work. | N/A | |
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Framingham | MassDOT | Roundabout Construction at Salem End Road, Badger Road and Gates Street | 609280 | PRC approved (2018) | 2019 | $2,520,000 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Weston | Weston | Intersection Improvements - Boston Post Road (Route 20) at Wellesley Street | 608940 | 25% resubmitted (8/20/2021) | 2018 | $2,394,045 | 6 | Design Public Hearing targeted for December 2021. | 45.6 | Yes |
| Weston | Weston | Intersection Improvements - Signalization of Route 20 at Highland Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 6 | Added through subregional outreach. | N/A | |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Natick | Natick | Cochituate Rail Trail Extension, from MBTA Station to Mechanic Street | 610691 | PRC approved (4/30/2020) | 2020 | $4,500,110 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Framingham | Framingham | Intersection Improvements at Route 126/135/MBTA and CSX Railroad | 606109 | PRC approved (2010) | 2019 | $115,000,000 | 3 | LRTP project (FFYs 2030-34). | N/A | |
| Natick | Natick | Bridge Replacement, Route 27 (North Main Street) over Route 9 (Worcester Street) and Interchange Improvements | 605313 | 25% resubmitted (2/12/2020) | 2018 | $45,097,350 | 3 | LRTP project (FFYs 2025-29). High priority for District 3. Updated 25% design anticipated February 2022. | 56.4 | Yes |
| North Suburban Planning Council | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Burlington | Burlington | Town Center Complete Streets Improvements | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | N/A | ||
| Burlington, Billerica | MassDOT | Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 3A | 610704 | 25% submitted (1/12/2021) | 2020 | $4,406,512 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Lynnfield | Lynnfield | Reconstruction of Summer Street | 609381 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $21,521,921 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Reading | Reading | Reading Downtown Improvement Project | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | $7-$8 million | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Stoneham | Stoneham | Reconstruction of South Main Street, from Town Center to South Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | N/A | ||
| Wakefield | Wakefield | Main Street Reconstruction | 610545 | PRC approved (2019) | 2020 | $26,382,000 | 4 | 41.8 | Yes | |
| Winchester | Winchester | Town Center Complete Streets Improvements | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | N/A | ||
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Stoneham | Stoneham | Intersection Improvements at Main Street (Route 28), Franklin Street, and Central Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Stoneham, Wakefield | Stoneham, Wakefield | Mystic Highlands Greenway Project | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | N/A | ||
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Burlington | MassDOT | Improvements at I-95 (Route 128)/Route 3 Interchange | 609516 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $3,001,500 | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| Reading | MassDOT | Improvements on I-95 | 609527 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $14,980,000 | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| North Shore Task Force | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Beverly, Manchester-by-the-Sea | MassDOT | Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 127 | 607707 | PRC approved (2013) | 2018 | $2,300,000 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Danvers | Danvers | Reconstruction on Collins Street, from Sylvan Street to Centre and Holten Streets | 602310 | 75% submitted (3/5/2010) | 2017 or earlier | $5,183,121 | 4 | Updated 75% design submission needed for project to move forward. Last scored for FFYs 2020-24 TIP. | 46 | |
| Ipswich | Ipswich | Reconstruction of County Road, from South Main Street to East Street | 611975 | PRC approved (2021) | 2020 | $5,653,500 | 4 | 45.4 | Yes | |
| Ipswich | Ipswich | Argilla Road Adaptation Project | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | $4,000,000 | 4 | Municipal priority for funding. | N/A | |
| Marblehead | Marblehead | Bridge Replacement, M-04-001, Village Street over Marblehead Rail Trail (Harold B. Breare Bridge) | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2019 | N/A | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Manchester-by-the-Sea | Manchester-by-the-Sea | Pine Street - Central Street (Route 127) to Rockwood Heights Road | N/A | Pre-PRC; PNF submitted (12/27/16) | 2017 or earlier | N/A | 4 | N/A | ||
| Manchester-by-the-Sea | Manchester-by-the-Sea | Bridge Replacement, M-02-001 (8AM), Central Street (route 127) over Saw Mill Brook | 610671 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $4,350,000 | 4 | 34.8 | Yes | |
| Salem | MassDOT | Reconstruction of Bridge Street, from Flint Street to Washington Street | 5399 | 25% submitted (8/20/2004) | 2017 or earlier | $24,810,211 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Salem | Salem | Boston Street Improvements | 609437 | 25% resubmitted (10/7/2021) | 2019 | $12,480,000 | 4 | 56.1 | Yes | |
| Wenham | Wenham | Safety Improvements on Route 1A | 609388 | 25% submitted (12/21/2020) | 2019 | $3,629,036 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Wenham | Wenham | Roadway Reconstruction on Larch Row and Dodges Row | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2019 | $800,000 | 4 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Essex | Essex | Targeted Safety Improvements on Route 133 (John Wise Avenue) | 609315 | PRC approved (2019) | 2019 | $2,135,440 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Peabody, Salem | Peabody, Salem | Riverwalk Project | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | MVP grant issued for project design. | N/A | |
| Swampscott | Swampscott | Rail Trail Construction | 610666 | 25% submitted (1/27/2021) | 2019 | $7,700,000 | 4 | 62.4 | Yes | |
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Beverly | Beverly | Route 128 and Brimbal Avenue Interchange Project (Phase II) | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 4 | Project not programmed in LRTP (meets MPO roadway classification requirement). | N/A | |
| South Shore Coalition | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Holbrook | Holbrook | Corridor Improvements and Related Work on South Franklin Street (Route 37) from Snell Street to King Road | 608543 | PRC approved (2017) | 2018 | $4,000,200 | 5 | N/A | ||
| Rockland | Rockland | Reconstruction of VFW Drive/Weymouth Street, from Union Street to the Hingham Town Line | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | $12,100,000 | 5 | N/A | ||
| Weymouth | MassDOT | Reconstruction on Route 3A, Including Pedestrian and Traffic Signal Improvements | 608231 | PRC approved (2016) | 2017 or earlier | $10,780,100 | 6 | Pre-25% package submitted in July 2021. | N/A | |
| Weymouth | MassDOT | Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 3A | 608483 | PRC approved (2016) | 2018 | $2,400,000 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Cohasset | Cohasset | Intersection Improvements at Route 3A and King Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 5 | Added through subregional outreach. | N/A | |
| Hull | Hull | Intersection Improvements at George Washington Boulevard and Barnstable Road/ Logan Avenue | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 5 | Added through subregional outreach. | N/A | |
| South West Advisory Planning Committee | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Bellingham | Bellingham | South Main Street (Route 126) - Elm Street to Douglas Drive Reconstruction | N/A | Pre-PRC; PNF submitted (3/13/17) | 2017 or earlier | N/A | 3 | N/A | ||
| Franklin | MassDOT | Resurfacing and Intersection Improvements on Route 140, from Beaver Street to I-495 Ramps | 607774 | PRC approved (2014) | 2018 | $4,025,000 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Medway | Medway | Improvements on Route 109 West of Highland Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Milford | MassDOT | Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 16 | 612091 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $4,192,500 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Millis | Millis | Town Center Improvements | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Wrentham | Wrentham | Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 1 | 608497 | PRC approved (2016) | 2020 | N/A | 5 | 25% design anticipated July 2022. | N/A | |
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Medway | Medway | Traffic Signalization at Trotter Drive and Route 109 | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Sherborn | Sherborn | Intersection Improvements at Route 16 and Maple Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Wrentham | Wrentham | Intersection Improvements on Route 1A at North and Winter Street | 610676 | 25% submitted (8/13/2021) | 2020 | $2,649,000 | 5 | N/A | Yes | |
| Wrentham | Wrentham | Intersection Improvements at Randall Road and Route 1A | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | $2,649,000 | 5 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Wrentham | Wrentham | Intersection Improvements at Route 1A and Route 140 | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 5 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Franklin | Franklin | Southern New England Trunk Trail (SNETT) Extension, from Grove Street to Franklin Town Center | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | ||
| Hopkinton | Hopkinton | Campus Trail Connector, Shared Use Trail Construction | 611932 | PRC approved (2020) | 2020 | $1,750,700 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Norfolk, Walpole, and Wrentham | Norfolk | Metacomet Greenway | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 5 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Sherborn | Sherborn | Upper Charles River Trail Extension to Framingham City Line | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Bellingham | MassDOT | Ramp Construction & Relocation, I-495 at Route 126 (Hartford Avenue) | 604862 | PRC approved (2006) | 2017 or earlier | $13,543,400 | 3 | High priority for District 3 | N/A | |
| Wrentham | Wrentham | I-495 North Slip Ramp Improvements at Route 1A | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2020 | N/A | 5 | Project at conceptual stage. | N/A | |
| Three Rivers Interlocal Council | ||||||||||
| Complete Streets | ||||||||||
| Canton, Milton | MassDOT | Roadway Improvements on Route 138 | 608484 | PRC approved (2016) | 2020 | $18,467,500 | 6 | Milton also in ICC subregion. Project a high priority for the TRIC subregion. District is working to refine scope. | N/A | |
| Medfield | Medfield | Reconstruction of Route 109 | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Added through subregional outreach. | N/A | |
| Milton | MassDOT | Reconstruction on Granite Avenue, from Neponset River to Squantum Street | 608406 | 25% submitted (2/10/2017) | 2017 or earlier | $3,665,146 | 6 | Milton also in ICC subregion. | N/A | |
| Milton | Milton | Adams Street Improvements, from Randolph Avenue to Eliot Street | 610820 | PRC approved (2020) | 2020 | $1,799,330 | 6 | Milton also in ICC subregion. | N/A | |
| Needham | Needham | Reconstruction of Highland Avenue, from Webster Street to Great Plains Avenue | 612536 | PRC approved (2021) | 2021 | $10,402,402 | 6 | Needham also in ICC subregion. | N/A | |
| Westwood | Westwood | Reconstruction of Canton Street | 608158 | PRC reapproved (2021) | 2017 or earlier | $14,254,274 | 6 | Priority for municipality. | N/A | |
| Intersection Improvements | ||||||||||
| Foxborough | Foxborough | Intersection Signalization at Route 140 (Commercial Street) and Walnut Street | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | $5,000,000 | 5 | Added through subregional outreach. Town has advanced design outside of TIP process. District supports project. | N/A | |
| Medfield | Medfield | Intersection Improvements at West Street and North Meadows Road (Route 27) | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 3 | Added through subregional outreach. | N/A | |
| Milton | Milton | Intersection Improvements - Squantum Street at Adams Street | 608955 | 25% submitted (11/19/2020) | 2018 | $2,311,203 | 6 | Milton also in ICC subregion. | 34.4 | Yes |
| Bicycle and Pedestrian | ||||||||||
| Canton | Canton | Warner Trail Extension, from Sharon to Blue Hills Reservation | N/A | Pre-PRC | 2021 | N/A | 6 | Added through subregional outreach. Feasibility study currently underway. | N/A | |
| Major Infrastructure | ||||||||||
| Canton, Westwood | MassDOT | Interchange Improvements at I-95 / I-93 / University Avenue / I-95 Widening | 87790 | 25% submitted (7/25/14) | 2017 or earlier | $202,205,994 | 6 | Project not programmed in LRTP. Last scored for FFYs 2020-24 TIP. | 47 | |
Table A-2
FFYs 2023–27 Regional Target Projects and Their Relationships to Plans and Performance Measures
|
ID |
Project Name |
MPO Investment Program |
Project Description |
MPO Municipalities |
Programming Year (FFY) |
Planning Relationships |
Relationships to Performance Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
609204 |
Belmont–Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) |
Bicycle and Pedestrian |
Connect the Fitchburg Cutoff Bike Path at Brighton Street with the Clark Street pedestrian bridge west of Belmont Center. Construct an underpass beneath the commuter rail tracks at Channing Road and Alexander Avenue. |
Belmont |
2026 |
This project will extend the MassDOT Off-Street High Comfort Bike Network, as identified in the 2019 Massachusetts Bicycle Plan. |
This project is expected to improve safety for bicyclists and pedestrians, including by constructing an underpass to allow for safe passage beneath the commuter rail tracks. It will add more than a mile of community path and connect to the existing Fitchburg Cutoff Bike Path. By extending and improving the region’s bicycle network and improving access to local destinations, this project is expected to increase non-SOV travel. It is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
609211 |
Peabody–Independence Greenway Extension |
Bicycle and Pedestrian |
Extend the Independence Greenway from the North Shore Mall to central Peabody. |
Peabody |
2024 |
This project will extend the MassDOT Off-Street High Comfort Bike Network, as identified in the 2019 Massachusetts Bicycle Plan. |
This project is expected to improve safety for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will create more than a mile of bike trail network and bring the Independence Greenway’s total length to eight miles. By extending the region’s bicycle network, this project is expected to increase non-SOV travel. It is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
610544 |
Peabody–Multi-Use Path Construction of Independence Greenway at Interstate 95 and Route 1 |
Bicycle and Pedestrian |
Construct a new multi-use paved path along the abandoned railbed between two existing segments of the Independence Greenway in Peabody and create a connection to the existing Border to Boston trailhead at Lowell Street. |
Peabody |
2025 |
This project will extend the MassDOT Off-Street High Comfort Bike Network, as identified in the 2019 Massachusetts Bicycle Plan. |
This project will create nearly two miles of multi-use trail, connect other segments of the Independence Greenway, and create a link to the Border to Boston trail. By connecting these sections of the regional bike network, this project is expected to increase non-SOV travel. Improved signalization near ramps to Route 1 may help facilitate motorized and nonmotorized traffic flow and reduce PHED on this NHS corridor. This project is also expected to improve safety for bicyclists and pedestrians and to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
610666 |
Swampscott–Rail Trail Construction |
Bicycle and Pedestrian |
Create a 2.1-mile rail trail that connects to the existing Marblehead Rail Trail. Construct a pedestrian bridge at Paradise Road (Route 1A). |
Swampscott |
2027 |
This project would connect sections of the MassDOT Off-Street High Comfort Bike Network, as identified in the 2019 Massachusetts Bicycle Plan. |
This project will create a 2.1 mile multi-use trail that connects to the existing Marblehead Rail Trail and provides an off-road trail segment for the East Coast Greenway. By connecting these sections of the regional bike network and supporting access to local destinations, this project is expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is also expected to improve safety for bicyclists and pedestrians and to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12702 |
Acton–Bicycle Parking along the Bruce Freeman Rail Trail |
Community Connections |
Install three bike racks at key locations along Great Road and the Bruce Freeman Rail Trail. |
Acton |
2023 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel in the region by enhancing bicycle amenities on the region’s bicycle network. This project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12704 |
Belmont–Chenery Middle School Bicycle Parking |
Community Connections |
Install a shelter over an existing bicycle rack at Chenery Middle School, which may serve as a proof-of-concept for future bicycle parking expansion. |
Belmont |
2023 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel in the region by enhancing bicycle amenities. It is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12695 |
Cambridge–Bluebikes Station Replacement and System Expansion |
Community Connections |
Install two new BlueBikes bikeshare stations and replace five existing stations to ensure a state-of-good-repair. |
Cambridge |
2023 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by enhancing and expanding bicycling options in Cambridge. It is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12114 |
Canton–Royall Street Shuttle |
Community Connections |
Establish a shuttle service connecting Canton’s Royall Street employment cluster with the MBTA Route 128 commuter rail station and Ashmont, Mattapan Trolley, and Quincy Adams rapid transit stations. |
Canton |
2022 (Past) |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by providing a new transit option. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Canton. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12700 |
Cape Ann Transportation Authority (CATA)–CATA On Demand Microtransit Service Expansion |
Community Connections |
Expand existing CATA On Demand microtransit service to Rockport and to an additional neighborhood in Gloucester, and to help customers reach a wider array of essential destinations. |
Gloucester, Rockport |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by expanding CATA’s microtransit service to new areas and supporting its ability to serve customers beyond those commuting to transit or specific employment centers. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Gloucester and Rockport. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12696 |
Malden, Medford–BlueBikes System Expansion |
Community Connections |
Construct three new BlueBikes bikeshare stations in Medford and one in Malden. |
Malden, Medford |
2023 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by expanding bicycling options in Medford and Malden. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12701 |
MetroWest Regional Transit Authority (MWRTA) –CatchConnect Microtransit Service Expansion |
Community Connections |
Expand MWRTA’s CatchConnect microtransit service to Hudson and Marlborough, which will support connections to MWRTA’s fixed-route network. |
Hudson, Marlborough |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by expanding microtransit service to new areas. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Hudson and Marlborough. This project is expected to help reduce CO2 emissions. |
S12703 |
Montachusett Regional Transit Authority (MART) –MART Microtransit Service |
Community Connections |
Establish an on-demand microtransit service that will serve Bolton, Boxborough, Littleton, and Stow. |
Bolton, Boxborough, Littleton, and Stow |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by providing a new transit option. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Boxborough, Bolton, Littleton, and Stow. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12125 |
Newton–Newton Microtransit Service |
Community Connections |
Implement a new dynamically routed microtransit service that will provide shared, first- and last-mile rides between three MBTA rail lines and the Wells Avenue Business District before expanding citywide. |
Newton |
2021–22 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by providing a new transit option. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Newton. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12694 |
Newton–NewMo Microtransit Service Expansion |
Community Connections |
Expand an existing Newton-wide microtransit service (see project S12125) to include stops in six neighboring municipalities. |
Newton |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by expanding the reach of Newton’s existing microtransit service. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in multiple MPO communities. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12698 |
Salem–BlueBikes System Expansion |
Community Connections |
Construct three new BlueBikes bikeshare stations to expand the bikeshare network in Salem. |
Salem |
2023 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by expanding bicycling options in Salem. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12699 |
Stoneham–Stoneham Shuttle Service |
Community Connections |
Create a shuttle service to foster east-west connections between Stoneham and neighboring communities. |
Stoneham |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by providing a new transit option. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes Stoneham. It is expected to help reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
S12697 |
Watertown–Pleasant Street Shuttle Service Expansion |
Community Connections |
Expand a recently-launched shuttle service along the Pleasant Street corridor in Watertown by reducing headways. Support the service’s transition to using electric vehicles. |
Cambridge, |
2023–25 |
N/A |
This project may increase non-SOV travel by supporting more frequent service on the Pleasant Street corridor. It may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS by providing an alternative to SOV travel on NHS routes in Cambridge and Watertown. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608348 |
Beverly–Reconstruction of Bridge Street |
Complete Streets |
Improve the roadway cross section, pavement, signals, and bicycle and pedestrian accommodations in the project corridor. |
Beverly |
2023 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 HSIP all-mode crash cluster location, and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project improves signal and geometry improvements that may support increased reliability and reduced PHED on nearby Route 62, which is on the NHS. It will also provide bicycle-on-shoulder lanes and improved sidewalks, which may encourage non-SOV travel. This project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
606453 |
Boston–Improvements on Boylston Street |
Complete Streets |
Improve the roadway cross section, signals, and bicycle and pedestrian accommodations in the project corridor. |
Boston |
2024 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 HSIP all-mode crash cluster location, a 2010–19 HSIP bicycle crash cluster location, and a 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster location. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than two lane miles of substandard NHS pavement, will address reliability needs on an unreliable NHS segment, and may also reduce PHED on that segment. It will improve substandard sidewalks and add bicycle lanes in the project corridor; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. The project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
610932 |
Brookline–Rehabilitation of Washington Street |
Complete Streets |
Replace signals, reconstruct sidewalks and pavement, and provide protected bicycle facilities and dedicated bus pull-out spaces in the Washington Street corridor between Washington Square and Brookline Village. |
Brookline |
2027 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps two 2010–19 HSIP bicycle crash cluster locations and a 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster location. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve substandard sidewalks, implement bicycle lanes, upgrade signals to include TSP, and add bus shelters to the corridor; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
611983 |
Chelsea–Park and Pearl Street Reconstruction |
Complete Streets |
Improve safety and mobility on Park and Pearl Street by improving signals and roadway geometry, reconstructing sidewalks, and adding bicycle facilities.
|
Chelsea |
2027 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 HSIP all-mode crash cluster location, a 2010–19 HSIP bicycle crash cluster location, and two 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster locations. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project will reconstruct sidewalks, improve bicycle amenities, and implement TSP; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608007 |
Cohasset, Scituate– Corridor Improvements and Related Work on Justice Cushing Highway (Route 3A) from Beechwood Street to Henry Turner Bailey Road |
Complete Streets |
Improve the corridor from the Beechwood Street intersection to the Cohasset/Scituate town line. Upgrade traffic signal equipment, make geometric modifications at intersections, and provide bicycle and pedestrian accommodations. |
Cohasset, Scituate |
2024 |
This project location was studied in “Route 3A Subregional Priority Roadway Study in Cohasset and Scituate” (CTPS, 2014). |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 HSIP all-mode crash cluster location and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to add sidewalks and bicycle lanes in the project corridor, which may encourage non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
607899 |
Dedham–Pedestrian Improvements along Bussey Street |
Complete Streets |
Improve the corridor by reconstructing sidewalks, making minor geometric improvements at the at the intersection with Colburn Street and Clisby Avenue, and provide shared bicycle accommodations. |
Dedham |
2023 |
N/A |
This project is expected to improve transportation safety, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will upgrade sidewalks in the project area, which may encourage non-SOV travel. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
609257 |
Everett– Rehabilitation of Beacham Street, from Route 99 to Chelsea City Line |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct Beacham Street to reduce vehicular collisions and improve bicycle and pedestrian travel. |
Everett |
2025 |
N/A |
This project is expected to improve transportation safety, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve substandard sidewalks and include a shared-use path—both features may encourage non-SOV travel and improve safety performance. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
605168 |
Hingham–Intersection Improvements at Route 3A/Summer Street Rotary |
Complete Streets |
Improve multimodal access between Hingham Center, residential areas, and Hingham Harbor and make safety improvements, including by establishing a small roundabout at the intersection of Route 3A and Summer Street. |
Hingham |
2025 |
This project location was studied in “Summer Street/George Washington Boulevard Subregional Priority Roadway Study in Hingham and Hull” (CTPS, 2016). |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than a lane mile of substandard pavement on the NHS, and the geometric improvements included in the project are expected to help reduce delay and potentially PHED on the NHS. The project is expected to improve substandard sidewalks, add new sidewalks, and add bicycle accommodations, including a shared-use path. These features may support increases in non-SOV travel. The project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
605743 |
Ipswich–Resurfacing and Related Work on Central and South Main Streets |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct the roadway between Mineral Street and Poplar Street to improve the roadway surface. Make minor geometric improvements at intersections, include pedestrian crossings, and improve sidewalks. |
Ipswich |
2024 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than a lane mile of substandard pavement on the NHS. It will upgrade substandard sidewalks, and it is expected to add bicycle lanes; both features may encourage non-SOV travel. The project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
609054 |
Littleton–Reconstruction of Foster Street |
Complete Streets |
Add turning lanes, consolidate curb cuts, and improve bicycle, pedestrian, and vehicular accommodations in the project corridor.
|
Littleton |
2024 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will include a shared-use path, which is expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
603739
|
Lynn–Rehabilitation of Essex Street |
Complete Streets |
Make key bicycle and pedestrian safety improvements and operational improvements, such as signal upgrades, in the project corridor. |
Lynn |
2024 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps five 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster locations and three 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster locations. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. Planned improvements to signals and roadway geometry in the corridor may help improve reliability on nearby unreliable NHS segments and may also reduce PHED on those segments. It is expected to reconstruct substandard sidewalks and add bicycle lanes; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
609246 |
Lynn– Reconstruction of Western Avenue |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct Western Avenue between Centre Street and Eastern Avenue. Improve signal timing, intersection design, and bus stop locations. Implement bicycle and ADA-compliant pedestrian improvements. |
Lynn |
2027 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps five 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster locations, two 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster locations and one 2010–19 HSIP bicycle crash cluster location. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians, and it will improve nearly 4 lane miles of substandard pavement on the NHS. The signal improvements included in the project are expected reduce delay and may help reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS. It will reconstruct sidewalks and add bike lanes, TSP, and bus amenities; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608045 |
Milford–Rehabilitation on Route 16, from Route 109 to Beaver Street |
Complete Streets |
Improve vehicular safety and traffic flow through the implementation of a road diet, additional roadway reconstruction, bicycle and pedestrian accommodations, and enhanced signalization on Route 16 (East Main Street) from Route 109 (Medway Road) to Beaver Street. |
Milford |
2026 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location, and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project is also expected to upgrade substandard sidewalks, add new sidewalks, and add shared-use paths; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. |
Newton, Weston– |
Complete Streets |
Replace a deteriorated bridge over the Charles River. Reconstruct the Route 30 corridor in the vicinity of the I-95 and I-90 interchange, including several I-95 on-ramps. Improve sidewalks and pedestrian amenities, add a bike lane, and develop a segment of shared-use path along the Charles River. |
Newton, Weston |
2024 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster locations and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will replace a deteriorated NHS bridge structure and will improve one lane mile of substandard pavement on the NHS. Signal and geometric improvements on Route 30 and reconfiguration of the Interstate 95 ramps may improve reliability on the NHS. The shared-use path, sidewalk improvements, and bike lane included in the project are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions.
|
|
608933 |
Peabody–Rehabilitation of Central Street |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct pavement and sidewalks, provide bicycle accommodations, upgrade signals, and improve other features within the project corridor. |
Peabody |
2023 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve nearly two lane miles of pavement on the NHS. Upgrades to signals and other elements may address improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project corridor and potentially reduce PHED. The project will upgrade existing sidewalks and add bike lanes; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608707 |
Quincy–Reconstruction of Sea Street |
Complete Streets |
Improve safety in the project corridor by modifying roadway geometry, upgrading signals, constructing median islands, reconstructing sidewalks, and providing bicycle accommodations.
|
Quincy |
2023 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve sidewalks, which may encourage non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce transportation-related pollutants and precursor emissions, including carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide, and volatile organic compounds. |
609432 |
Salem–Boston Street Improvements |
Complete Streets |
Incorporate complete streets elements and a separated bicycle path into the corridor. Add a new signal at Boston Street and Aborn Street and upgrade existing signals at other intersections along the corridor. |
Salem |
2026 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster location, and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve more than a lane mile of substandard NHS pavement. The project includes signal and geometry improvements and is expected to reduce delay, which may reduce PHED and improve reliability on the NHS. It will implement sidewalks on both sides of the corridor and add separated bicycle facilities; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
607777 |
Watertown–Rehabilitation of Mount Auburn Street (Route 16) |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct the corridor from the Cambridge city line to east of Watertown Square. Revise roadway geometry; implement a roadway diet, safety improvements, and bicycle and pedestrian accommodations; and upgrade traffic signal equipment. |
Watertown |
2023 |
This project changes network capacity and is considered regionally significant for air quality modeling. |
The project area overlaps one 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster locations and is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than six lane miles of pavement on the NHS. Signal and other improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project corridor and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve sidewalks and provide bicycle accommodations; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608954 |
Weston–Reconstruction on Route 30 |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct Route 30 within the Town of Weston. Implement geometric improvements and signal additions or upgrades at intersections. Construct a shared-use path the length of the project corridor. |
Weston |
2026 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It includes geometric and signal improvements and is expected to reduce delay, which may help reduce PHED and improve reliability on nearby NHS segments. The shared-use path and pedestrian improvements included in the project are expected to increase non-SOV travel. This project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608051 |
Wilmington (MassDOT)–Reconstruction of Route 38 (Main Street), from Route 62 to the Woburn City Line |
Complete Streets |
Add bicycle lanes, provide sidewalks, improve traffic signals, and reconstruct turn lanes within the project corridor. |
Wilmington |
2025 |
Sections of the Route 38 and 129 corridors in Wilmington are identified as priority bottlenecks in the Destination 2040 Needs Assessment. A portion of this corridor was studied in “Safety and Operations Analysis at Selected Intersections: Main Street at Church Street and Burlington Avenue” (CTPS, 2012). |
The project area overlaps a 2015–17 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project will improve over four lane miles of substandard pavement on the NHS and replace a culvert on the project corridor with a bridge. Signal and geometric improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project corridor and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve existing sidewalks, add new sidewalks, and provide bicycle accommodations—all of these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
607244 |
Winthrop–Revere Street Roadway Improvements |
Complete Streets |
Reconstruct and reclaim pavement; reconstruct sidewalks; and improve intersections and bicycle and pedestrian accommodations in the project corridor. |
Winthrop |
2023 |
N/A |
The project area is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than a mile of substandard sidewalks and add bicycle accommodations, which may encourage non-SOV travel. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions.
|
610662 |
Woburn–Roadway and Intersection Improvements at Woburn Common, Route 38 (Main Street), Winn Street, Pleasant Street, and Montvale Avenue |
Complete Streets |
Improve safety and congestion within the Woburn Common area by making safety and operational improvements, reconfiguring the Woburn Common rotary, and reconstructing and realigning roadways. The project will also reconstruct sidewalks, add bike lanes, and upgrade or add signals in the area. |
Woburn |
2025 |
N/A |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location and a 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster location. The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve nearly two lane miles of substandard pavement on the NHS. Signal and geometric improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project area and potentially reduce PHED. The project will reconstruct sidewalks to support pedestrian safety and mobility. It is also expected to include bicycle accommodations and to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
603739 |
Wrentham (MassDOT)– Construction of Interstate 495/Route 1A Ramps |
Complete Streets |
Construct ramps at the interchange of Route 1A and Interstate 495 to accommodate increased traffic volumes resulting from nearby development.
|
Wrentham |
2024 |
This project area was studied as part of “Route 1A Corridor Study in Wrentham” (CTPS, 2017). |
The project area overlaps two 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster locations and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project is expected to reduce vehicle delay and may support reductions of PHED on nearby NHS roadways. It will add sidewalks and bicycle lanes, which may support non-SOV travel. It is also expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608436 |
Ashland–Rehabilitation and Rail Crossing Improvements on Cherry Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Improve the safety features on Cherry Street and Main Street to establish a Federal Railroad Administration Quiet Zone surrounding the railroad crossings on those two roadways. Install roadway medians, enhance existing railroad crossing signals and gates, reconstruct pavement, construct sidewalks, and improve drainage in the project area. |
Ashland |
2024 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance at a railroad crossing location, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. |
608067 |
Burlington, Woburn–Intersection Reconstruction at Route 3 (Cambridge Road) and Bedford Road and South Bedford Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Reconstruct the intersection and all traffic signal equipment. Enhance roadway geometry to provide exclusive turn lanes for intersection approaches. Reconstruct existing sidewalks, construct new sidewalks, and add bicycle lanes and ADA-compliant bus stops, where feasible. |
Burlington, Woburn |
2025 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. The project is expected to improve existing sidewalks and add new sidewalks at the intersection, as well as add new bike lanes; all of these features may encourage non-SOV travel. The geometric improvements included in the project are expected to help reduce delay and potentially PHED on nearby NHS routes. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions.
|
608889 |
Framingham–Traffic Signal Installation at Edgell Road and Central Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Install traffic signals and make geometric improvements at the intersection of Edgell Road and Central Street. Add bicycle lanes, cross walks, and ensure sidewalks are ADA/AAB-compliant. |
Framingham |
2023 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It also includes improvements to bicycle and pedestrian accommodations to support non-motorized travel through the intersection, which may encourage non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
605857 |
Norwood–Intersection Improvements at Route 1 and University Avenue/Everett Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Upgrade traffic signals and make associated geometric improvements at the intersection of Route 1, University Avenue and Everett Street. Construct an additional travel lane in each direction on Route 1, lengthen left-turn lanes, upgrade pedestrian crossings and bicycle amenities, and rehabilitate sidewalks. |
Norwood, Westwood |
2025–26 |
The Route 1 corridor in Norwood is identified as a priority bottleneck in the Destination 2040 Needs Assessment. This location was studied in “Route 1 at Everett Street and University Avenue” (CTPS, 2014). |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve nearly three lane miles of pavement on the NHS. Signal and geometric improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project area and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve substandard sidewalks and add new sidewalks and bicycle accommodations, all of which may encourage non-SOV travel. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
606130 |
Norwood–Intersection Improvements at Route 1A and Upland Road/Washington Street and Prospect Street/ Fulton Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Make intersection improvements at two locations on Route 1A. Install traffic and pedestrian signals and widen Washington Street and Upland Road to accommodate turn lanes. Reconstruct existing sidewalks to meet ADA/AAB standards. |
Norwood |
2023 |
N/A |
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will upgrade existing sidewalks, and add new sidewalks and bicycle accommodations in the project area, all of which may encourage non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
608940 |
Weston–Intersection Improvements at Boston Post Road (Route 20) at Wellesley Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Address safety, congestion, and connectivity concerns at the intersection of Route 20, Boston Post Road, and Wellesley Street by installing a new signal system, implementing geometric improvements, replacing and adding sidewalks, and adding bicycle lanes. |
Weston |
2026 |
This project intersects a priority bottleneck location identified in the Destination 2040 Needs Assessment. |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. Signal and geometric improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project area and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve and add sidewalks and add bicycle lanes; these features may encourage non-SOV travel. It is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
609253 |
Wilmington– Intersection Improvements at Lowell Street (Route 129) and Woburn Street |
Intersection Improvements |
Improve traffic safety and efficiency at the intersection of Lowell Street (Route 129) and Woburn Street by making geometric modifications to the roadway, installing new pedestrian signals, adding crosswalks, and providing bicycle lanes. |
Wilmington |
2023 |
Sections of the Route 38 and 129 corridors are identified as priority bottlenecks in the Destination 2040 Needs Assessment. A portion of this corridor was studied in “Safety and Operations Analysis at Selected Intersections: Main Street at Church Street and Burlington Avenue” (CTPS, 2012). |
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location and the project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve more than half of a lane mile of pavement on the NHS. Signal and geometric improvements included in the project may improve reliability on unreliable NHS segments within the project area and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve existing sidewalks, and it is expected to add new sidewalks and bicycle lanes, all of which may encourage non-SOV travel. The project is expected to reduce CO2 and other transportation-related emissions. |
606226 |
Boston–Reconstruction of Rutherford Avenue |
Major Infrastructure: Roadway |
Reconstruct Rutherford Avenue from Sullivan Square to the North Washington Street Bridge to create a multimodal urban boulevard. |
Boston |
2025–27 |
This project is included in Destination 2040, the MPO’s LRTP.
|
The project is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It is expected to improve four NHS bridge structures and more than 7 lane miles of NHS pavement. The project area overlaps many NHS segments considered to be unreliable, and the project includes changes to roadway geometry and signals that are expected to improve reliability on the NHS and potentially reduce PHED. The project will improve existing sidewalks and is expected to add new sidewalks and a range of bicycle and pedestrian accommodations within the corridor, all of which are expected to increase non-SOV travel. It was analyzed as part of a set of recommended LRTP projects, and MPO staff estimate that this set will decrease CO2 emissions in the region compared to a no-build scenario. |
607981 |
Somerville–McGrath Boulevard Reconstruction |
Major Infrastructure: |
Remove the existing McCarthy Viaduct and replace it with an at-grade urban boulevard. Rationalize intersections, improve signalization, and create off-street pedestrian and bicycle facilities. Improve bus operations by installing floating/in-lane bus stops, transit signal priority, and bus queue-jump lanes at key intersections.
|
Somerville |
2027 |
This project is included in Destination 2040, the MPO’s LRTP.
|
The project area overlaps a 2017–19 all-mode HSIP crash cluster location, a 2010–19 HSIP pedestrian crash cluster location, and a 2010–19 HSIP bicycle crash cluster location. It is expected to improve safety performance, including for bicyclists and pedestrians. It will improve one NHS bridge and improve more than four lane miles of substandard pavement on the NHS. The geometric and signal improvements included in the project may reduce PHED and improve reliability on this portion of the NHS network. The project will improve bus operations and amenities, reconstruct and reconfigure sidewalks, and add off-street bicycle and pedestrian facilities; these features are expected to increase non-SOV travel. It was analyzed as part of a set of recommended LRTP projects, and MPO staff estimate that this set will decrease CO2 emissions in the region compared to a no-build scenario. |
S12706 |
Boston–Forest Hills Improvement Project* |
Transit Modernization |
Make platform repairs, replace elevators and construct a new elevator/stair tower to connect the station’s upper and lower busways. Implement accessibility, wayfinding, safety, and station brightening upgrades. Improve the station roof.
|
Boston |
2024 |
Forest Hills station improvements are listed the MBTA’s 2018 Transit Asset Management Plan (see Appendix F: Project-Based Listing of Investment Priorities.) |
This project makes safety, state-of-good-repair, and modernization improvements to one of the MBTA’s passenger facilities. These upgrades may increase ridership by making the station more accessible to all users and easier to navigate, which may increase transit ridership and non-SOV travel. |
S12705 |
Lynn–Lynn Station Improvements, Phase II |
Transit Modernization |
Reconstruct the existing rail platform. Construct two new elevators. Upgrade lighting and other amenities. Make structural repairs to the viaduct northeast of the station.
|
Lynn |
2023 |
Lynn Station improvements are listed the MBTA’s 2018 Transit Asset Management Plan (see Appendix F: Project-Based Listing of Investment Priorities.) |
This project makes safety, state-of-good-repair, and modernization improvements to one of the MBTA’s passenger facilities. These upgrades may increase ridership by making the station more accessible to all users and easier to navigate, which may increase transit ridership and non-SOV travel. |
Notes: HSIP cluster locations are identified by MassDOT. Substandard pavement and sidewalk designations are based on data provided by MassDOT and project proponents and on MPO assessments conducted for TIP evaluations. The estimated lane miles of substandard NHS pavement improved is based on MPO staff’s assessment of pavement condition in the project area and their assessment of the portion of the project on the NHS. The IRI thresholds used to classify pavement are based on the TIP criteria the MPO adopted in 2020: less than 95 is good, 95 to 170 is fair, and greater than 170 is poor.
* The MPO is contributing funds to this project, which is generally funded by MassDOT or the MBTA.
AAB = Architectural Access Board. ADA = Americans with Disabilities Act. CO2 = carbon dioxide. CTPS = Central Transportation Planning Staff. FFY = federal fiscal year. HSIP = Highway Safety Improvement Program. IRI = International Roughness Index. MassDOT = Massachusetts Department of Transportation. MBTA = Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority. MCRT = Mass Central Rail Trail. MPO = metropolitan planning organization. N/A = not applicable. NHS = National Highway System. PHED = peak hours of excessive delay. SOV = single-occupancy vehicle. TSP = transit signal priority.
Source: Boston Region MPO staff.
Table A-3
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Project Evaluation Results: Multiple MPO Investment Programs
| Proponent | Project Number | Project Name | MAPC Subregion | Project Status (as of 3/17/22) | Project Cost | Cost/Lane Mile* | Total Score | Total Base Score | Total Equity Score | Safety | Safety Equity Score | System Preservation and Modernization | System Preservation Equity Score | Capacity Management and Mobility | Capacity Management Equity Score | Clean Air and Sustainable Communities | Clean Air Equity Score | Economic Vitality |
| Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections Program | ||||||||||||||||||
| Swampscott | 610666 | Rail Trail Construction | NSTF | 25% Rejected 1/27/21 | $7,700,000 | $3.67 million | 66.4 | 59 | 7.4 | 13 | 2 | 5 | 0.8 | 18 | 3.6 | 12 | 1 | 11 |
| Belmont | 609204 | Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) | ICC | 25% Submitted 1/5/22 | $18,780,698 | $13.81 million | 64.6 | 57 | 7.6 | 15 | 2 | 8 | 1.4 | 18 | 3.6 | 7 | 0.6 | 9 |
| Possible Points | 100 | 80 | 20 | 20 | 5.6 | 14 | 4.8 | 18 | 7.2 | 14 | 2.4 | 14 | ||||||
| Complete Streets Program | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lynn | 609246 | Reconstruction of Western Avenue | ICC | PRC Approved 12/6/18 | $40,980,000 | $10.25 million | 74.9 | 63 | 11.9 | 18 | 3.5 | 14 | 3 | 10 | 3.5 | 11 | 1.9 | 10 |
| Chelsea | 611983 | Park and Pearl Street Reconstruction | ICC | PRC Approved 1/28/21 | $10,451,525 | $15.59 million | 69.9 | 55 | 14.9 | 14 | 3.6 | 14 | 4.6 | 11 | 5.1 | 6 | 1.6 | 10 |
| Salem, Peabody | 609437 | Boston Street Improvements | NSTF | 25% Resubmitted 10/7/21 | $12,480,000 | $7.85 million | 67.8 | 57 | 10.8 | 12 | 2.7 | 15 | 3.5 | 11 | 3.5 | 8 | 1.1 | 11 |
| Brookline | 610932 | Rehabilitation of Washington Street | ICC | PRC Approved 9/24/20 | $25,888,631 | $10.79 million | 62.4 | 55 | 7.4 | 14 | 2.1 | 13 | 2.1 | 11 | 2.5 | 7 | 0.7 | 10 |
| Weston | 608954 | Reconstruction on Route 30 | MWRC | 25% Submitted 10/19/20 | $15,203,814 | $1.79 million | 49.2 | 43 | 6.2 | 11 | 1.6 | 10 | 1.6 | 10 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 3 |
| Ipswich | 611975 | Roadway Improvements on County Street | NSTF | PRC Approved 1/28/21 | $5,653,500 | $6.28 million | 45.4 | 40 | 5.4 | 7 | 1 | 12 | 1.6 | 8 | 2 | 8 | 0.8 | 5 |
| Wakefield | 610545 | Main Street Reconstruction | NSPC | PRC Approved 12/19/19 | $26,382,000 | $6.58 million | 40.8 | 37 | 3.8 | 12 | 1.7 | 10 | 1.3 | 6 | 1.6 | 0 | -0.8 | 9 |
| Manchester-by-the-Sea | 610671 | Bridge Replacement, Central Street over Saw Mill Brook | NSTF | PRC Approved 12/19/19 | $4,350,000 | $36.25 million | 34.8 | 32 | 2.8 | 7 | 0.8 | 14 | 1.7 | 2 | 0.3 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| Possible Points | 100 | 80 | 20 | 18 | 4.6 | 20 | 5.6 | 18 | 7.2 | 12 | 2.6 | 12 | ||||||
| Intersection Improvements Program | ||||||||||||||||||
| Weston | 608940 | Intersection Improvements at Boston Post Road (Route 20) at Wellesley Street | MWRC | 25% Resubmitted 5/18/21 | $1,219,250 | $4.20 million | 50.6 | 45 | 5.6 | 15 | 1.7 | 9 | 1.5 | 10 | 1.7 | 8 | 0.7 | 3 |
| Milton | 608955 | Intersection Improvements, Squantum Street at Adams Street | ICC/TRIC | 25% Submitted 11/29/20 | $2,311,250 | $16.51 million | 34.4 | 30 | 4.4 | 9 | 1.5 | 8 | 1.2 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 0.7 | 4 |
| Possible Points | 100 | 80 | 20 | 21 | 5.4 | 17 | 5.4 | 18 | 6.8 | 12 | 2.4 | 12 | ||||||
| Major Infrastructure Program | ||||||||||||||||||
| Somerville (MassDOT) | 607981 | McGrath Boulevard Reconstruction | ICC | PRC Approved 5/9/14 | $88,250,000 | $9.81 million | 72.2 | 63 | 9.2 | 13 | 2.1 | 19 | 2.7 | 13 | 3.3 | 8 | 1.1 | 10 |
| Natick (MassDOT) | 605313 | Bridge Replacement, Route 27 over Route 9 and Interchange Improvements | MWRC | 25% Resubmitted 2/12/20 | $45,097,350 | $14.69 million | 57.7 | 51 | 6.7 | 13 | 1.8 | 13 | 1.5 | 11 | 2.3 | 8 | 1.1 | 6 |
| Possible Points | 100 | 80 | 20 | 18 | 4.6 | 20 | 5.6 | 18 | 7.2 | 12 | 2.6 | 12 | ||||||
Table A-4
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Project Evaluation Results: Community Connections Program
| Proponent | Project Name | MAPC Subregion | Project Cost | Cost/Monthly User** | Total Score | Connectivity | Coordination | Plan Implementation | Transportation Equity | Mode Shift and Demand Projection | Fiscal Sustainability | |
| Newton | NewMo Microtransit Service Expansion | ICC | $712,459 | $101 | 87 | 18 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 24 | 10 | |
| Cambridge | Bluebikes Station Replacement and System Expansion | ICC | $349,608 | $27 | 78 | 18 | 4.5 | 12.5 | 9 | 24 | 10 | |
| Medford/ Malden | Bluebikes System Expansion | ICC | $145,821 | $81 | 78 | 17 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 24 | 10 | |
| Watertown | Pleasant Street Shuttle Service Expansion | ICC | $801,758 | $990 | 78 | 18 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 20 | 10 | |
| Salem | Bluebikes System Expansion | NSTF | $119,629 | $399 | 77 | 13 | 15 | 6 | 9 | 24 | 10 | |
| Stoneham | Stoneham Shuttle Service | NSPC | $637,453 | $247 | 72 | 15 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 17 | 10 | |
| CATA | CATA On Demand Microtransit Service Expansion | NSTF | $650,633 | $434 | 61.75 | 10.75 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 20 | 10 | |
| MWRTA | CatchConnect Microtransit Service Expansion | MWRC | $360,130 | $240 | 59 | 12 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 16 | 10 | |
| Acton | Bicycle Parking along the Bruce Freeman Rail Trail | MAGIC | $8,017 | $7 | 58 | 6 | 2 | 9 | 9 | 22 | 10 | |
| MART | Montachusett RTA Microtransit Service | MAGIC | $1,052,849 | $675 | 57 | 7 | 15 | 3 | 6 | 16 | 10 | |
| Belmont | Chenery Middle School Bicycle Parking | ICC | $4,376 | $12 | 49.75 | 4.75 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 18 | 10 | |
| Possible Points | 100 | 18 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 24 | 10 | |||||
| **All cost/user calculations are based on the demand estimates submitted by project proponents during the application process. For transit operating projects, cost/user is based on ridership after 6 months of service. | ||||||||||||
Table A-5
FFYs 2022–26 and 2023–27 TIP Evaluation Criteria: Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections Program
| MPO Goal Area | Safety: Transportation by all modes will be safe. (Up to 20 points) | |||
| Criterion | Project improves bicycle safety (up to 5 points) +5 High total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +3 Medium total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +1 Low total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +0 Project does not implement bicycle safety improvements |
Project improves pedestrian safety (up to 5 points) +5 High total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +3 Medium total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +1 Low total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +0 Project does not implement pedestrian safety improvements |
Project improves safety for all users (up to 3 points) +3 Project includes three or more eligible multimodal safety improvements +2 Project includes two eligible multimodal safety improvements +1 Project includes one eligible multimodal safety improvement +0 Project does not include any eligible multimodal safety improvements |
|
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Bonus (up to 2 points) +2 Improves bicycle safety at bicycle HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 2 points) +2 Improves pedestrian safety at pedestrian HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 3 points) +3 Addresses safety at multiple all-mode HSIP clusters OR a top-200 crash location +2 Addresses safety at one all-mode HSIP cluster |
|
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | No | |
| MPO Goal Area | System Preservation: Maintain and modernize the transportation system and plan for its resiliency. (Up to 14 points) | |||
| Criterion | Project incorporates resiliency elements into its design (up to 5 points) +1 Project implements recommendation(s) as identified in a Hazard Mitigation Plan, Municipal Vulnerability Plan, or climate adaptation plan ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves stormwater infrastructure ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project implements innovative resiliency solutions ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project designed to meet a range of future climate projections ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project demonstrates regional coordination on resiliency |
Project improves connectivity to critical facilities (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves access to critical facilities |
Project improves existing pedestrian facilities (up to 5 points) +5 Existing pedestrian facilities are in poor condition and improvements are included in the project +3 Existing pedestrian facilities are in fair condition and improvements are included in the project +1 Existing pedestrian facilities are in good condition and improvements are included in the project +0 Project does not improve existing pedestrian facilities |
Project improves other existing assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves three or more other assets +1 Project improves one or two other assets +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Penalty -1 Project is located in an existing or projected flood zone and doesn't specify how the project will address future flooding |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| MPO Goal Area | Capacity Management/Mobility: Use existing facility capacity more efficiently and increase healthy transportation options. (Up to 18 points) | |||
| Criterion | Project improves pedestrian network and ADA accessibility (up to 5 points) +5 Project adds new shared-use path +3 Project adds new high-quality sidewalks +1 Project adds new standard sidewalks +0 Project does not improve pedestrian network |
Project improves bicycle network (up to 5 points) +5 Project adds new separated bicycle facility (including shared-use paths) +3 Project adds new buffered bicycle facility +1 Project adds new standard bicycle facility +0 Project does not improve bicycle network |
||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Bonus (up to 4 points) +4 Project closes a gap in the pedestrian network +3 Project improves ADA accessibility beyond minimum required standards +2 Project creates or improves a pedestrian connection to transit +1 Project extends existing pedestrian network |
Bonus (up to 4 points) +4 Project closes a gap in the bicycle network +2 Project creates or improves a bicycle connection to transit +2 Project extends existing bicycle network +1 Project makes accommodations for bicycle parking or a bicycle share station |
||
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | ||
| MPO Goal Area | Clean Air/Sustainable Communities: Create an environmentally friendly transportation system. (Up to 14 points) | |||
| Criterion | Project reduces CO2 (up to 4 points) +4 300 or more annual tons of CO2 reduced +3 100–299 annual tons of CO2 reduced +2 50–99 annual tons of CO2 reduced +1 Less than 50 annual tons of CO2 reduced 0 No expected impact -1 Less than 50 annual tons of CO2 increased -4 50 or more annual tons of CO2 increased |
Project reduces other transportation-related emissions (up to 4 points) +4 1,500 or more total annual kilograms of other emissions reduced +3 750–1499 total annual kilograms of other emissions reduced +2 250–749 total annual kilograms of other emissions reduced +1 Less than 250 total annual kilograms of other emissions reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 total annual kilograms of other emissions increased -4 250 or more total annual kilograms of other emissions increased |
Enhances Natural Environment (up to 4 points) +1 Project improves water quality ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project selects a design alternative that avoids impacts to sensitive natural areas ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project reduces urban heat island effect ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project increases access to parks, open space, or other natural assets |
|
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | Bonus/Penalty (up to 2 points) +2 Project reduces NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels -2 Project increases NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels |
Penalty -1 Project is anticipated to lead to negative environmental outcomes |
|
| Equity Multiplier? | No | Yes | No | |
| MPO Goal Area | Economic Vitality: Ensure our transportation network provides a strong foundation for economic vitality. (Up to 14 points) | |||
| Criterion | Project serves sites targeted for future development (up to 4 points) +2 Project improves bicycle access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +2 Project improves pedestrian access to or within a site |
Project serves existing employment and population centers (up to 4 points) +4 Project mostly serves an existing area of concentrated development +2 Project partly serves an existing area of concentrated development +0 Project does not serve an existing area of concentrated development |
Project demonstrates proponent investment (up to 2 points) +2 20 percent or more of the project cost is provided +1 Less than 20 percent of the project cost is provided +0 No non-TIP funding is provided by the project proponent |
Project promotes access to affordable housing opportunities (up to 3 points) +3 10.4% or more of housing units are affordable in project area +2 6.6-10.3% of housing units are affordable in project area +1 1-6.5% of housing units are affordable in project area +0 Less than 1% of housing units are affordable in project area |
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project proponent supports design process through pilot project OR robust community outreach process |
N/A |
| Equity Multiplier? | No | No | No | No |
| Total Base Points Possible | 80 | |||
| Total Equity Points Possible | 20 | |||
| Total Possible Points | 100 | |||
Table A-6
Evaluation Criteria for FFYs 2022 and 2023 Community Connections Program
| OBJECTIVE | CRITERIA | DATA TO USE | SUBCRITERIA/SCORING |
| SCORING CRITERIA (90 possible points) | |||
| NETWORK OR CONNECTIVITY VALUE (18 points) | |||
| The primary purpose of the Community Connections Program is to close gaps in the transportation network, especially those in the first or last mile between transit and a destination. Projects will be awarded points based on how effectively a proposed project closes different types of gaps and makes travel easier or more efficient. |
Connection to existing activity hubs and residential developments (9/6 points) |
Application materials, CTPS GIS layers reflecting relevant destinations and employment and population density | Projects can earn points for any combination of conditions, up to the noted overall maximum. Area projects (up to 9 points) 0 If the project area includes* no dense employment concentrations, or dense residential concentrations, or Major Civic Destinations. +2 for each dense employment concentration OR dense residential concentration included in the project area, up to a maximum of 6 points +1 if the project targets a specific dense employment concentration, OR dense residential concentration, or Major Civic Destination +.25 points for each Major Civic Destination included in the project area, up to a maximum of 2 points Point projects (up to 6 points) 0 points if the project has no locations/stops within** ½ mile of a dense employment concentration OR a dense residential concentration +1 point for each location/stop within ½ mile of a dense employment concentration OR a dense residential concentration, up to a maximum of 4 points +2 points for each location/stop within ¼ mile of a dense employment concentration OR a dense residential concentration, up to a maximum of 4 points +.25 points for each location/stop within a ½ mile of a Major Civic Destination, up to a maximum of 1 point +.5 points for each location/stop within a ¼ mile of a Major Civic Destination, up to a maximum of 1 point *A project area includes a dense employment or residential concentration if it contains more than 50% of a transportation analysis zone (TAZ) that meets employment or residential density thresholds **For dense employment or residential concentrations, ”Within” is defined as the location being within the specified distance of the centroid of the relevant TAZs |
| Connection to existing transit hubs (6 points) |
Application materials, CTPS GIS layers reflecting transit stops and routes | Projects can earn points for any combination of conditions, up to the noted overall maximum. Area Projects (up to 9 points) 0 if the project area does not include any transit stops for any mode +1 for each bus stop with infrequent service in the project area, up to a maximum of 4 points +2 for each commuter rail station in the project area, up to a maximum of 4 points +3 for each bus stop with frequent service in the project area, up to a maximum of 6 points +4 for each rapid transit stop in the project area, up to a maximum of 8 points Point Projects (up to 6 points) 0 If none of the project locations are within 1/2 mile of any transit stations/routes +1 if there is one bus stop with infrequent service within ½ mile of a project location +2 if there are multiple instances of a bus stop with infrequent service within ½ mile of a project location +3 if there is a commuter rail station within ½ mile of a project location +4 if there is a bus stop with frequent service within ¼ mile of a project location +5 if there are multiple instances of bus stops with frequent service within ¼ mile of a project location +6 if there is at least one rapid transit stop within ¼ mile of a project location |
|
| Connection to other transportation infrastructure (6 points) | Application materials, CTPS GIS layers including bicycle infrastructure (derived from MAPC trailmap and other sources) and MassDOT road inventory with enhanced sidewalk data | Area Projects (not eligible for points in this subcriterion) n/a Point Projects (up to 6 points) 0 if none of the project locations are within 250 feet of sidewalks or protected bicycle infrastructure +1 for each project location within 250 feet of a sidewalk, up to a maximum of 2 points +1 for each project location within 250 feet of protected bicycle infrastructure, up to a maximum of 2 points +2 if any project location is within 250 feet of BOTH a sidewalk and protected bicycle infrastructure |
|
| Coordination or cooperation between multiple entities (15 points) | |||
| The MPO prioritizes collaboration among different entities in the transportation planning process. Cooperative project planning and execution is particularly important for first-mile and last-mile connections of the type that the Community Connections Program is intended to facilitate. The cooperation can involve actors from both the public and private sectors. |
Number of collaborating entities (15 points) |
Application materials | +3 for each collaborating entity beyond the sponsor, up to a maximum of 9 points -15 for Bus Lane, TSP, or E-Ink projects that do not have a letter of support from the MBTA Additionally +3 If the project consists of collaborators from multiple sectors (i.e., public and private, or public and nonprofit) +3 If each listed collaborator has provided a formal letter of support to the MPO |
| Inclusion in and consistency with local and regional plans (15 points) | |||
| A comprehensive planning process is important to ensure that projects occur in an environment of collaboration and careful consideration rather than independently. This criterion proposes to award points based on the extent to which a proposed project has been included in prior plans at both the local and regional levels, and whether it meets the goals of those plans. | Inclusion in local plans (6 points) |
Application materials, local plans | Project is scored based on the best condition it meets. +3 if the project supports a theme, idea, or concept in a local comprehensive plan or equivalent document. +6 If the project is specifically included as a need or priority in a local comprehensive plan or equivalent document |
| Inclusion in MPO plans (6 points) |
Application materials, LRTP Needs Assessment, UPWP Database, MAPC plans | Project earns points for each condition met. +3 If the project is identified as a need in a current or previous LRTP Needs Assessment or another regional plan +3 if the project or a large element thereof is recommended in MPO/MAPC technical studies |
|
| Inclusion in statewide plans (3 point) |
Application materials, LRTP Needs Assessment | +3 If the project is included as a need or priority in MassDOT or other statewide planning studies |
|
| TRANSPORTATION EQUITY (18 points) | |||
| The MPO seeks to prioritize investments that benefit equity populations, while minimizing any burdens associated with MPO-funded projects for these populations. | Serves one or more transportation equity demographics, as identified by the MPO (18 points) | Application materials, CTPS GIS layers | See detailed scoring criteria handout: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1YXBvJoj2FM2UJp0qd88Ew_n_KR5OscyS/edit?usp=sharing&ouid=110620465990841651473&rtpof=true&sd=true |
| GENERATION OF MODE SHIFT (12 points) | |||
| Another primary purpose of the Community Connection Program is to enable modal shift from SOV to transit or other modes. This criterion awards points based on the project’s effectiveness at creating mode shift and/or enabling trips that were previously impossible by non-SOV modes. |
Allow new trips that would not be otherwise possible without a car (12 points) |
Application materials | This criterion will be scored by MPO staff based on materials and narrative provided in the project application, considering factors such as: •Whether the project competes with or complements existing transit service •If the project brings non-SOV transportation options to an area that previously had few or none •Whether the project provides complementary connections to existing non-SOV transportation services and infrastructure •Whether the project serves a particular, identified transportation purpose that includes or facilitates mode shift •If relevant, whether the project shows it has a viable path to fiscal independence at the end of the MPO grant period •Reliability of projected local or other non-MPO financial contributions •If the project serves a population that travels through the project area but does not live adjacent to or within it •The quality and innovation of the project's marketing plan, when relevant |
| DEMAND PROJECTION (12 points) |
|||
| Gaining an understanding of how many transportation network users a project will reach is crucial for understanding its cost-effectiveness. | Overall demand estimate (6 points) | Application materials | 0 If the application contains no estimates of demand or usage +3 If the application contains estimates of demand or usage, but no documentation of methods used to create them or background information +6 If the application contains estimates of demand or usage that are backed by extensive documentation of methods used to create the estimates and/or other relevant background information |
| Staff evaluation of demand estimate (6 points) | Application materials | 0 If staff judge that demand/usage projections are unrealistic or not present +3 if staff judge that demand/usage projections are somewhat realistic +6 If staff judge that demand/usage projections are realistic |
|
| BUDGET SHEET (10 points) | |||
| Quality of information provided (10 points) | Application materials | 0 if there is no budget sheet present or the budget sheet does not contain useful information +5 if the budget sheet is incomplete or inaccurate, but usable with work +10 if the budget sheet is completed with all necessary information |
|
| Definitions Area projects: Those that are geographically defined as a polygon, rather than delivered at a particular point or points. Examples: microtransit covering an entire town, or an education project for a neighborhood. Point projects: Those that are delivered at a particular point or points and can be geographically defined as such. Examples: bike racks, fixed-route transit (the stops are the points) Population density concentration: any TAZ with more than 4,000 people per square mile. Employment density concentration: any TAZ with more than 4,000 jobs per square mile Frequent service: Follows the MBTA Service Delivery Policy. Stops with frequent service defined are defined in a CTPS layer used in pilot round CC scoring and for the Destination 2040 Needs Assessment. This layer measures frequency at the stop level rather than the route level; that is, a stop with four buses per hour, from two different routes, is considered a frequent stop. |
|||
| ADA = Americans with Disabilities Act. CMAQ = Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement Program. CTPS = Central Transportation Planning Staff. FFY = federal fiscal year. GIS = geographic information systems. GTFS = general transit feed specification. LRTP = Long-Range Transportation Plan. MAPC = Metropolitan Area Planning Council. MassDOT = Massachusetts Department of Transportation. MBTA = Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority. MPO = Metropolitan Planning Organization. MVP = Municipal Vulnerability Program. SOV = single occupancy vehicle. TAD = Traffic and Design. TAZ = transportation analysis zone. TIP = Transportation Improvement Program. | |||
Table A-7
FFYs 2022–26 and 2023–27 TIP Evaluation Criteria: Complete Streets Program
| MPO Goal Area | Safety: Transportation by all modes will be safe. (Up to 18 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project addresses severe-crash location (up to 3 points) +3 EPDO value of 1000 or more +2 EPDO value of 250 to 999 +1 EPDO value of less than 250 +0 No EPDO value |
Project addresses high-crash location (up to 3 points) +3 Crash rate of 6.45 or greater +2 Crash rate between 4.25 and 6.45 +1 Crash rate between 2.05 and 4.25 +0 Crash rate below 2.05 |
Project addresses truck-related safety issue (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no implementation of truck safety improvements |
Project improves bicycle safety (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no inclusion of bicycle safety improvements |
Project improves pedestrian safety (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no inclusion of pedestrian safety improvements |
Project improves safety for all users (up to 2 points) +2 Project includes three or more eligible multimodal safety improvements +1 Project includes one or two eligible multimodal safety improvements +0 Project does not include any eligible multimodal safety improvements |
||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves bicycle safety at bicycle HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves pedestrian safety at pedestrian HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 2 points) +2 Addresses safety at multiple all-mode HSIP clusters OR a top-200 crash location +1 Addresses safety at one all-mode HSIP cluster |
||
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | ||
| MPO Goal Area | System Preservation: Maintain and modernize the transportation system and plan for its resiliency. (Up to 20 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project incorporates resiliency elements into its design (up to 5 points) +1 Project implements recommendation(s) as identified in a Hazard Mitigation Plan, Municipal Vulnerability Plan, or climate adaptation plan ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves stormwater infrastructure ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project implements innovative resiliency solutions ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project designed to meet a range of future climate projections ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project demonstrates regional coordination on resiliency |
Improves evacuation route (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves an evacuation route, diversion route, or alternate diversion route |
Improves connectivity to critical facilities (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves access to critical facilities |
Project improves existing transit assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant improvements to existing transit assets +1 Project makes moderate improvements to existing transit assets +0 Project does not modernize or improve the condition of existing transit assets |
Project improves existing pedestrian facilities (up to 3 points) +3 Existing pedestrian facilities are in poor condition and improvements are included in the project +2 Existing pedestrian facilities are in fair condition and improvements are included in the project +1 Existing pedestrian facilities are in good condition and improvements are included in the project +0 Project does not improve existing pedestrian facilities |
Project improves existing bridges (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves existing bridge(s) from poor to good condition through rehabilitation or replacement +1 Project improves existing bridge(s) from fair to good condition through rehabilitation or replacement 0 Project does not include bridge improvements |
Project improves existing pavement condition (up to 2 points) +2 Current roadway condition is poor and pavement improvements are included in the project +1 Current roadway condition is fair and pavement improvements are included in the project +0 Current roadway condition is good |
Project improves other existing assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves three or more other assets +1 Project improves one or two other assets +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Penalty -1 Project is located in an existing or projected flood zone and doesn't specify how the project will address future flooding |
N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project reduces or removes vehicle weight/height restrictions OR improves bridge on a key roadway |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves pavement on a key corridor OR improves roadway substructure |
N/A | |
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| MPO Goal Area | Capacity Management/Mobility: Use existing facility capacity more efficiently and increase healthy transportation options. (Up to 18 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces transit passenger delay (up to 3 points) +3 Project results in significant passenger delay reductions +2 Project results in moderate passenger delay reductions +1 Project results in limited passenger delay reductions +0 Project does not make meaningful reductions in passenger delay |
Project invests in New Transit Assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant investments in new transit assets +1 Project makes moderate investments in new transit assets +0 Project does not invest in new transit assets |
Project improves pedestrian network and ADA accessibility (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new sidewalks on high-utility link +2 Project adds new sidewalks on medium-utility link +1 Project adds new sidewalks on low-utility link +0 Project does not improve pedestrian network |
Project improves bicycle network (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new separated bicycle facility (including shared-use paths) +2 Project adds new buffered bicycle facility +1 Project adds new standard bicycle facility +0 Project does not improve bicycle network |
Project improves truck movement (up to 2 points) +2 Project significantly improves truck movement +1 Project somewhat improves truck movement +0 Project makes minimal improvements to truck movement or does not address criteria |
Project addresses unreliable corridor (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses a corridor with a level of travel time reliability above 1.25 +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Bonus/Penalty (+/- up to 1 point) +1 Project invests in bus-priority infrastructure on MPO-identified priority corridor -1 Project increases transit vehicle delays or negatively impacts transit vehicle movement |
N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the pedestrian network +1 Project enhances ADA accessibility beyond minimum required standards +1 Project creates or improves pedestrian connection to transit |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the bicycle network +1 Project creates or improves a bicycle connection to transit +1 Project makes accommodations for bicycle parking or bicycle share station +1 Project is on a high-utility link |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses key freight corridor or makes accommodations for freight deliveries |
N/A | ||
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| MPO Goal Area | Clean Air/Sustainable Communities: Create an environmentally friendly transportation system. (Up to 12 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces CO2 (up to 3 points) +3 750 or more annual tons of CO2 reduced +2 250-749 annual tons of CO2 reduced +1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 increased -3 250 or more annual tons of CO2 increased |
Project reduces other transportation-related emissions (up to 3 points) +3 1,000 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +2 250-999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -3 250 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased |
Enhances Natural Environment (up to 4 points) +1 Project improves water quality ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project selects a design alternative that avoids impacts to sensitive natural areas ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project reduces urban heat island effect ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project increases access to parks, open space, or other natural assets |
|||||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | Bonus/Penalty (up to 2 points) +2 Project reduces NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels -2 Project increases NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels |
Penalty -1 Project is anticipated to lead to negative environmental outcomes |
|||||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | Yes | No | |||||
| MPO Goal Area | Economic Vitality: Ensure our transportation network provides a strong foundation for economic vitality. (Up to 12 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project serves sites targeted for future development (up to 3 points) +1 Project improves bicycle access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves pedestrian access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves transit access to or within a site |
Project serves existing employment and population centers (up to 3 points) +3 Project mostly serves an existing area of concentrated development +1 Project partly serves an existing area of concentrated development +0 Project does not serve an existing area of concentrated development |
Project demonstrates proponent investment (up to 2 points) +2 20 percent or more of the project cost is provided +1 Less than 20 percent of the project cost is provided +0 No non-TIP funding is provided by the project proponent |
Project promotes access to affordable housing opportunities (up to 3 points) +3 10.4% or more of housing units are affordable in project area +2 6.6-10.3% of housing units are affordable in project area +1 1-6.5% of housing units are affordable in project area +0 Less than 1% of housing units are affordable in project area |
||||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project proponent supports design process through pilot project OR robust community outreach process |
N/A | ||||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | No | No | No | ||||
| Total Base Points Possible | 80 | |||||||
| Total Equity Points Possible | 20 | |||||||
| Total Possible Points | 100 | |||||||
Table A-8
FFYs 2022–26 and 2023–27 TIP Evaluation Criteria: Intersection Improvements Program
| MPO Goal Area | Safety: Transportation by all modes will be safe. (Up to 21 points) | ||||||
| Criterion | Project addresses severe-crash location (up to 3 points) +3 EPDO value of 300 or more +2 EPDO value of 100 to 299 +1 EPDO value of less than 100 +0 No EPDO value |
Project addresses high-crash location (up to 3 points) Signalized Intersection: +3 Crash rate of 1.69 or greater +2 Crash rate between 1.02 and 1.69 +1 Crash rate between 0.35 and 1.02 +0 Crash rate below 0.35 Unsignalized Intersection: +3 Crash rate of 1.36 or greater +2 Crash rate between 0.78 and 1.36 +1 Crash rate between 0.20 and 0.78 +0 Crash rate below 0.20 |
Project addresses truck-related safety issue (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no implementation of truck safety improvements |
Project improves bicycle safety (up to 3 points) +3 High total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +2 Medium total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +1 Low total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +0 Project does not include bicycle safety improvements |
Project improves pedestrian safety (up to 3 points) +3 High total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +2 Medium total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +1 Low total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +0 Project does not include pedestrian safety improvements |
Project improves safety for all users (up to 3 points) +3 Project includes three or more eligible multimodal safety improvements +2 Project includes two eligible multimodal safety improvements +1 Project includes one eligible multimodal safety improvement +0 Project does not include any eligible multimodal safety improvements |
|
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves bicycle safety at bicycle HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves pedestrian safety at pedestrian HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 2 points) +2 Addresses safety at multiple all-mode HSIP clusters OR a top-200 crash location +1 Addresses safety at one all-mode HSIP cluster |
|
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | |
| MPO Goal Area | System Preservation: Maintain and modernize the transportation system and plan for its resiliency. (Up to 17 points) | ||||||
| Criterion | Project incorporates resiliency elements into its design (up to 5 points) +1 Project implements recommendation(s) as identified in a Hazard Mitigation Plan, Municipal Vulnerability Plan, or climate adaptation plan ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves stormwater infrastructure ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project implements innovative resiliency solutions ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project designed to meet a range of future climate projections ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project demonstrates regional coordination on resiliency |
Improves evacuation route (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves an evacuation route, diversion route, or alternate diversion route |
Improves connectivity to critical facilities (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves access to critical facilities |
Project improves existing transit assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant improvements to existing transit assets +1 Project makes moderate improvements to existing transit assets +0 Project does not modernize or improve the condition of existing transit assets |
Project improves existing pedestrian facilities (up to 3 points) +3 Existing pedestrian facilities are in poor condition and improvements are included in the project +2 Existing pedestrian facilities are in fair condition and improvements are included in the project +1 Existing pedestrian facilities are in good condition and improvements are included in the project +0 Project does not improve existing pedestrian facilities |
Project improves existing pavement condition (up to 2 points) +2 Current roadway condition is poor and pavement improvements are included in the project +1 Current roadway condition is fair and pavement improvements are included in the project +0 Current roadway condition is good |
Project improves other existing assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves three or more other assets +1 Project improves one or two other assets +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Penalty -1 Project is located in an existing or projected flood zone and doesn't specify how the project will address future flooding |
N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves pavement on a key corridor OR improves roadway substructure |
N/A | |
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| MPO Goal Area | Capacity Management/Mobility: Use existing facility capacity more efficiently and increase healthy transportation options. (Up to 18 points) | ||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces transit passenger delay (up to 3 points) +3 Project results in significant passenger delay reductions +2 Project results in moderate passenger delay reductions +1 Project results in limited passenger delay reductions +0 Project does not make meaningful reductions in passenger delay |
Project invests in New Transit Assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant investments in new transit assets +1 Project makes moderate investments in new transit assets +0 Project does not invest in new transit assets |
Project improves pedestrian network and ADA accessibility (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new sidewalks on high-utility link +2 Project adds new sidewalks on medium-utility link +1 Project adds new sidewalks on low-utility link +0 Project does not improve pedestrian network |
Project improves bicycle network (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new separated bicycle facility (including shared-use paths) +2 Project adds new buffered bicycle facility +1 Project adds new standard bicycle facility +0 Project does not improve bicycle network |
Project improves truck movement (up to 2 points) +2 Project significantly improves truck movement +1 Project somewhat improves truck movement +0 Project makes minimal improvements to truck movement or does not address criteria |
Project addresses unreliable corridor (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses a corridor with a level of travel time reliability above 1.25 +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
|
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Bonus/Penalty (+/- up to 1 point) +1 Project invests in bus-priority infrastructure on MPO-identified priority corridor -1 Project increases transit vehicle delays or negatively impacts transit vehicle movement |
N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the pedestrian network +1 Project enhances ADA accessibility beyond minimum required standards +1 Project creates or improves pedestrian connection to transit |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the bicycle network +1 Project creates or improves a bicycle connection to transit +1 Project makes accommodations for bicycle parking or bicycle share station +1 Project is on a high-utility link |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses key freight corridor or makes accommodations for freight deliveries |
N/A | |
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| MPO Goal Area | Clean Air/Sustainable Communities: Create an environmentally friendly transportation system. (Up to 12 points) | ||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces CO2 (up to 3 points) +3 750 or more annual tons of CO2 reduced +2 250-749 annual tons of CO2 reduced +1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 increased -3 250 or more annual tons of CO2 increased |
Project reduces other transportation-related emissions (up to 3 points) +3 1,000 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +2 250-999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -3 250 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased |
Enhances Natural Environment (up to 4 points) +1 Project improves water quality ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project selects a design alternative that avoids impacts to sensitive natural areas ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project reduces urban heat island effect ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project increases access to parks, open space, or other natural assets |
||||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | Bonus/Penalty (up to 2 points) +2 Project reduces NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels -2 Project increases NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels |
Penalty -1 Project is anticipated to lead to negative environmental outcomes |
||||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | Yes | No | ||||
| MPO Goal Area | Economic Vitality: Ensure our transportation network provides a strong foundation for economic vitality. (Up to 12 points) | ||||||
| Criterion | Project serves sites targeted for future development (up to 3 points) +1 Project improves bicycle access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves pedestrian access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves transit access to or within a site |
Project serves existing employment and population centers (up to 3 points) +3 Project mostly serves an existing area of concentrated development +1 Project partly serves an existing area of concentrated development +0 Project does not serve an existing area of concentrated development |
Project demonstrates proponent investment (up to 2 points) +2 20 percent or more of the project cost is provided +1 Less than 20 percent of the project cost is provided +0 No non-TIP funding is provided by the project proponent |
Project promotes access to affordable housing opportunities (up to 3 points) +3 10.4% or more of housing units are affordable in project area +2 6.6-10.3% of housing units are affordable in project area +1 1-6.5% of housing units are affordable in project area +0 Less than 1% of housing units are affordable in project area |
|||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project proponent supports design process through pilot project OR robust community outreach process |
N/A | |||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | No | No | No | |||
| Total Base Points Possible | 80 | ||||||
| Total Equity Points Possible | 20 | ||||||
| Total Possible Points | 100 | ||||||
Table A-9
FFYs 2022–26 and 2023–27 TIP Evaluation Criteria: Major Infrastructure Program
| MPO Goal Area | Safety: Transportation by all modes will be safe. (Up to 18 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project addresses severe-crash location (up to 3 points) +3 EPDO value of 1000 or more +2 EPDO value of 250 to 999 +1 EPDO value of less than 250 +0 No EPDO value |
Project addresses high-crash location (up to 3 points) For corridor projects: +3 Crash rate of 6.45 or greater +2 Crash rate between 4.25 and 6.45 +1 Crash rate between 2.05 and 4.25 +0 Crash rate below 2.05 ------------------------------------------------------------------ For intersection and interchange projects: Signalized Intersection: +3 Crash rate of 1.69 or greater +2 Crash rate between 1.02 and 1.69 +1 Crash rate between 0.35 and 1.02 +0 Crash rate below 0.35 Unsignalized Intersection: +3 Crash rate of 1.36 or greater +2 Crash rate between 0.78 and 1.36 +1 Crash rate between 0.20 and 0.78 +0 Crash rate below 0.20 |
Project addresses truck-related safety issue (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of truck safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no implementation of truck safety improvements |
Project improves bicycle safety (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of bicycle safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no inclusion of bicycle safety improvements |
Project improves pedestrian safety (up to 2 points) +2 High total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +1 Medium total effectiveness of pedestrian safety improvements +0 Low total effectiveness or no inclusion of pedestrian safety improvements |
Project improves safety for all users (up to 2 points) +2 Project includes three or more eligible multimodal safety improvements +1 Project includes one or two eligible multimodal safety improvements +0 Project does not include any eligible multimodal safety improvements |
||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves bicycle safety at bicycle HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Improves pedestrian safety at pedestrian HSIP cluster |
Bonus (up to 2 points) +2 Addresses safety at multiple all-mode HSIP clusters OR a top-200 crash location +1 Addresses safety at one all-mode HSIP cluster |
||
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | ||
| MPO Goal Area | System Preservation: Maintain and modernize the transportation system and plan for its resiliency. (Up to 20 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project incorporates resiliency elements into its design (up to 5 points) +1 Project implements recommendation(s) as identified in a Hazard Mitigation Plan, Municipal Vulnerability Plan, or climate adaptation plan ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves stormwater infrastructure ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project implements innovative resiliency solutions ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project designed to meet a range of future climate projections ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project demonstrates regional coordination on resiliency |
Improves evacuation route (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves an evacuation route, diversion route, or alternate diversion route |
Improves connectivity to critical facilities (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves access to critical facilities |
Project improves existing transit assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant improvements to existing transit assets +1 Project makes moderate improvements to existing transit assets +0 Project does not modernize or improve the condition of existing transit assets |
Project improves existing pedestrian facilities (up to 3 points) +3 Existing pedestrian facilities are in poor condition and improvements are included in the project +2 Existing pedestrian facilities are in fair condition and improvements are included in the project +1 Existing pedestrian facilities are in good condition and improvements are included in the project +0 Project does not improve existing pedestrian facilities |
Project improves existing bridges (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves existing bridge(s) from poor to good condition through rehabilitation or replacement +1 Project improves existing bridge(s) from fair to good condition through rehabilitation or replacement 0 Project does not include bridge improvements |
Project improves existing pavement condition (up to 2 points) +2 Current roadway condition is poor and pavement improvements are included in the project +1 Current roadway condition is fair and pavement improvements are included in the project +0 Current roadway condition is good |
Project improves other existing assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project improves three or more other assets +1 Project improves one or two other assets +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Penalty -1 Project is located in an existing or projected flood zone and doesn't specify how the project will address future flooding |
N/A | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project reduces or removes vehicle weight/height restrictions OR improves bridge on a key roadway |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project improves pavement on a key corridor OR improves roadway substructure |
N/A | |
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| MPO Goal Area | Capacity Management/Mobility: Use existing facility capacity more efficiently and increase healthy transportation options. (Up to 18 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces transit passenger delay (up to 3 points) +3 Project results in significant passenger delay reductions +2 Project results in moderate passenger delay reductions +1 Project results in limited passenger delay reductions +0 Project does not make meaningful reductions in passenger delay |
Project invests in New Transit Assets (up to 2 points) +2 Project makes significant investments in new transit assets +1 Project makes moderate investments in new transit assets +0 Project does not invest in new transit assets |
Project improves pedestrian network and ADA accessibility (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new sidewalks on high-utility link +2 Project adds new sidewalks on medium-utility link +1 Project adds new sidewalks on low-utility link +0 Project does not improve pedestrian network |
Project improves bicycle network (up to 3 points) +3 Project adds new separated bicycle facility (including shared-use paths) +2 Project adds new buffered bicycle facility +1 Project adds new standard bicycle facility +0 Project does not improve bicycle network |
Project improves truck movement (up to 2 points) +2 Project significantly improves truck movement +1 Project somewhat improves truck movement +0 Project makes minimal improvements to truck movement or does not address criteria |
Project addresses unreliable corridor (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses a corridor with a level of travel time reliability above 1.25 +0 Project does not meet or address criteria |
||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | Bonus/Penalty (+/- up to 1 point) +1 Project invests in bus-priority infrastructure on MPO-identified priority corridor -1 Project increases transit vehicle delays or negatively impacts transit vehicle movement |
N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the pedestrian network +1 Project enhances ADA accessibility beyond minimum required standards +1 Project creates or improves pedestrian connection to transit |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project closes a gap in the bicycle network +1 Project creates or improves a bicycle connection to transit +1 Project makes accommodations for bicycle parking or bicycle share station +1 Project is on a high-utility link |
Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project addresses key freight corridor or makes accommodations for freight deliveries |
N/A | ||
| Equity Multiplier? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| MPO Goal Area | Clean Air/Sustainable Communities: Create an environmentally friendly transportation system. (Up to 12 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project reduces CO2 (up to 3 points) +3 750 or more annual tons of CO2 reduced +2 250-749 annual tons of CO2 reduced +1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 annual tons of CO2 increased -3 250 or more annual tons of CO2 increased |
Project reduces other transportation-related emissions (up to 3 points) +3 1,000 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +2 250-999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -3 250 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased |
Enhances Natural Environment (up to 4 points) +1 Project improves water quality ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project selects a design alternative that avoids impacts to sensitive natural areas ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project reduces urban heat island effect ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project increases access to parks, open space, or other natural assets |
|||||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | Bonus/Penalty (up to 2 points) +2 Project reduces NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels -2 Project increases NOx emissions in area in top 20% of regional NOx levels |
Penalty -1 Project is anticipated to lead to negative environmental outcomes |
|||||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | Yes | No | |||||
| MPO Goal Area | Economic Vitality: Ensure our transportation network provides a strong foundation for economic vitality. (Up to 12 points) | |||||||
| Criterion | Project serves sites targeted for future development (up to 3 points) +1 Project improves bicycle access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves pedestrian access to or within a site ------------------------------------------------------------------ +1 Project improves transit access to or within a site |
Project serves existing employment and population centers (up to 3 points) +3 Project mostly serves an existing area of concentrated development +1 Project partly serves an existing area of concentrated development +0 Project does not serve an existing area of concentrated development |
Project demonstrates proponent investment (up to 2 points) +2 20 percent or more of the project cost is provided +1 Less than 20 percent of the project cost is provided +0 No non-TIP funding is provided by the project proponent |
Project promotes access to affordable housing opportunities (up to 3 points) +3 10.4% or more of housing units are affordable in project area +2 6.6-10.3% of housing units are affordable in project area +1 1-6.5% of housing units are affordable in project area +0 Less than 1% of housing units are affordable in project area |
||||
| Bonus/Penalty (if applicable) | N/A | N/A | Bonus (up to 1 point) +1 Project proponent supports design process through pilot project OR robust community outreach process |
N/A | ||||
| Equity Multiplier? | No | No | No | No | ||||
| Total Base Points Possible | 80 | |||||||
| Total Equity Points Possible | 20 | |||||||
| Total Possible Points | 100 | |||||||
Table A-10
Evaluation Criteria for FFYs 2021-25 TIP and Prior TIP Cycles (Archived)
| OBJECTIVES | CRITERIA | SUBCRITERIA/SCORING |
| SAFETY: Transportation by all modes will be safe. | ||
| Reduce the number and severity of crashes and safety incidents for all modes Reduce serious injuries and fatalities from transportation Make investments and support initiatives that help protect transportation customers, employees, and the public from safety and security threats |
Crash severity value: EPDO index (0–5 points) |
+5 EPDO value of 300 or more +4 EPDO value between 200 and 299 +3 EPDO value between 100 and 199 +2 EPDO value between 50 and 99 +1 EPDO value less than 50 +0 No EPDO value |
| Crash rate (intersections and corridors) (0–5 points) |
Intersection Evaluation Score Signalized Unsignalized +5 ≥ 1.69 ≥ 1.36 +4 1.31–1.69 1.03–1.36 +3 0.93–1.31 0.70–1.03 +2 0.55–0.93 0.37–0.70 +1 0.36–0.55 0.21–0.37 +0 < 0.36 < 0.21 |
|
| Corridor Interstate Principal Arterials or Other Evaluation Other Freeways Minor Arterials Score Expressways Major–Minor Collectors +5 ≥ 1.81 ≥ 6.45 +4 1.40–1.81 5.35–6.45 +3 1.00–1.40 4.25–5.35 +2 0.59–1.00 3.15– 4.25 +1 0.40–0.59 2.05–3.15 +0 < 0.40 < 2.05 |
||
| Improves truck-related safety issue (0–5 points) |
+3 High total effectiveness of truck safety countermeasures +2 Medium total effectiveness of truck safety countermeasures +1 Low total effectiveness of truck safety countermeasures +0 Does not implement truck safety countermeasures |
|
| If project scores points above, then it is eligible for additional points below: +2 Improves truck safety at HSIP Cluster |
||
| Improves bicycle safety (0–5 points) |
+3 High total effectiveness of bicycle safety countermeasures +2 Medium total effectiveness of bicycle safety countermeasures +1 Low total effectiveness of bicycle safety countermeasures +0 Does not implement bicycle safety countermeasures |
|
| If project scores points above, then it is eligible for additional points below: +2 Improves bicycle safety at HSIP Bicycle Cluster +1 Improves bicycle safety at HSIP Cluster |
||
| Improves pedestrian safety (0–5 points) |
+3 High total effectiveness of pedestrian safety countermeasures +2 Medium total effectiveness of pedestrian safety countermeasures +1 Low total effectiveness of pedestrian safety countermeasures +0 Does not implement pedestrian safety countermeasures |
|
| If project scores points above, then it is eligible for additional points below: +2 Improves pedestrian safety at HSIP Pedestrian Cluster +1 Improves pedestrian safety at HSIP Cluster |
||
| Improves safety or removes an at-grade railroad crossing (0–5 points) |
+5 Removes an at-grade railroad crossing +3 Significantly improves safety at an at-grade railroad crossing +1 Improves safety at an at-grade railroad crossing +0 Does not include a railroad crossing |
|
| SAFETY (30 possible points) | ||
| SYSTEM PRESERVATION AND MODERNIZATION: Maintain and modernize the transportation system and plan for its resiliency. | ||
| Maintain the transportation system, including roadway, transit, and active transportation infrastructure, in a state of good repair Modernize transportation infrastructure across all modes Prioritize projects that support planned response capability to existing or future extreme conditions (sea level rise, flooding, and other natural and security-related man-made impacts) |
Improves substandard roadway bridge(s) (0–3 points) |
+3 Condition is structurally deficient and improvements are included in the project +1 Condition is functionally obsolete and improvements are included in the project +0 Does not improve substandard bridge or does not include a bridge |
| Improves substandard pavement (0–6 points) |
+6 IRI rating greater than 320: Poor condition and pavement improvements are included in the project +4 IRI rating between 320 and 191: Fair condition and pavement improvements are included in the project +0 IRI rating less than 190: Good or better condition |
|
| Improves substandard traffic signal equipment (0–6 points) |
+6 Poor condition and improvements are included in the project +4 Fair condition and improvements are included in the project +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| Improves transit asset(s) (0–3 points) |
+2 Brings transit asset into state of good repair +1 Meets an identified-need in an asset management plan +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| Improves substandard sidewalk(s) (0–3 points) |
+3 Poor condition and sidewalk improvements are included in the project +2 Fair condition and sidewalk improvements are included in the project +0 Sidewalk condition is good or better |
|
| Improves emergency response (0–2 points) |
+1 Project improves an evacuation route, diversion route, or alternate diversion route |
|
| +1 Project improves an access route to or in proximity to an emergency support location |
||
| Improves ability to respond to extreme conditions (0–6 points) |
+2 Addresses flooding problem and/or sea level rise and enables facility to function in such a condition |
|
| +1 Brings facility up to current seismic design standards | ||
| +1 Addresses critical transportation infrastructure |
||
| +1 Protects freight network elements |
||
| +1 Implements hazard mitigation or climate adaptation plans | ||
| SYSTEM PRESERVATION AND MODERNIZATION (29 possible points) | ||
| CAPACITY MANAGEMENT AND MOBILITY: Use existing facility capacity more efficiently and increase transportation options. | ||
| Improve access to and accessibility of all modes, especially transit and active transportation Support roadway management and operations strategies to improve travel reliability, mitigate congestion, and support non-single-occupant-vehicle travel Emphasize capacity management through low-cost investments; prioritize projects that focus on lower-cost operations/ management-type improvements such as intersection improvements, transit priority, and Complete Streets solutions Improve reliability of transit Increase percentage of population and employment within one-quarter mile of transit stations and stops Support community-based and private-initiative services to meet first- and last-mile, reverse commute, and other non-traditional transportation needs, including those of people 75 years old or older and people with disabilities Support strategies to better manage automobile and bicycle parking capacity and usage at transit stations Fund improvements to bicycle and pedestrian networks aimed at creating a connected network of bicycle and accessible sidewalk facilities by expanding existing facilities and closing gaps Increase percentage of population and places of employment with access to facilities on the bicycle network Eliminate bottlenecks on the freight network, improve freight reliability, and enhance freight intermodal connections |
Reduces transit vehicle delay (0–4 points) |
+3 5 hours or more of daily transit vehicle delay reduced +2 1–5 hours of daily transit vehicle delay reduced +1 Less than one hour of daily transit vehicle delay reduced +0 Does not reduce transit delay |
| If project scores points above, then it is eligible for additional points below: |
||
| Improves pedestrian network and ADA accessibility (0–5 points) |
+2 Adds new sidewalk(s) (including shared-use paths) | |
| +2 Improves ADA accessibility |
||
| +1 Closes a gap in the pedestrian network |
||
| +0 Does not improve pedestrian network | ||
| Improves bicycle network (0–4 points) |
+3 Adds new physically separated bicycle facility (including shared-use paths) +2 Adds new buffered bicycle facility +1 Adds new standard bicycle facility |
|
| +1 Closes a gap in the bicycle network +0 Does not improve bicycle network |
||
| Improves intermodal accommodations/ connections to transit (0–6 points) |
+6 Meets or addresses criteria to a high degree +4 Meets or addresses criteria to a medium degree +2 Meets or addresses criteria to a low degree +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| Improves truck movement (0–4 points) |
+3 Meets or addresses criteria to a high degree +2 Meets or addresses criteria to a medium degree +1 Meets or addresses criteria to a low degree +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| If project scores points above, then it is eligible for additional points below: +1 Addresses MPO-identified bottleneck location |
||
| Reduces vehicle congestion (0–6 points) |
+6 400 hours or more of daily vehicle delay reduced +4 100–400 hours of daily vehicle delay reduced +2 Less than 100 hours of daily vehicle delay reduced +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| CAPACITY MANAGEMENT AND MOBILITY (29 possible points) | ||
| CLEAN AIR/SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES: Create an environmentally friendly transportation system. | ||
| Reduce greenhouse gases generated in the Boston region by all transportation modes Reduce other transportation-related pollutants Minimize negative environmental impacts of the transportation system Support land use policies consistent with smart, healthy, and resilient growth |
Reduces CO2 (-5–5 points) |
+5 1,000 or more annual tons of CO2 reduced +4 500–999 annual tons of CO2 reduced +3 250–499 annual tons of CO2 reduced +2 100–249 annual tons of CO2 reduced +1 Less than 100 annual tons of CO2 reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 100 annual tons of CO2 increased -3 250–499 annual tons of CO2 increased -4 500–999 annual tons of CO2 increased -5 1,000 or more annual tons of CO2 increased |
| Reduces other transportation-related emissions (VOC, NOx, CO) (-5–5 points) |
+5 2,000 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +4 1,000–1999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +3 500–999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +2 250–499 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced +1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO reduced 0 No impact -1 Less than 250 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -2 250–499 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -3 500–999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -4 1,000–1999 total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased -5 2,000 or more total kilograms of VOC, NOx, CO increased |
|
| Addresses environmental impacts (0–4 points) |
+1 Addresses water quality | |
| +1 Addresses cultural resources/open space |
||
| +1 Addresses wetlands/resource areas |
||
| +1 Addresses wildlife preservation/protected habitats |
||
| +0 Does not meet or address criteria | ||
| Is in an EOEEA-certified "Green Community" (0–2 points) |
+2 Project is located in a “Green Community” +0 Project is not located in a "Green Community" |
|
| CLEAN AIR/SUSTAINABLE COMMUNITIES (16 possible points) | ||
| TRANSPORTATION EQUITY: Ensure that all people receive comparable benefits from, and are not disproportionately burdened by, MPO investments, regardless of race, color, national origin, age, income, ability, or sex. | ||
| Prioritize MPO investments that benefit equity populations Minimize potential harmful environmental, health, and safety effects of MPO funded projects for all equity populations Promote investments that support transportation for all ages (age-friendly communities) Promote investments that are accessible to all people regardless of ability |
Serves Title VI/non-discrimination populations (-10–12 points) |
+2 Serves minority (high concentration) population (>2,000 people) +1 Serves minority (low concentration) population (≤ 2,000 people) |
| +2 Serves low-income (high concentration) population (>2,000 people) +1 Serves low-income (low concentration) population (≤ 2,000 people) |
||
| +2 Serves limited-English proficiency (high concentration) population (>1,000 people) +1 Serves limited-English proficiency (low concentration) population (≤ 1,000 people) |
||
| +2 Serves elderly (high concentration) population (>2,000 people) +1 Serves elderly (low concentration) population (≤ 2,000 people) |
||
| +2 Serves zero vehicle households (high concentration) population (>1,000 people) +1 Serves zero vehicle households (low concentration) population (≤ 1,000 people) |
||
| +2 Serves persons with disabilities (high concentration) population (>1,000 people) +1 Serves persons with disabilities (low concentration) population (≤ 1,000 people) |
||
| +0 Does not serve Title VI or non-discrimination populations -10 Creates a burden for Title VI/non -discrimination populations |
||
| TRANSPORTATION EQUITY (12 possible points) | ||
| ECONOMIC VITALITY: Ensure our transportation network provides a strong foundation for economic vitality. | ||
| Respond to mobility needs of the workforce population Minimize the burden of housing and transportation costs for residents in the region Prioritize transportation investments that serve residential, commercial, and logistics targeted development sites and "Priority Places" identified in the MBTA's Focus 40 plan Prioritize transportation investments consistent with compact-growth strategies of the regional transportation plan |
Serves targeted development site (0–6 points) |
+2 Provides new transit access to or within site +1 Improves transit access to or within site +1 Provides for bicycle access to or within site +1 Provides for pedestrian access to or within site +1 Provides for improved road access to or within site +0 Does not provide any of the above measures |
| Provides for development consistent with the compact growth strategies of MetroFuture (0–5 points) |
+2 Mostly serves an existing area of concentrated development +1 Partly serves an existing area of concentrated development +1 Supports local zoning or other regulations that are supportive of smart growth development +2 Complements other local financial or regulatory support that fosters economic revitalization in a manner consistent with smart growth development principles +0 Does not provide any of the above measures |
|
| Provides multimodal access to an activity center (0–4 points) |
+1 Provides transit access (within a quarter mile) to an activity center | |
| +1 Provides truck access to an activity center |
||
| +1 Provides bicycle access to an activity center |
||
| +1 Provides pedestrian access to an activity center |
||
| +0 Does not provide multimodal access |
||
| Leverages other investments (non-TIP funding) (0–3 points) |
+3 Meets or addresses criteria to a high degree (>30 percent of the project cost) +2 Meets or addresses criteria to a medium degree (10–30 percent of the project cost) +1 Meets or addresses criteria to a low degree (< 10 percent of the project cost) +0 Does not meet or address criteria |
|
| ECONOMIC VITALITY (18 possible points) | ||
| TOTAL SCORE (134 possible points) | ||
Table A-11
Evaluation Criteria for FFY 2021 Community Connections Program (Archived)
| Key | ||
| Blue = Criteria that apply to all projects | ||
| Green = Criteria for capital projects | ||
| Red/Pink = Criteria for operating projects | ||
| OBJECTIVE | CRITERIA | FACTORS |
| PROJECT ELIGIBILITY VERIFICATION | ||
| Each project funded through this program must show an air quality benefit when analyzed through the MPO’s air quality analysis process. Projects must be ready to begin construction or operation by October 2020. Project sponsors or proponents must demonstrate that they have gained support from stakeholders and have the institutional capacity to carry out the project within the MPO timeframe. |
Air Quality Analysis | Projects must pass a spreadsheet-based air quality benefit test based on a variety of data inputs customized to the type of project. |
| Proponent's Project Management Capacity |
Names, experience, and time commitment of project management staff, as provided by the proponent. | |
| GENERAL SCORING CRITERIA (30 possible points) | ||
| Network or connectivity value (6 points) | ||
| The primary purpose of the Community Connections Program is to close gaps in the transportation network, especially those in the first or last mile between transit and a destination. Projects will be awarded points based on how effectively a proposed project closes different types of gaps and makes travel easier or more efficient. |
Connection to existing activity hubs and residential developments (2 points) |
Proximity of the project or service to employment, residential, and civic activity hubs, such as dense areas of employment or housing. |
| Connection to existing transit hubs (2 points) |
Proximity of the project to transit service, with added incentive for connecting to frequent or high-quality service. | |
| Connection to other transportation infrastructure (2 points) | Proximity of the project to sidewalk or protected or off-road bicycle infrastructure. | |
| Coordination or cooperation between multiple entities (5 points) | ||
| The MPO prioritizes collaboration among different entities in the transportation planning process. Cooperative project planning and execution is particularly important for first-mile and last-mile connections of the type that the Community Connections Program is intended to facilitate. The cooperation can involve actors from both the public and private sectors. |
Number of collaborating entities (5 points) |
Number and variety (judged by sector of origin) of entities collaborating to support the project. |
| Inclusion in and consistency with local and regional plans (5 points) | ||
| A comprehensive planning process is important to ensure that projects occur in an environment of collaboration and careful consideration rather than independently. This criterion proposes to award points based on the extent to which a proposed project has been included in prior plans at both the local and regional levels, and whether it meets the goals of those plans. | Inclusion in local plans (2 points) |
Whether the project is included as a need or priority in a local comprehensive plan. |
| Inclusion in MPO plans (2 points) |
Whether the project is identified as a need in the LRTP Needs Assessment or recommended in an MPO or MAPC study. | |
| Inclusion in statewide plans (1 point) |
Whether the project is included as a need or priority in a MassDOT or other statewide study. | |
| Transportation equity (5 points) | ||
| The MPO seeks to target investments to areas that benefit a high percentage of low-income and minority populations; minimize any burdens associated with MPO-funded projects in low-income and minority areas; and break down barriers to participation in MPO-decision making. | Serves a demographic of transportation equity concern, as identified by the MPO (5 points) | The extent to which the project serves equity populations. |
| Generation of mode shift (4 points) | ||
| Another primary purpose of the Community Connection Program is to enable modal shift from SOV to transit or other modes. This criterion would award points based on the project’s effectiveness at creating mode shift and/or enabling trips that were previously impossible by non-SOV modes. |
Allow new trips that would not be otherwise possible without a car (4 points) |
Whether the project adds to overall non-automotive mobility by creating new connections or making trips possible that were not previously, without detracting from or competing with existing transit options. |
| Demand projection (4 points) | ||
| Gaining an understanding of how many transportation network users a project will reach is crucial for understanding its cost-effectiveness. | Overall demand estimate (2 points) | Presence of demand/usage estimates and quality of analysis used to support them in the application materials. |
| Staff evaluation of demand estimate (2 points) | Whether staff judge the demand/usage projections realistic. | |
| TYPE-SPECIFIC EVALUATION CRITERIA: CAPITAL PROJECTS (30 points) | ||
| SAFETY BENEFITS (12 points) | ||
| Bicycle safety (6 points) | ||
| Improving safety on the regional transportation network is one of the MPO’s key goals. This criterion would award points to projects that improve safety for the most vulnerable users of the network – people walking and people riding bicycles. An overall score of the effectiveness of bicycle safety countermeasures will be made through professional judgement comparing existing facilities, safety issues, use, and desired/anticipated use to the proposed bicycle safety countermeasures planned to be implemented as part of the project. | Total effectiveness of bicycle safety countermeasures (6 points) | Existing and potential bicyclist usage of the infrastructure and effectiveness of the expected safety improvements. |
| Pedestrian safety (6 points) | ||
| An overall score of the effectiveness of pedestrian safety countermeasures will be made through professional judgement comparing existing facilities, safety issues, use, and desired/anticipated use to the proposed pedestrian safety countermeasures planned to be implemented as part of the project. | Total effectiveness of pedestrian safety countermeasures (6 points) | Existing and potential pedestrian usage of the infrastructure and effectiveness of the expected safety improvements. |
| Lifecycle cost-effectiveness (10 points) | ||
| In addition to the initial construction costs, the MPO is concerned that projects funded through the Community Connection Program remain fiscally sustainable after MPO-awarded funding runs out. Projects proposed to the program should be cost-effective compared to potential alternatives, and proponents should demonstrate that local maintenance budgets will be able to accommodate the increased costs of maintaining the project. | Lifecycle Alternatives Analysis (5 Points) | Presence of a cost-effectiveness analysis in the application and whether the analysis is qualitative or quantitative. |
| Maintenance budget and plan (5 Points) | Identification of a maintenance plan for the project, including the entity responsible for it and a source of funds. | |
| Resilience to weather and environmental hazards (8 points) | ||
| Resilience in the face of increasingly destructive storms and weather hazards is a growing concern in the Boston region, and is codified in the MPO’s System Preservation goal. Project proponents should demonstrate that their project will not cause damage to a sensitive ecosystem and that it will be able to resist damage from extreme weather events. | Impact on areas of environmental concern (6 points) | Magnitude of the project's environmental impact, positive or negative. |
| Relationship to resilience plans (2 points) | Whether the project is included in local resilience plans. | |
| TYPE-SPECIFIC CRITERIA: OPERATIONAL PROJECTS | ||
| Long-Term Financial Plan (12 points) | ||
| Annual operating costs (2 points) | Whether the estimate of operating costs is present and realistic. | |
| Annual maintenance costs (1 point) | Whether the estimate of maintenance costs is present and realistic. | |
| All other costs (1 point) | Whether the estimate of other costs is present and realistic. | |
| Fare structure (2 points) | Presence of a detailed description of the proposed fare structure and explanation thereof. | |
| Plan for fiscal sustainability (6 points) | Whether the application identifies full funding for the project (reflecting a local match to MPO funds) for 0, 1, 2, 3 or more years. | |
| Service Plan (10 points) | ||
| Service Plan (4 points) | Presence of details on: • Plans for ADA compliance • Frequency and routing of service • How the service plans meet the need of projected riders |
|
| Operational/contracting plan (4 points) | Presence of details on administrative and/or contracting plans and the background of the operator. | |
| Marketing plan (2 points) | Presence of a detailed description of a marketing plan. | |
| Performance Monitoring Plan (8 points) | ||
| Data management plan (3 points) | Inclusion of plans for data collection, analysis for monitoring service, and sharing the data with the MPO. | |
| Passenger survey (2 points) | Whether the application describes plans for a ridership survey and the frequency with which it will be administered. | |
| Trip-level boarding counts (1 point) | Presence of plans for trip-level data collection. | |
| Stop-level data collection (1 point) | Presence of plans for stop-level data collection. | |
| Marketing evaluation (1 point) | Presence of plans for an evaluation of the marketing effort. | |
| ADA = Americans with Disabilities Act. CMAQ = Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement Program. CTPS = Central Transportation Planning Staff. FFY = federal fiscal year. GIS = geographic information systems. GTFS = general transit feed specification. LRTP = Long-Range Transportation Plan. MAPC = Metropolitan Area Planning Council. MassDOT = Massachusetts Department of Transportation. MBTA = Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority. MPO = Metropolitan Planning Organization. MVP = Municipal Vulnerability Program. SOV = single occupancy vehicle. TAD = Traffic and Design. TAZ = transportation analysis zone. TIP = Transportation Improvement Program. | ||
The Global Warming Solutions Act of 2008 (GWSA) required statewide reductions in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of 25 percent below 1990 levels by the year 2020, and 80 percent below 1990 levels by 2050. As part of the GWSA, the Executive Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs developed the Massachusetts Clean Energy and Climate Plan (CECP), which outlined programs to attain the 25 percent reduction by 2020—including a 7.6 percent reduction attributed to the transportation sector.
The Commonwealth’s 13 metropolitan planning organizations (MPOs) are integrally involved in helping to achieve GHG emissions reductions mandated under the GWSA. The MPOs work closely with the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) and other involved agencies to develop common transportation goals, policies, and projects that will help to reduce GHG emissions levels statewide, and meet the specific requirements of the GWSA regulation, Global Warming Solutions Act Requirements for the Transportation Sector and the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (310 CMR 60.05). The purpose of this regulation is to assist the Commonwealth in achieving its adopted GHG emissions reduction goals by requiring the following:
The Commonwealth’s MPOs are meeting the requirements of this regulation through the transportation goals and policies contained in their LRTPs, the major projects planned in their LRTPs, and the mix of new transportation projects that are programmed and implemented through their TIPs.
The GHG tracking and evaluation processes enable the MPOs and MassDOT to identify the anticipated GHG impacts of the planned and programmed projects, and to use GHG impacts as criteria to prioritize transportation projects. This approach is consistent with the GHG emissions reduction policies that promote healthy transportation modes through prioritizing and programming an appropriate balance of roadway, transit, bicycle, and pedestrian investments, as well as policies that support smart growth development patterns by creating a balanced multimodal transportation system.
MassDOT coordinated with MPOs and regional planning agencies to implement GHG tracking and to evaluate projects during the development of the LRTPs that were adopted in September 2011. This collaboration continued during the development of the LRTPs and amendments adopted in 2016, and for the TIPs produced for federal fiscal years (FFYs) 2016–19, 2017–21, 2018–22, 2019–23, 2020–24, 2021–25, and 2022–26. Working together, MassDOT and the MPOs have attained the following milestones:
In addition to monitoring the GHG impacts of projects in the LRTP that will add capacity to the transportation system, it also is important to monitor and evaluate the GHG impacts of all transportation projects that are programmed in the TIP. The TIP includes both the larger, capacity-adding projects from the LRTP and smaller projects, which are not included in the LRTP but that may affect GHG emissions. The principal objective of this tracking is to enable the MPOs to evaluate the expected GHG impacts of different projects and to use this information as criteria to prioritize and program projects in future TIPs.
In order to monitor and evaluate the GHG impacts of TIP projects, MassDOT and the MPOs have developed approaches for identifying anticipated GHG emissions impacts of different types of projects. Since carbon dioxide (CO2) is the largest component of GHG emissions overall and is the focus of regulation 310 CMR 60.05, CO2 has been used to measure the GHG emissions impacts of transportation projects in the TIP and LRTP.
All TIP projects have been sorted into two categories for analysis: 1) projects with quantified CO2 impacts, and 2) projects with assumed CO2 impacts. Projects with quantified impacts consist of capacity-adding projects from the LRTP and projects from the TIP that underwent a Congestion Mitigation and Air Quality Improvement (CMAQ) program spreadsheet analysis. Projects with assumed impacts are those that would be expected to produce a minor decrease or increase in emissions, and those that would be assumed to have no CO2 impact.
Projects with quantified impacts include capacity-adding projects in the LRTP that were analyzed using the Boston Region MPO’s travel demand model set. No independent calculations were done for these projects during the development of the TIP.
MassDOT’s Office of Transportation Planning provided spreadsheets that are used to determine projects’ eligibility for funding through the CMAQ program. Typically, MPO staff uses data from projects’ functional design reports, which are prepared at the 25-percent design phase, to conduct these calculations. Staff used these spreadsheets to calculate estimated projections of CO2 for each project, in compliance with GWSA regulations. These estimates are shown in Tables B-1 and B-2. A note of “to be determined” is shown for those projects for which a functional design report was not yet available.
As part of the development of the FFYs 2023–27 TIP, analyses were done for the types of projects described below. A summary of steps performed in the analyses is provided.
For an intersection reconstruction or signalization project that typically reduces delay and, therefore, idling, the following steps are taken:
For a shared-use path that would enable more walking and biking trips and reduce automobile trips, the following steps are taken:
For a program that replaces old buses with new buses that reduce emissions or run on cleaner fuel, the following steps are taken:
Calculations may be performed on the project types listed below; however, there are no projects of these types in this TIP:
Projects with assumed CO2 impacts are those that could produce a minor decrease or increase in emissions, but the change in emissions cannot be calculated with any precision. Examples include a bicycle rack installation, Safe Routes to School project, or transit marketing or customer service improvement. These projects are categorized as producing an assumed nominal increase or decrease in emissions.
Projects that do not change the capacity or use of a facility—for example, a resurfacing project that restores a roadway to its previous condition, or a bridge rehabilitation or replacement that restores the bridge to its previous condition—are assumed to have no CO2 impact.
More details about these projects are discussed in Chapter 3. The following tables display the GHG impact analyses of projects funded in the FFYs 2023–27 Highway Program (Table B-1) and Transit Program (Table B-2). Table B-3 summarizes the GHG impact analyses of highway projects completed before FFY 2023. Table B-4 summarizes the GHG impact analyses of transit projects completed before FFY 2023. A project is considered completed when the construction contract has been awarded or the transit vehicles have been purchased.
Table B-1
Greenhouse Gas Regional Highway Project Tracking: FFYs 2023–27 Programmed Projects
| Project ID Number | Project Name | GHG Analysis Type | GHG CO2 Impact (kg/yr) | GHG Impact Description |
| S12702 | Acton - Bicycle Parking along the Bruce Freeman Rail Trail | Quantified | 1,024 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 607748 | Acton - Intersection and Signal Improvements on Route 2 and Route 111 (Massachusetts Ave) at Piper Rd and Taylor Rd | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 610722 | Acton, Boxborough, Littleton - Pavement Preservation Route 2 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609531 | Arlington - Stratton School Improvements (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612099 | Ashland - Bridge Replacement, A-14-006, Cordaville Road over Sudbury River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608436 | Ashland - Rehabilitation and Rail Crossing Improvements on Cherry Street | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612173 | Bellingham - Bridge Replacement, B-06-022, Maple Street over Interstate 495 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12704 | Belmont - Chenery Middle School Bicycle Parking | Quantified | 771 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 609204 | Belmont - Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) | Quantified | 26,347 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 608514 | Beverly - Bridge Replacement, B-11-001, Bridge Street over Bass River (Hall-Whitaker Drawbridge) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608348 | Beverly - Reconstruction of Bridge St | Quantified | 387,153 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 605276 | Beverly, Salem - Drawbridge Replacement/Rehabilitation of B-11-005=S-01-013, Kernwood Avenue over Danvers River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12703 | Bolton, Boxborough, Littleton, Stow - Montachusett RTA Microtransit Service | Quantified | 24,602 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 612663 | Boston - Bridge Preservation, B-16-053 (4T3), Brookline Avenue over Interstate 90 and Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612664 | Boston - Bridge Preservation, B-16-179, Austin Street over Interstate 93, and B-16-281, Interstate 93 Upper and Lower Deck | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612662 | Boston - Bridge Preservation, B-16-235 (39T and 3A0), Route 1A over Chelsea Street/Bremen Street and Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 606902 | Boston - Bridge Reconstruction/Rehab, B-16-181, West Roxbury Parkway over MBTA | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 606496 | Boston - Bridge Rehabilitation, B-16-052, Bowker Overpass over Mass. Pike, MBTA/CSX, and Ipswich Street and Ramps | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608197 | Boston - Bridge Rehabilitation, B-16-107, Canterbury St over Amtrak Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 606901 | Boston - Bridge Replacement, B-16-109, River Street Bridge over MBTA/AMTRAK | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612519 | Boston - Bridge Replacement, B-16-165, Blue Hill Avenue over Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 606728 | Boston - Bridge Replacement, B-16-365, Storrow Drive over Bowker Ramps | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612624 | Boston - Deck Replacement, B-16-056, Cambridge Street Over Interstate 90, Includes Preservation of B-16-057, Lincoln Street Pedestrian Overpass over Interstate 90 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 610537 | Boston - Ellis Elementary Traffic Calming (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| S12706 | Boston - Forest Hills Improvement Project | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 611954 | Boston - Guide and Traffic Sign Replacement on I-90/I-93 within Central Artery/Tunnel System | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 606453 | Boston - Improvements on Boylston St, from Intersection of Brookline Ave and Park Dr to Ipswich St | Quantified | 1,920,790 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 606226 | Boston - Reconstruction of Rutherford Ave, from City Square to Sullivan Square | Quantified | LRTP project included in the statewide model | |
| 606476 | Boston - Roadway, Ceiling, Arch & Wall Reconstruction and Other Control Systems in Sumner Tunnel | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608208 | Boston, Milton, Quincy - Interstate Maintenance and Related Work on Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608009 | Boxborough - Bridge Replacement, B-18-002, Route 111 over Interstate 495 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 607684 | Braintree - Bridge Replacement, B-21-017, Washington Street (ST 37) over MBTA/CSX Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612196 | Braintree - Bridge Replacement, B-21-067, JW Maher Highway over Monatiquot River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608498 | Braintree, Quincy, Weymouth - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 53 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612050 | Braintree, Weymouth - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 3 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12210 | Brookline - Improvements at William H. Lincoln School (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 610932 | Brookline - Rehabilitation of Washington Street | Quantified | 36,431 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 609516 | Burlington - Improvements at Interstate 95 (Route 128)/Route 3 Interchange | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612034 | Burlington, Woburn - Interstate Maintenance and Related Work on Interstate 95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12695 | Cambridge - Bluebikes Station Replacement and System Expansion | Quantified | 20,484 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 606449 | Cambridge - Bridge Replacement, C-01-008, First Street Bridge and C-01-040, Land Boulevard Bridge/Broad Canal Bridge | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 611987 | Cambridge - Bridge Replacement, C-01-026, Memorial Drive over Brookline Street | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 610776 | Cambridge - Superstructure Replacement, C-01-031, US Route 3/Route 16/Route 2 over MBTA Red Line | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609438 | Canton - Bridge Replacement, C-02-042, Revere Court over West Branch of the Neponset River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 610541 | Canton - Interim Interchange Improvements at Interstate 95/Route 128/Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12114 | Canton - Royall Street Shuttle | Quantified | 702,115 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 609053 | Canton, Dedham, Norwood - Highway Lighting Improvements at Interstate 93 and Interstate 95/Route 128 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612615 | Canton, Milton - Roadway Reconstruction on Route 138, From Royall Street to Dollar Lane | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612051 | Canton, Milton, Randolph - Interstate Maintenance and Related Work on Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608952 | Chelsea - Bridge Superstructure Replacement, C-09-013, Washington Avenue, Carter Street, and County Road/Route 1 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12211 | Chelsea - Improvements at Mary C. Burke Elementary (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 611983 | Chelsea - Park and Pearl Street Reconstruction | Quantified | 10,214 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 609532 | Chelsea - Targeted Safety Improvements and Related Work on Broadway, from Williams Street to City Hall Avenue | Quantified | -25,503 | Quantified increase in emissions |
| 608007 | Cohasset, Scituate - Corridor Improvements and Related Work on Justice Cushing Highway (Route 3A) from Beechwood Street to Henry Turner Bailey Road | Quantified | 5,849 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 612607 | Danvers - Rail Trail West Extension (Phase 3) | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 610782 | Danvers, Middleton - Bridge Replacement, D-03-009=M-20-005, Andover Street (SR 114) over Ipswich River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608818 | Danvers, Middleton - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 114 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12212 | Dedham - Improvements at Avery Elementary School (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 607899 | Dedham - Pedestrian Improvements Along Bussey St, Including Superstructure Replacement, D-05-010, Bussey Street over Mother Brook | Quantified | 3,331 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 611969 | Everett - Intersection Improvements on Route 16 | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 609257 | Everett - Reconstruction of Beacham Street | Quantified | 4,038 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 608480 | Foxborough - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 1 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12640 | Framingham - High-Risk At-Grade Railroad Crossing Countermeasures on Route 126 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12205 | Framingham - Improvements at Harmony Grove Elementary School (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 608889 | Framingham - Traffic Signal Installation at Edgell Road and Central Street | Quantified | 233,257 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 609402 | Framingham, Natick - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 9 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12700 | Gloucester, Rockport - CATA On Demand Microtransit Service Expansion | Quantified | 33,400 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 609467 | Hamilton - Bridge Replacement, H-03-002, Winthrop Street over Ipswich River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 605168 | Hingham - Improvements on Route 3A from Otis Street/Cole Road, Including Summer Street and Rotary; Rockland Street to George Washington Boulevard | Quantified | 284,736 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 607977 | Hopkinton, Westborough - Reconstruction of Interstate 90/Interstate 495 Interchange | Quantified | LRTP project included in the statewide model | |
| S12701 | Hudson, Marlborough - MWRTA CatchConnect Microtransit Service Expansion | Quantified | 11,936 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 605743 | Ipswich - Resurfacing and Related Work on Central and South Main Streets | Quantified | 4,356 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 603722 | Lexington - Bridge Replacement, L-10-010, Route 2A (Marrett Road) over Interstate 95/Route 128 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609054 | Littleton - Reconstruction of Foster Street | Quantified | 1,140 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 609254 | Lynn - Intersection Improvements at Two Intersections on Broadway | Quantified | 73,291 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| S12705 | Lynn - Lynn Station Improvements Phase II | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 609246 | Lynn - Reconstruction of Western Avenue | Quantified | 902,708 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 609252 | Lynn - Rehabilitation of Essex Street | Quantified | 411,394 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 612599 | Lynn - Targeted Safety and Multimodal Improvements (Playbook Priority Corridors) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 610919 | Lynn, Nahant - Northern Strand Extension | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 607329 | Lynnfield, Wakefield - Rail Trail Extension, from the Galvin Middle School to Lynnfield/Peabody Town Line | Quantified | 158,032 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| S12696 | Malden, Medford - Bluebikes System Expansion | Quantified | 2,637 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 610543 | Malden, Revere - Improvements at Route 1 (Northbound) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 604564 | Maynard - Bridge Replacement, M-10-004, Route 62 (Main Street) over the Assabet River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 611974 | Medford - Intersection Improvements at Main Street and South Street | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612001 | Medford - Milton Fuller Roberts Elementary School (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 611982 | Medford - Shared-Use Path Connection at the Route 28/Wellington Underpass | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 612499 | Medford - South Medford Connector Bike Path | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 610726 | Medford, Winchester, Stoneham - Interstate Pavement Preservation on Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609530 | Medway - Holliston Street and Cassidy Lane Improvements (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 608522 | Middleton - Bridge Replacement, M-20-003, Route 62 (Maple Street) over Ipswich River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608045 | Milford - Rehabilitation on Route 16, from Route 109 to Beaver Street | Quantified | -16,555 | Quantified increase in emissions |
| 607342 | Milton - Intersection and Signal Improvements at Route 28 (Randolph Ave) and Chickatawbut Road | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 608955 | Milton - Intersection Improvements, Squantum Street at Adams Street | Quantified | 104,106 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 612178 | Natick - Bridge Replacement, N-03-010, Speen Street over Railroad MBTA/CSX | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 605313 | Natick - Bridge Replacement, Route 27 Over Route 9 and Interchange Improvements | Quantified | 539,400 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 610680 | Natick - Lake Cochituate Path | Quantified | 1,749 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 607420 | Natick - Superstructure Replacement, N-03-012, Boden Lane over CSX/MBTA | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612182 | Newton - Bridge Replacement, N-12-040, Boylston Street Over Green Line D Branch | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 611997 | Newton - Horace Mann Elementary School Improvements (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| S12694 | Newton - NewMo Microtransit Service Expansion | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| S12125 | Newton - Newton Microtransit Service | Quantified | 24,809 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 610674 | Newton - Reconstruction of Commonwealth Avenue (Route 30), from East of Auburn Street to Ash Street | Quantified | 16,846 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 110980 | Newton, Weston - Bridge Rehabilitation, N-12-010=W-29-005, Commonwealth Avenue (Route 30) over the Charles River | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 608609 | Newton, Westwood - Steel Superstructure Cleaning (Full Removal) and Painting of Two Bridges: N-12-056 and W-31-006 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 605321 | Norwood - Bridge Preservation, N-25-026, Providence Highway (State Route 1) over the Neponset River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 605857 | Norwood - Intersection Improvements at Route 1 and University Avenue/Everett Street | Quantified | 1,092,131 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 606130 | Norwood - Intersection Improvements at Route 1A and Upland Road/Washington Street and Prospect Street/Fulton Street | Quantified | 131,840 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 609211 | Peabody - Independence Greenway Extension | Quantified | 36,651 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 610544 | Peabody - Multi-Use Path Construction of Independence Greenway at Interstate 95 and Route 1 | Quantified | 24,423 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 608933 | Peabody - Rehabilitation of Central Street | Quantified | 150,913 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 608707 | Quincy - Reconstruction of Sea Street | Quantified | -30,437 | Quantified increase in emissions |
| 612049 | Randolph - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 24 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609399 | Randolph - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 28 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609527 | Reading - Improvements on Interstate 95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12124 | Regionwide - Community Connections Program | Qualitative | Impact on emissions will be calculated when specific projects are chosen for funding through this program | |
| S12113 | Regionwide - Transit Modernization Program | Qualitative | Impact on emissions will be calculated when specific projects are chosen for funding through this program | |
| 612184 | Revere - Bridge Replacement, R-05-015, Revere Beach Parkway over Broadway | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612100 | Revere - Improvements at Beachmont Veterans Elementary (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612523 | Revere - State Road Beachmont Connector | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| S12698 | Salem - Bluebikes System Expansion | Quantified | 460 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 609437 | Salem - Boston Street Improvements | Quantified | 58,786 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 612075 | Salem - Bridge Replacement, S-01-024, Jefferson Avenue over Parallel Street | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| S12209 | Sharon - Improvements at Cottage Street Elementary School (SRTS) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612496 | Somerville - Bridge Preservation, S-17-031, Interstate 93 (Northbound and Southbound) from Route 28 to Temple Street (Phase 2) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 607981 | Somerville - McGrath Boulevard Construction | Quantified | 136,345 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 608562 | Somerville - Signal and Intersection Improvements on Interstate 93 at Mystic Avenue and McGrath Highway (Top 200 Crash Location) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| 612028 | Stoneham - Deck Replacement and Superstructure Repairs, S-27-006 (2l2), (ST 28) Fellsway West over Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 610665 | Stoneham - Intersection Improvements at Route 28 (Main Street), North Border Road and South Street | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| S12699 | Stoneham - Stoneham Shuttle Service | Quantified | 41,707 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 608255 | Stow - Bridge Replacement, S-29-011, Box Mill Road over Elizabeth Brook | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 610660 | Sudbury, Wayland - Mass Central Rail Trail (MCRT) | Quantified | TBD | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 610666 | Swampscott - Rail Trail Construction | Quantified | 138,430 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure |
| 612076 | Topsfield - Bridge Replacement, T-06-013, Perkins Row over Mile Brook | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 612048 | Waltham - Interstate Maintenance and Related Work in Interstate 95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608564 | Watertown - Intersection Improvements at Route 16 and Galen Street | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | |
| S12697 | Watertown - Pleasant Street Shuttle Service Expansion | Quantified | 183,575 | Quantified decrease in emissions from new/additional transit service |
| 607777 | Watertown - Rehabilitation of Mount Auburn St (Route 16) | Quantified | 634,598 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 608940 | Weston - Intersection Improvements at Boston Post Road (Route 20) at Wellesley Street | Quantified | 102,453 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 608954 | Weston - Reconstruction on Route 30 | Quantified | 357,681 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 607327 | Wilmington - Bridge Replacement, W-38-002, Route 38 (Main Street) over the B&M Railroad | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608929 | Wilmington - Bridge Replacement, W-38-003, Butters Row over MBTA | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 608703 | Wilmington - Bridge Replacement, W-38-029 (2KV), ST 129 Lowell Street over Interstate 93 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| 609253 | Wilmington - Intersection Improvements at Lowell Street (Route 129) and Woburn Street | Quantified | 494,211 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 608051 | Wilmington - Reconstruction of Route 38 (Main Street), from Route 62 to the Woburn City Line | Quantified | 492,160 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 607244 | Winthrop - Reconstruction and Related Work Along Winthrop Street and Revere Street Corridor | Quantified | 252,816 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project |
| 610662 | Woburn - Roadway and Intersection Improvements at Woburn Common, Route 38 (Main Street), Winn Street, Pleasant Street, and Montvale Avenue | Quantified | 736,275 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 608067 | Woburn, Burlington - Intersection Reconstruction at Route 3 (Cambridge Road) & Bedford Road and South Bedford Street | Quantified | 168,263 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
| 603739 | Wrentham - Construction of Interstate 495/Route 1A Ramps | Quantified | 1,233,486 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement |
Table B-2
Greenhouse Gas Regional Transit Project Tracking: FFYs 2023–27 Programmed Projects
| Regional Transit Authority | Project Description | GHG Analysis Type | GHG CO2 Impact (kg/yr) | GHG Impact Description |
| CATA | Acquire - Shop Equipment / Computers / Software | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| CATA | Replace 30’ Buses/Trolleys (2) | Quantified | 530 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement |
| CATA | Buy Assoc. Capital Maintenance Items | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| CATA | Preventive Maintenance | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| CATA | Repave Parking Lot | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| CATA | Repave Parking Lot | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| CATA | Replace 30-foot Buses (3) | Quantified | 1,278 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement |
| MBTA | Elevator Program | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Bus Overhaul Program (156 Hybrid, 175 CNG, 44 60ft Hybrid) | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MBTA | Procurement of 40 ft Enhanced Electric Hybrid Buses - FFY 2023 to FFY 2027 | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MBTA | DMA Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Midlife Overhaul of 25 New Flyer Allison Hybrid 60ft Articulated Buses | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Overhaul of 155 Option New Flyer Buses | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Procurement of Bi-Level Commuter Rail Coaches | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Mattapan HSL Transformation | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Signal Program - Red/Orange Line | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Charlestown Bus - Seawall Rehab | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Harvard Square Busway Repairs | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Harvard/Central Elevator | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Hingham Ferry Dock Modification | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Bridges - Design | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | East Cottage Street Bridge | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Emergency Bridge Design / Inspection & Rating | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Norfolk Avenue Bridge | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Structural Repairs Systemwide | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Tunnel Inspection Systemwide | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Green Line Train Protection | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | 45 High Street - Data Center Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Alewife Crossing Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Worcester Line Track and Station Accessibility Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Green Line Central Tunnel Track and Signal Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Systemwide Asset Management Program Phase 4 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Power Systems Resiliency Program | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | MCRS2 v17 and Business Process Update | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Red Line Interlock Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Codman Yard Expansion and Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Downtown Crossing Vertical Transportation Improvements Phase 2 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Elevator Program Multiple Location Design | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Lynn Station & Parking Garage Improvements Phase II | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Newton Commuter Rail Stations | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Newton Highlands Green Line Station Accessibility Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Ruggles Station Improvements Phase 2 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | South Attleboro Station Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | MBTA Catamaran Overhauls | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Mattapan Trolley Select System Upgrade | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Blue Line Vehicle Mid‐Life Overhaul | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Blue Line Infrastructure Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Quincy Bus Facility Modernization | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Arborway Bus Facility ‐ Design Funding | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | North Cambridge Bus Facility Modernization |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Bus Priority Project Construction | Quantified | TBD | Emissions reduction will be analyzed when bus priority locations have been determined |
| MBTA | North Station Draw 1 Bridge Replacement | Quantified | TBD | Elements of the project, including construction of a pedestrian bridge, will be analyzed when project design advances |
| MBTA | Longfellow Approach | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | East Street Bridge Replacement (Dedham) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Bridge Program Pipeline ‐ Rehabilitation, Repair and Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Systemwide Culvert Inspection and Load Rating | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Future Rolling Stock Fleet (25 Commuter Rail) | Quantified | TBD | Emissions reduction will be analyzed based on the type of Commuter Rail cars (electrified or multi-mode) |
| MBTA | Rolling Stock ‐ Locomotive and Coach State of Good Repair and Resiliency | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Green Line Central Tunnel Signal ‐ 25 Cycle | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Traction Power Substation Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | South Boston to Forest Hills Duct Bank Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Ashmont Branch Track Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Braintree Line Track Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Unit Substation Replacement Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Oak Grove Station Vertical Transportation Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Forest Hills Improvement Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | E Branch Accessibility & Capacity Improvements |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | B Branch Accessibility & Capacity Improvements |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Riverside Vehicle Maintenance Facility Modifications & Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Green Line Extension Vehicle Maintenance Facility Modifications & Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Lake Street Complex Demolition and Reconfiguration | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Reservoir Yard and Non‐Revenue Track Optimization and Reconfiguration | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Commuter Rail Facilities State of Good Repair | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Procurement of 40ft Battery Electric Buses and Related Infrastructure | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MBTA | Systemwide Tunnel Flood Mitigation Program | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Option Order Procurement of 194 New Flyer Hybrid 40ft Buses | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MBTA | Hybrid Bus Overhaul (New Flyer XDE40 ‐ SR 1881) | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MBTA | Green Line Type 10 Light Rail Fleet Replacement |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MBTA | Reliability Centered Maintenance ‐ Blue, Orange and Red Line | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Terminal, Intermodal (Transit) - Framingham Commuter Rail Station | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Terminal, Intermodal (Transit) - Blandin | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Technology Support/Capital Outreach |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Non-Fixed Route ADA Paratransit Service | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Front Entrance Blandin (FEB) Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Buy Replacement Van (16) | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MWRTA | AFC Transition | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | |
| MWRTA | Buy Replacement Van (10) | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MWRTA | Buy Replacement Van (14) | Quantified | TBD | To be determined |
| MWRTA | MWRTA Modernization - Fleet Electrification |
Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions |
Table B-3
Greenhouse Gas Regional Highway Project Tracking: Completed Projects
| Project ID Number | Project Name | GHG Analysis Type | GHG CO2 Impact (kg/yr) | GHG Impact Description | FFY of Contract Award |
| 606134 | Boston- Traffic Signal Improvements on Blue Hill Ave and Warren St | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2019 | |
| 608651 | Braintree- Adaptive Signal Controls on Route 37 (Granite Street) | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2019 | |
| 605110 | Brookline- Intersection and Signal Improvements at Route 9 and Village Square (Gateway East) | Quantified | 67,056 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2019 |
| 605287 | Chelsea - Route 1 Viaduct Rehabilitation (Southbound/Northbound) on C-09-007 and C-09-011 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2019 | |
| 600518 | Hingham - Intersection Improvements at Derby St, Whiting St, and Gardner St | Quantified | -145,683 | Quantified increase in emissions | 2019 |
| 604952 | Lynn-Saugus - Bridge replacement, L-18-016=S-05-008, Route 107 over the Saugus River (AKA – Belden G. Bly Bridge) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2019 | |
| 607133 | Quincy - Superstructure Replacement, Q-01-039, Robertson Street over I-93/US 1/SR 3 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2019 | |
| 604989 | Southborough - Reconstruction of Main St (Route 30), from Sears Rd to Park St | Quantified | 231,813 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2019 |
| 608823 | Wellesley- Newton- Weston - Pavement Resurfacing and Related Work on I-95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2019 | |
| 609222 | Arlington – Spy Pond Sediment Removal | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 604123 | Ashland - Reconstruction on Route 126 (Pond St) from Framingham Town Line to Holliston Town Line | Quantified | 148,097 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 608347 | Beverly - Intersection improvements at 3 locations: Cabot St (Route 1A/97) at Dodge St (Route 1A), County Way, Longmeadow Rd and Scott St, McKay St at Balch St and Veterans Memorial Bridge (Route 1A) at Rantoul, Cabot, Water, and Front Sts | Quantified | 582,422 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement | 2020 |
| 604173 | Boston - Bridge Replacement, B-16-016, North Washington Street over the Boston Inner Harbor | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 608608 | Braintree - Highway Lighting Improvements at I-93/Route 3 Interchange | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 607954 | Danvers - Bridge Replacement, D-03-018, ST 128 over Waters River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 608378 | Danvers, Topsfield, Boxford, Rowley - Interstate Maintenance and Related Work on Interstate 95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 607428 | Hopedale, Milford - Resurfacing and Intersection Improvements on Route 16 (Main St), from Water St West to Approximately 120 Feet West of the Milford/Hopedale Town Line and the Intersection of Route 140 | Quantified | 201,148 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 606043 | Hopkinton - Signal and Intersection Improvements on Route 135 | Quantified | 1,298,625 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 608275 | Malden - Exchange St Downtown Improvement Project | Quantified | 13,519 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 608835 | Medford - Improvements at Brook Elementary School | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2020 | |
| 606635 | Needham, Newton - Reconstruction of Highland Ave, Needham St and Charles River Bridge, N-04-002, from Webster St (Needham) to Route 9 (Newton) | Quantified | 1,186,210 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 609101 | Peabody - Pavement Preservation and Related Work on Route 128 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 608205 | Reading to Lynnfield - Guide and Traffic Sign Replacement on a Section of I-95 (SR 128) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 608743 | Salem - Improvements at Bates Elementary School | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2020 | |
| 605342 | Stow - Bridge Replacement, Route 62 (Gleasondale Rd) over the Assabet River | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| 602261 | Walpole - Reconstruction on Route 1A (Main Street), from the Norwood Town Line to Route 27, Includes W-03-024 over the Neponset River | Quantified | 230,473 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2020 |
| 608791 | Winchester - Improvements at Vinson-Owen Elementary School | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Boston - Columbus Avenue Bus Lane Construction | Quantified | 98,855 | Quantified decrease in emissions from transit priority project | 2021 |
| 607888 | Boston - Multi-use Path Construction on New Fenway | Quantified | 54,724 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2021 |
| 610724 | Chelmsford, Medford, Somerville, Stoneham - Interstate Pavement Preservation on Interstate 93 and Interstate 495 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2021 | |
| S10788 | Concord - Bruce Freeman Rail Trail Bike Shelters | Quantified | 2,707 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2021 |
| S10786 | Cambridge - Concord Avenue Transit Signal Priority | Quantified | 645,520 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement | 2021 |
| 607652 | Everett - Reconstruction of Ferry St, South Ferry St and a Portion of Elm St | Quantified | 435,976 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2021 |
| 608210 | Foxborough, Plainville, Wrentham, Franklin – Interstate Maintenance Resurfacing Work on Interstate 495 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2021 | |
| 608228 | Framingham - Reconstruction of Union Ave, from Proctor St to Main St | Quantified | -217,978 | Quantified increase in emissions | 2021 |
| 606501 | Holbrook - Reconstruction of Union St (Route 139), from Linfield St to Centre St and Water St | Quantified | 4,097 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2021 |
| 601607 | Hull - Reconstruction of Atlantic Ave and Related Work | Quantified | 6,586 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2021 |
| 608146 | Marblehead - Intersection Improvements at Pleasant St and Village, Vine, and Cross Streets | Quantified | 531 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement | 2021 |
| 607305 | Reading - Intersection Signalization at Route 28 and Hopkins St | Quantified | 7,088 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement | 2021 |
| S10787 | Sharon - Carpool Marketing | Qualitative | Qualitative reduction in emissions | 2021 | |
| S10785 | Somerville - Davis Square Signal Improvements | Quantified | 4,214 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2021 |
| 607761 | Swampscott - Intersection and Signal Improvements at Route 1A (Paradise Rd) at Swampscott Mall | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2021 | |
| 604996 | Woburn - Bridge Replacement, W-43-017, New Boston Street over MBTA | Quantified | LRTP project included in the statewide model | 2021 | |
| S12122 | Acton - Acton Parking Management System | Qualitative | Qualitative decrease in emissions | 2022 | |
| 608229 | Acton - Intersection and Signal Improvements at Kelley's Corner | Quantified | 111,958 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2022* |
| S12115 | Arlington, Newton, Watertown - BlueBikes Expansion | Quantified | 6,570 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2022 |
| 608443 | Ayer, Littleton - Intersection Improvements on Route 2A at Willow Rd and Bruce St | Quantified | 52,101 | Quantified decrease in emissions from traffic operational improvement | 2022* |
| 607738 | Bedford - Minuteman Bikeway Extension from Loomis St to the Concord Town Line | Quantified | 21,098 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2022* |
| 608887 | Bellingham - South Main St (Route 126) - Douglas Dr to Mechanic St reconstruction (Route 140) | Quantified | 24,363 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2022 |
| 604173 | Boston - Bridge Replacement, B-16-016, North Washington Street over the Boston Inner Harbor | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| 608943 | Boston - Neponset River Greenway Construction, Including New Bridge B-16-309 (C6Y) over Dorchester Bay | Quantified | 239,055 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2022* |
| 607670 | Boston - Superstructure Replacement, B-16-067 (3GV), Maffa Way and B-16-068=S-17-027 (3GW), Mystic Avenue over Orange and MBTA/BMRR | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022* | |
| 609090 | Boston, Milton, Quincy - Highway Lighting System Replacement on Interstate 93, from Neponset Avenue to the Braintree Split | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022* | |
| S12121 | Brookline - Transit App Education Program | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| S12116 | Cambridge - Alewife Wayfinding Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| S10780 | Cambridge, Somerville - Green Line Extension Project - Extension to College Ave with the Union Square Spur | Quantified | LRTP project included in the statewide model | 2022 | |
| 608599 | Canton, Norwood - Stormwater Improvements along Route 1 and Interstate 95 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| 608078 | Chelsea - Reconstruction on Broadway (Route 107) from City Hall to Revere city line | Quantified | 93,278 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2022 |
| 608495 | Concord, Lexington, Lincoln - Resurfacing and Related Work on Route 2A | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022* | |
| 609060 | Danvers, Lynnfield, Peabody - Guide and Traffic Sign Replacement on Interstate 95/Route 128 (Task ‘A’ Interchange) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| S12119 | Everett, Malden - Main Street Transit Signal Priority | Quantified | 715,743 | Quantified decrese in emissions from transit signal priority project | 2022 |
| 602077 | Lynn - Reconstruction on Route 129 (Lynnfield Street), from Great Woods Road to Wyoma Square | Quantified | 12,761 | Quantified decrease in emissions from Complete Streets project | 2022* |
| 604952 | Lynn, Saugus - Bridge Replacement, L-18-016=S-05-008, Route 107 over the Saugus River (AKA - Belden G. Bly Bridge) | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| S12118 | Malden, Medford - BlueBikes Expansion | Quantified | 2,028 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bike share project | 2022 |
| 609066 | Newton, Weston - Multi-Use Trail Connection, from Recreation Road to Upper Charles River Greenway Including Reconstruction of Pedestrian Bridge N-12-078=W-29-062 | Quantified | 378 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2022* |
| 608866 | Newton, Weston - Steel Superstructure Cleaning (Full Removal) and Painting of Three bridges: N-12-051, W-29-011, and W-29-028 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| S12117 | Regionwide - MBTA Systemwide Bike Racks | Quantified | 42,656 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle infrastructure | 2022 |
| 608164 | Sudbury, Concord - Bike Path Construction (Bruce Freeman Rail Trail) | Quantified | 49,903 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle and pedestrian infrastructure | 2022* |
| S12120 | Wellesley - Bicycle Infrastructure | Quantified | 2,069 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bicycle infrastructure | 2022 |
Table B-4
Greenhouse Gas Regional Transit Project Tracking: Completed Projects
| Regional Transit Authority | Project Description | GHG Analysis Type | GHG CO2 Impact (kg/yr) | GHG Impact Description | FFY of Contract Award |
| CATA | Buy replacement 30-foot buses (3) | Quantified | 60,730 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2018 |
| MWRTA | Buy replacement -less than 30-foot CNG buses (6) | Quantified | 125,266 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2018 |
| MWRTA | Buy replacement paratransit vehicles (9) | Quantified | 23,069 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2018 |
| CATA | Buy Replacement 35-foot Bus (2) | Quantified | 40,487 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2019 |
| MWRTA | Buy Replacement Capitol Bus | Quantified | 1,894 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2019 |
| CATA | Buy Replacement Van (2) | Quantified | 724 | Quantified decrease in emissions from bus replacement | 2020 |
| MBTA | Option Order Procurement of 194 New Flyer Hybrid 40 ft Buses | Quantified | TBD | To be determined | 2020 |
| MBTA | Procurement of Battery Electric 40ft Buses and Related infrastructure | Quantified | TBD | To be determined | 2020 |
| MBTA | Green Line Type 10 Light Rail Fleet Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Robert Street Bridge | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | GL B-Branch Infrastructure Improve | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | GL C-Branch Surface Improve | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | GL E-Branch Surface Improve | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Green Line (Non-GLX) Grade Crossings | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Green Line D Branch Track and Signal Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Forest Hills Improvement Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Green Line B-Branch Consolidation | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Natick Center Station Accessibility Project | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Oak Grove Station Vertical Transportation Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2020 | |
| MBTA | Somerville-Medford - Green Line Extension Project - Extension to College Ave with the Union Square Spur | Quantified | LRTP project included in the statewide model | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Bridge Bundling Contract | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Emergency Bridge Repair | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Gloucester Drawbridge Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Tunnel Rehabilitation | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | F40 Commuter Rail Locomotive Overhaul | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Systemwide Asset Management Program Phase 3 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | North Station Terminal Signal | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Systemwide Radio | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Silver Line Gateway - Phase 2 | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Symphony Station Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Worcester Union Station Accessibility and Infrastructure Improvements | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Bridge Bundling Contract | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Dorchester Avenue Bridge | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Saugus Drawbridge Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Systemwide Bridge Inspection and Rating | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | South Elm Street Bridge Replacement | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | SCADA Upgrades | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Braintree and Quincy Adams Garage Rehabilitation | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Wollaston Station / Quincy Center Garage Demolition |
Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Winchester Center Station | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 | |
| MBTA | Overhaul of 33 Kawasaki 900 Series Bi-Level Coaches | Qualitative | No assumed impact/negligible impact on emissions | 2022 |
In the course of developing the Transportation Improvement Program (TIP), the staff of the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) regularly engages with municipalities and the general public to provide information about the milestones, deadlines, and key decision points in the development process. Staff publicly shares materials and information used by the MPO board for decision-making via the TIP development web page: www.bostonmpo.org/tip-dev. This process affords the public ongoing opportunities to provide input to the MPO board during the development of the TIP and prior to the release of the draft TIP for the official public review period. This appendix documents the input received during the development of the FFYs 2023–27 TIP and comments received during the public review period.
In light of the changing conditions for public engagement due to the COVID-19 pandemic, MPO staff greatly increased the use of virtual public involvement (VPI) tactics such as online workshops and virtual information sessions. All Boston Region MPO meetings throughout the FFYs 2023–27 TIP development cycle were hosted remotely, allowing project proponents and members of the public to participate via internet or telephone and provide comments without the need to travel to attend a meeting in person. MPO staff have received significant feedback from many stakeholders in support of the continued provision of virtual engagement options going forward.
When in-person MPO meetings resume, staff intend to facilitate a hybrid meeting setup to allow for both in-person and online participation by project proponents and the public. Whenever possible, staff also plan on transitioning public engagement events, such as workshops, focus groups, information sessions, and presentations, to a hybrid model. These efforts should continue to provide a greater level of accessibility and transparency to the TIP process than is achievable through in-person meetings alone.
MPO staff-initiated public engagement activities for the FFYs 2023–27 TIP in September 2021 and maintained communication with municipal, state agency, and public stakeholders throughout the TIP development process. The primary direct-engagement events at which staff received input were the virtual subregional committee meetings held by the Metropolitan Area Planning Council (MAPC) and the TIP How-To virtual information sessions with municipal TIP contacts and Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) district project engineers. These events offered individuals the opportunity to directly engage with staff to ask questions, voice concerns, provide suggestions, and propose new projects for funding.
The MPO board held a series of discussions at its regular meetings as the TIP was developed in stages that focused on project solicitation, project evaluation, and programming of funds. Staff informed the public at each stage via its standard communication channels (email, Twitter, Instagram, and the MPO website). As a result, the MPO received a number of oral and written comments while developing the draft TIP. The comments directed to the MPO board are summarized below in Table C-1.
In addition to the MPO’s standard public engagement efforts conducted annually as a part of the development of the new TIP, the MPO provided a new avenue for engagement in the months leading up to the FFYs 2023–27 TIP cycle through the creation of the TIP Project Cost Ad Hoc Committee. (See Chapter 2 for more information on this committee’s work.) This committee began hosting public meetings in June 2021, immediately following the endorsement of the FFYs 2022–26 TIP. These meetings offered all stakeholders, including the public, a chance to engage the committee in its policymaking efforts, bringing an even greater level of public participation to the MPO’s TIP process. The committee’s final policy proposals were released for a 21-day public comment period in September 2021. Comments received on those proposals are included in Table C-1 below.
Table C-1
Public Comments Received during Development of the FFYs 2023–27 TIP
| Project | Name | Support / Oppose / Request / Concern | Comment |
| Projects under consideration for TIP funding (FFYs 2023–27) | |||
| Bicycle Parking along the Bruce Freeman Rail Trail (Acton) (#S12702) | Municipal: Franny Osman, Acton Transportation Advisory Committee; Mary Smith, Acton Green Advisory Board | Support | Supports inclusion of Acton's bicycle parking project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes that this project will help Acton work towards several town-wide goals, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved bicycle access, and greater connectivity to local recreation, businesses, and transit services. |
| Chenery Middle School Bicycle Parking (Belmont) (#S12704) | Municipal: Catherine Bowen, Belmont School Committee; David Coleman, Belmont Transportation Advisory Committee; Ben Ligon, Chenery Middle School Teacher Organizations: Belmont High School Climate Action Club; Chenery Middle School PTO; Dean Hickman, Chair, Sustainable Belmont Belmont resident: Jeff Roth |
Support | Supports inclusion of Chenery Middle School's bicycle parking project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights the benefits of the project, including supporting increased bicycling to school, reduced auto traffic near the school, improved safety, and a reduction in emissions. |
| Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) (Belmont) (#609204) |
Legislative: Sen. Will Brownsberger; Rep. Dave Rogers Municipal: Marty Bitner, Belmont Energy Committee; Catherine Bowen, Belmont School Committee; Amy Checkoway, Belmont School Committee Chair; Wesley Chin, Belmont Department of Public Health; Glenn Clancy, Belmont Director of Community Development; David Coleman, Belmont Transportation Advisory Committee; Bonnie Friedman, Belmon Community Path Project Committee; Patrice Garvin, Belmont Town Administrator; Russ Leino, Belmont Community Path Project Committee; Gloria Leipzig, Chair, Belmont Housing Authority; Bill Lovallo, Belmont High School Building Committee; Mark Paolillo, Belmont Select Board; Vincent Stanton, Belmont Community Path Project Committee Organizations: Belmont High School Climate Action Club, Friends of the Belmont Community Path Belmont residents: Edin Insanic, Jeff Roth |
Support | Supports inclusion of the Belmont Community Path in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Benefits of the project include increased connectivity to transit, educational facilities, and local businesses; expansion of the regional bicycle network and the filling in of a missing gap of the MCRT between Cambridge and Waltham; safety improvements for bicyclists and pedestrians; increased mode shift opportunities; increased recreational opportunities; improved health of Path users; and the creation of new public space in Belmont Center. The project will improve safe travel for Belmont students and allow mainly off-road travel into downtown Boston. Cites the robust public process that has been undertaken by the Town in support of the project. |
| Community Path, Belmont Component of the MCRT (Phase 1) (Belmont) (#609204) |
Belmont residents: Paul Cobuzzi, Eunice Flanders, Allison Lenk, Aleida Leza, Naomi Okugawa, Darin Takemoto, Margaret Merrie Watters, Wayne Wild, Xiaoyun Xie | Oppose | Opposes the design of the Belmont Community Path and the project's potential inclusion in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. States the Town of Belmont and the Community Path Project Committee (CPPC) have not conducted adequate outreach to project abutters, that abutters are not represented at the CPPC, and that the project's design process has not been fully responsive to abutters' concerns. The proposed design, in which the Community Path runs along the north side of the commuter rail tracks, will adversely affect project abutters; the project would abut Belmont High School if moved to the south side of the tracks. Adverse impacts to abutters include noise and light pollution, decreased property values, increased litter, drainage problems, damage to private property including mature trees, and increased crime. Additional concerns include safety issues due to the proximity of the Path to the commuter rail tracks and the project cost. Concerns also exist about the necessary right of way for the project and the extent to which there will be impacts on abutters' properties. |
| Rehabilitation of Washington Street (Brookline) (#610932) |
Legislative: Rep. Tommy Vitolo Municipal: Rich Benevento, WorldTech Engineering, on behalf of the Town of Brookline; Erin Gallentine, Brookline Commissioner of Public Works; Robert King, Brookline Director of Engineering and Transportation; James Lee, Brookline Commission on Disability; David Trevvett, Brookline Pedestrian Advisory Committee Brookline residents: Shonali Guadino, Jeff Wachter |
Support | Supports inclusion of the Rehabilitation of Washington Street in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Cites the importance of Washington Street as a key commercial corridor in Brookline and the importance of the project in enhancing safety, mobility, resiliency, and accessibility for all. Highlights the improvements this project will make for people walking, bicycling, and taking transit and the robust support for the project locally. |
| Bluebikes Station Replacement and System Expansion (Cambridge) (#S12695) | Organizations: Alewife Transportation Management Association, Harvard Square Business Association | Support | Supports inclusion of Cambridge's Bluebikes project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes the importance of the Bluebikes system for promoting sustainable multimodal access to key destinations throughout Cambridge and across the region, including both Alewife and Harvard Square. Highlight that this project will continue to expand the system to provide Bluebikes access to more people while also ensuring the existing system continues to meet users’ needs by maintaining a state of good repair for highly used stations and docks. |
| Reconstruction of Western Avenue (Lynn) (#609246) |
Municipal: Rich Benevento, WorldTech Engineering, on behalf of the City of Lynn; Aaron Clausen, City of Lynn | Support | Supports inclusion of the Reconstruction of Western Avenue in the FFYs 2022-26 TIP. Notes that Western Avenue is an important multimodal connector throughout the North Shore. Highlights the extent to which the project will advance equity, sustainability, safety, and economic vitality in Lynn by adding new or improved accommodations for people walking, bicycling and taking transit. Cites the broad support for the project locally. |
| BlueBikes System Expansion (Malden and Medford) (#S12696) |
Municipal: Mayor Breanna Lungo-Koehn, City of Medford; Medford Bicycle Advisory Commission; Tim McGivern, Chair, Medford Complete Streets Committee; Stephen Winslow, Malden City Councillor Organization: Bike to the Sea, Lyft |
Support | Supports inclusion of Medford and Malden's BlueBikes expansion project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights the importance of this project in enhancing access to the Northern Strand Trail, creating new alternative transportation options, and fostering greater connectivity between Medford and Malden and the surrounding Bluebikes communities, including so residents can access critical services, employement opportunities, and local businesses. |
| Montachusett RTA Microtransit Service (MART) (#S12703) | Organization: Bruno Fisher, Deputy Administrator, Montachusett RTA | Support | Supports inclusion of MART's microtransit project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes that this project will complement MART's existing fixed-route service in the region while supporting better access to critical services and employment opportunities for local residents. |
| CatchConnect Microtransit Service Expansion (MWRTA) (#S12701) | Legislative: Sen. Karen Spilka, Rep. Carmine Gentile Municipal: Kristina Johnson, Director of Planning and Community Development, Town of Hudson; Meghan Jop, Executive Director of General Government Services, Town of Wellesley; Thatcher Kezer III, Chief Operating Officer, City of Framingham Organization: MetroWest Center for Independent Living; Joseph Nolan, Chair, MWRTA Advisory Board |
Support | Supports inclusion of MWRTA's microtransit expansion project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights the importance of this project for expanding non-single-occupancy vehicle options, creating better connectivity across the MetroWest region, and improving access to jobs and services. The project will allow the existing service to expand to new communities while improving last-mile connections to other existing fixed-route MWRTA service in the region. |
| Bridge Replacement, Route 27 Over Route 9 and Interchange Improvements (Natick) (#605313) | Municipal: Natick Select Board Chair Karen Adelman-Foster; Jeremy Marsette, Natick Director of Public Works; Josh Ostroff, Natick Transportation Advisory Committee; Eric Sofen, Natick Trails Committee | Support | Supports inclusion of the reconstruction of the Route 9 and Route 27 interchange in Natick in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Cites the deteriorating condition of the Route 27 bridge today and the existing safety and accessibility issues plaguing the interchange. Highlights the importance of the project for improving connectivity and safey for people walking and bicycling and the critical nature of this project not just for Natick, but as a key connection in the region. |
| Newmo Microtransit Service Expansion (Newton) (#S12694) | Municipal: Mayor Ruthanne Fuller, City of Newton; Steve Magoon, Acting City Manager, City of Watertown Organizations: Charles River Regional Chamber; University of Massachusetts Amherst - Mount Ida Campus; Friends of Leo J. Martin Skiing |
Support | Supports inclusion of Newton's microtransit expansion project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes that this project will support the expansion of existing NewMo service to neighboring communities and key regional destinations while increasing the ability of the service to fill first- and last-mile gaps in the transportation network. Highlights the importance of the service for those who cannot drive, including seniors, low-income residents, youth, and people with disabilities. Cites the success of the existing service as a reason to further invest in this model. |
| Bluebikes System Expansion (Salem) (#S12698) | Municipal: City of Salem Bicycling Advisory Committee Organizations: BlueCross BlueShield of Massachusetts, Destination Salem, Salem State University |
Support | Supports inclusion of Salem's Bluebikes system expansion project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes the importance of this project for promoting healthy, sustainable transportation options in Salem, as it would help to create a critical mass of Bluebikes stations locally for the network to be successful. Highlights that this project will help advance key local planning goals while providing an additional mobility option for visitors to Salem. |
| McGrath Boulevard Construction (Somerville) (#607981) |
Municipal: Mayor Katjana Ballantyne, City of Somerville | Support | Supports inclusion of the McGrath Boulevard project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlighted the difficulty and safety concerns of crossing McGrath without a car and as a route to school, and challenges for pedestrians and cyclists. Stated that the project is a regional project with regionwide benefits, and has seen strong support from the MPO board and community in past years. |
| Stoneham Shuttle Service (Stoneham) (#S12699) | Legislative: Rep. Michael Day, Sen. Jason Lewis Municipal: Stoneham Select Board; Erin Wortman, Stoneham Director of Planning and Community Development, Organizations: Greater Boston Stage Company, Middlesex Investment Partners, Nobility Hill Tavern, Stoneham Chamber of Commerce, Stoneham Community Development Corporation, Zoo New England |
Support | Supports inclusion of Stoneham's shuttle service project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Notes that Stoneham seeks to address first- and last-mile connections for residents and businesses, build east-west capacity into existing MBTA service in Stoneham to increase local mobility, and enhance transportation equity throughout the area. Cites the broad public support for this project, as evidenced by the multi-stakeholder project application. |
| Swampscott Rail Trail (Swampscott)(#610666) | Legislative: Sen. Brendan Crighton Municipal: Sean Fitzgerald, Town Administrator; Marzie Galazka, Director, Swampscott Community and Economic Development; Tania Lillak, Chair, Swampscott Open Space and Recreation Plan Committee; Suzanne Wright, Swampscott School Committee Organizations: East Coast Greenway Alliance, Friends of the Swampscott Rail Trail, Solomon Foundation, Swampscott Conservancy |
Support | Supports inclusion of the Swampscott Rail Trail in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. The project will connect to the Northern Strand Community Trail and the Marblehead Rail Trail, and increase connectivity within Swampscott by providing safe connections to local businesses, transit, and recreational and educational facilities. In addition, the trail will provide open space in a densely populated community and provide opportunities for recreational and healthy activity. The project includes environmental-friendly aspects, including an edible walking forest and pollinator garden. The project is largely supported by community; the Town Meeting approved the project by a vote of 210 to 56. |
| Pleasant Street Shuttle Service Expansion (Watertown) (#S12697) | Municipal: Mark Sideris, Watertown City Council President Organizations: Amstel Heritage Watertown; Sophia Gallimore, Watertown TMA; Lincoln Property Company; Paradigm Properties; Watertown Mews; WeDriveU |
Support | Supports inclusion of Watertown's shuttle service project in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Cites the importance of this project in shortening headways and increasing ridership by adding a second vehicle to the route. Highlights that the elecrtification of the service supported by this project is in alignment with the town's comprehensive plan and climate change mitigation efforts. Cites that the project provides critical connectivity between transit hubs on a fast-growing corridor in Watertown. |
| Intersection Improvements Boston Post Road (Route 20) at Wellesley Street (Weston) (#608940) |
Municipal: Meghan Jop, Executive Director of General Government Services, Town of Wellesley | Support | Supports inclusion of Weston's intersection improvement project at Route 20 and Wellesley Street in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights the importance of this project not just for Weston, but for the whole region, as this intersection is a key connection point between several municipalities. Notes the improvements the project will make to safety and traffic congestion in the area. |
| Currently programmed projects (FFYs 2022–26) | |||
| Rehabilitation of Bridge Street (Beverly) (#608348) |
Municipal: Rich Benevento, WorldTech Engineering, on behalf of the City of Beverly | Support | Supports continued inclusion of the Rehabilitation of Bridge Street in the FFYs FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights that the project is on track for advertisement in FFY 2023. States that the cost increase seen during the FFYs 2023–27 TIP cycle for this project is not due to a change in project scope, but rather due to increasing material costs. |
| Reconstruction of Rutherford Avenue (Boston) (#606226) | Boston resident: Dan Jaffe | Concern | Expresses concern that the proposed delay of the Reconstruction of Rutherford Avenue in Boston from FFY 2023 to FFY 2025 will negatively impact the Charlestown neighborhood, including by perpetuating conditions that are currently unsafe and that are not meeting the needs of local residents. States that the currently proposed design for this project is in line with the neighborhood's goals and is the result of abundant feedback from local residents over many years. Requests that the project not be delayed any longer and that the City of Boston move forward with existing designs. |
| Rehabilitation of Central Street (Peabody) (#608933) | Municipal: Rich Benevento, WorldTech Engineering, on behalf of the City of Peabody | Support | Supports continued inclusion of the Rehabilitation of Central Street in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights that the project is on track for advertisement in FFY 2023, with 75 percent design plans anticipated to be submitted by May 2022. |
| Rehabilitation of Mount Auburn Street (Watertown) (#607777) |
Municipal: Rich Benevento, WorldTech Engineering, on behalf of the Town of Watertown | Support | Supports continued inclusion of the Rehabilitation of Mount Auburn Street in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Highlights that coordination with all stakeholders, including the MBTA, remains ongoing and that the project is on track for advertisement in FFY 2023, with 75 percent design plans anticipated to be submitted in May or June 2022. |
| Intersection Improvements at Lowell Street (Route 129) and Woburn Street (Wilmington) (#609253) |
Municipal: Valerie Gingrich, Director of Planning and Conservation, Town of Wilmington | Support | Supports the continued inclusion of the intersection improvement project at Lowell Street and Woburn Street in the FFYs 2023–27 TIP. Acknowledges the cost increase for the project during the FFYs 2023–27 TIP cycle and requests that the MPO continue to support the project at the higher cost. Notes that the cost increase is due to several factors, including adjustments to the project's proposed drainage system, increasing unit costs, and increasing costs to relocate utilities. Notes that the project remains critical for enhancing safety at this key intersection. |
| Other Comments | |||
| Support for Projects in Natick | Municipal: Natick Select Board Chair Karen Adelman-Foster | Support | Expresses support for several projects in Natick, including the Natick Center Cochituate Rail Trail connection (#610691), Lake Cochituate Path (#610680), Boden Lane Bridge (#607420), Spring Street Bridge (#610869), and Speen Street Bridge (#612178). Cites the importance of each of these projects in promoting safe, efficient mobility in Natick. |
| TIP Project Cost Ad Hoc Committee | Belmont residents: Cosmo Caterino, Aleida Leza | Support | Expresses support for the MPO's proposed cost-change policies, citing the desire to see these policies support a greater degree of MPO oversight over project costs and project development processes. States that increased MPO scrutiny over project costs should support projects that are more fiscally responsible. |
| TIP Project Cost Ad Hoc Committee | Municipal: Catherine Bowen, Belmont School Committee Member | Concern | Expresses broad support for the MPO's proposed cost-change policies, but cites concerns that the MPO's requirement that projects submit 25 percent design plans prior to being funded may have a chilling effect on the overall number of municipalities pursuing funding through the TIP process. |
The MPO board will voted to release a draft FFYs 2023–27 TIP document for public review at its April 28, 2022, meeting. This vote initiated an official 21-day public review period, which began on May 2, 2022, and close on May 23, 2022. The comments received during this public review period will be summarized in Table C-2. Draft responses from the MPO to the commenters will be presented at the May 26, 2022, MPO meeting and will be included in this section when the final version of the document is posted to the MPO’s website following a vote for endorsement.
Table C-2
Public Comments Received during the Public Review Period for the Draft FFYs 2023–27 TIP
This table will be included in the final version of the document when it is posted to the MPO’s website following a vote for endorsement.
Appendix D provides information about the geographic distribution of federal highway funding in the Boston region between federal fiscal years (FFYs) 2023 and 2027, including the distribution of the Boston Region MPO’s Regional Target Program funding (the MPO’s discretionary funding) and funding for projects and programs prioritized by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation. Funding amounts shown include the state’s matching funds that leverage the available federal funds.
Figures D-1 through D-4 summarize the distribution of the MPO’s Regional Target Program funding and all federal highway funding by subregion. Funding is shown for the time period covered by this TIP (FFYs 2023–27) and over a longer time horizon (FFYs 2011–27). Table D-1 shows the breakdown of this data for each municipality in the Boston region for FFYs 2023–27.
The analysis presented here provides details about how the MPO has allocated its federal transportation highway dollars across its geographic region by showing which municipalities and areas of the Boston region have received highway funding for the construction of transportation projects. This data was first compiled for FFYs 2008-13 in response to the Boston Region MPO’s 2014 Certification Review by the Federal Highway Administration and Federal Transit Administration.
Figure D-1
Distribution of Regional Target Funding by Subregion (FFYs 2023–27)
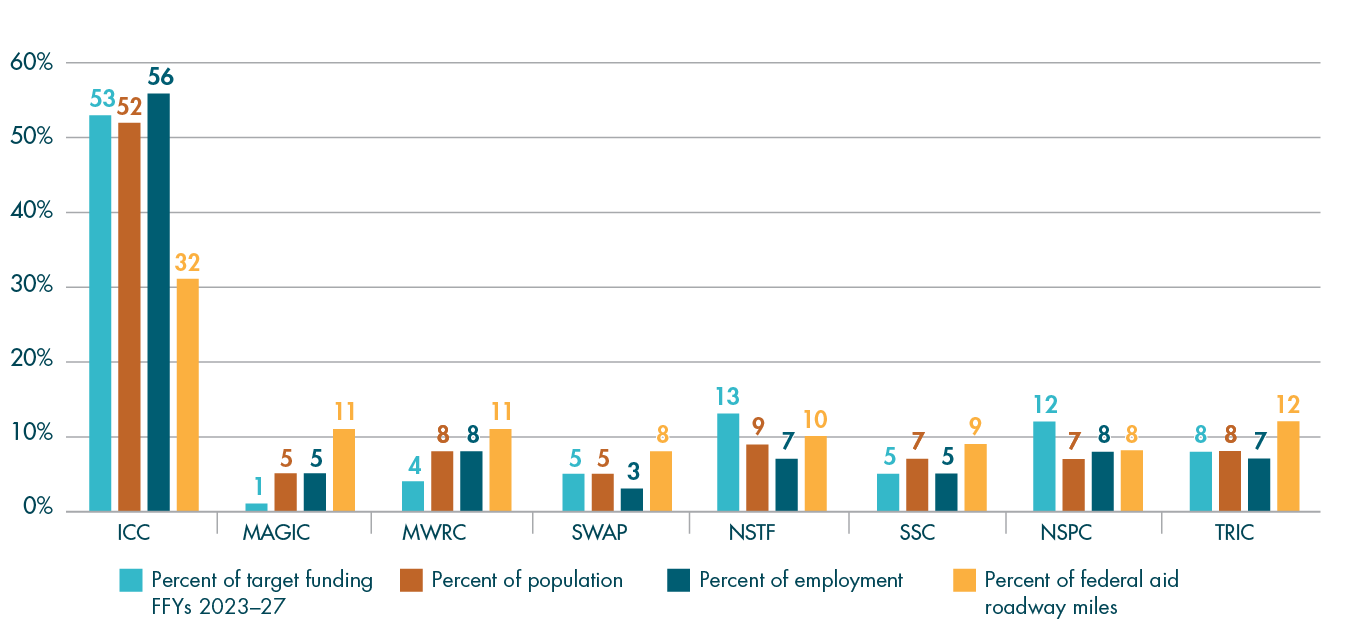
Figure D-2
Distribution of All Federal Highway Funding in the Boston Region by Subregion (FFYs 2023–27)
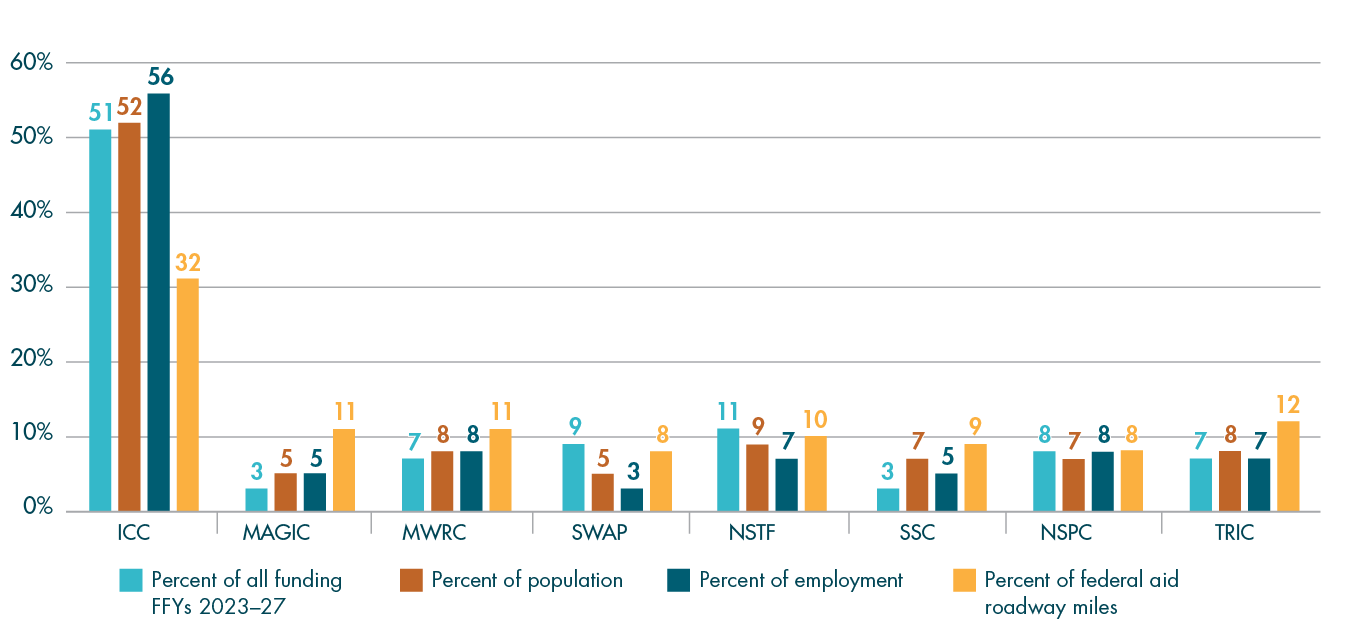
Figure D-3
Distribution of Regional Target Funding by Subregion (FFYs 2011–27)
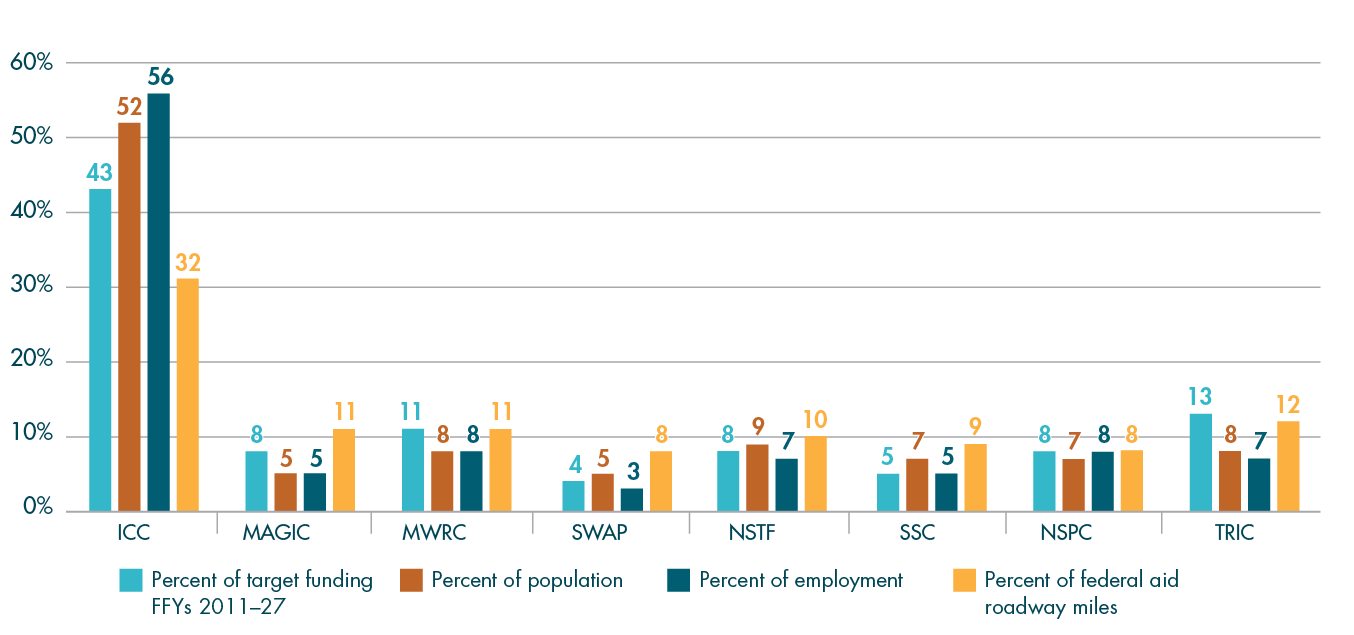
Figure D-4
Distribution of All Federal Highway Funding in the Boston Region by Subregion (FFYs 2011–27)
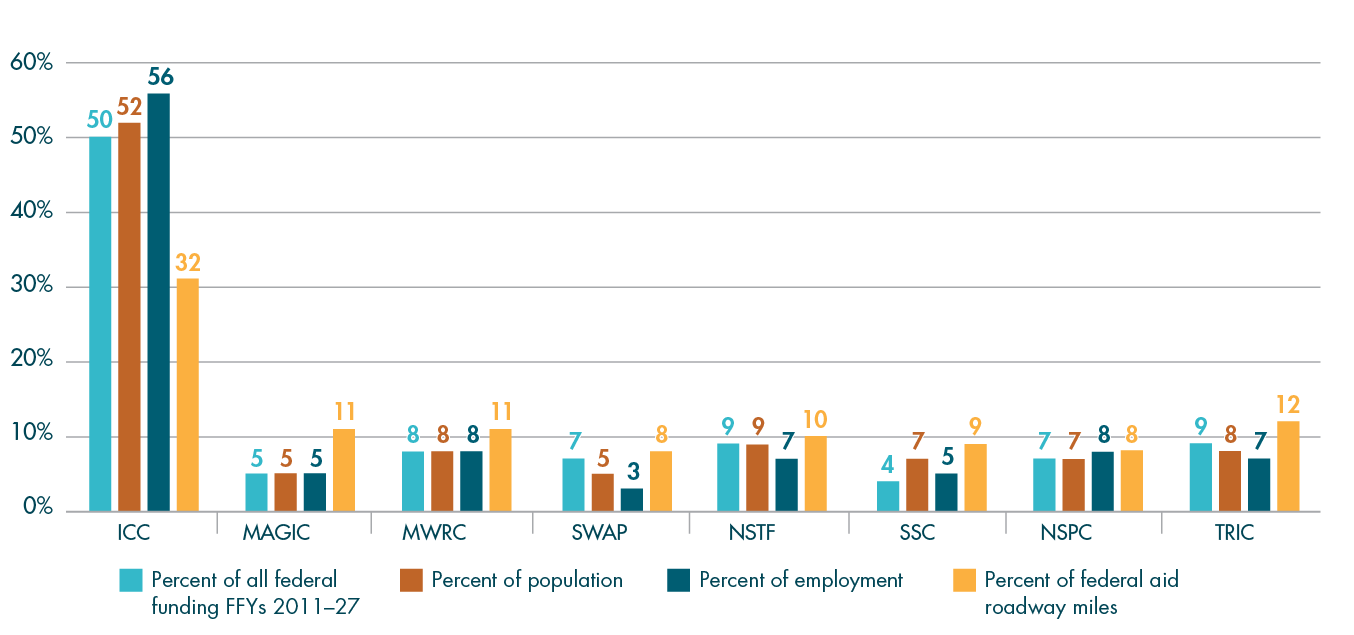
Table D-1
Federal Highway Programming for Municipalities in the Boston Region (FFYs 2023–27)
| MPO Municipality | Subregion | Community Type | Pct Pop. | Pct Empl. | Percent Federal Aid Roadway Miles (2016) | Regionally Prioritized Target Funding | Percent Regionally Prioritized Target Funding | State Prioritized Funding | Percent State Prioritized Funding | Total Funding (Regionally Prioritized and State Prioritized) | Percent Total Funding (Regionally Prioritized and State Prioritized) |
| Boston | Inner Core | Inner Core | 20.0% | 31.2% | 11.1% | $108,449,011 | 20.7% | $291,622,743 | 19.1% | $400,071,754 | 19.5% |
| Somerville | Inner Core | Inner Core | 2.5% | 1.2% | 1.2% | $20,000,000 | 3.8% | $209,381,819 | 13.7% | $229,381,819 | 11.2% |
| Hopkinton | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.5% | 1.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $147,018,157 | 9.6% | $147,018,157 | 7.2% |
| Beverly | NSTF | Regional Urban Center | 1.3% | 1.2% | 1.2% | $12,594,932 | 2.4% | $87,711,718 | 5.8% | $100,306,650 | 4.9% |
| Natick | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 1.1% | 1.3% | 1.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $89,799,350 | 5.9% | $89,799,350 | 4.4% |
| Cambridge | Inner Core | Inner Core | 3.4% | 6.0% | 1.8% | $349,608 | 0.1% | $81,254,354 | 5.3% | $81,603,962 | 4.0% |
| Wilmington | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 1.0% | 1.3% | $31,085,535 | 5.9% | $38,799,452 | 2.5% | $69,884,987 | 3.4% |
| Salem | NSTF | Regional Urban Center | 1.3% | 1.1% | 0.7% | $7,108,429 | 1.4% | $50,930,758 | 3.3% | $58,039,187 | 2.8% |
| Lynn | Inner Core | Regional Urban Center | 2.9% | 1.3% | 1.3% | $32,602,000 | 6.2% | $19,033,076 | 1.2% | $51,635,076 | 2.5% |
| Norwood | TRIC | Regional Urban Center | 0.9% | 1.3% | 1.0% | $32,790,150 | 6.3% | $4,855,382 | 0.3% | $37,645,532 | 1.8% |
| Milton | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.9% | 0.3% | 1.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $36,673,224 | 2.4% | $36,673,224 | 1.8% |
| Peabody | NSTF | Regional Urban Center | 1.7% | 1.3% | 1.4% | $32,464,982 | 6.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $32,464,982 | 1.6% |
| Chelsea | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.1% | 0.8% | 0.6% | $12,123,769 | 2.3% | $20,045,148 | 1.3% | $32,168,917 | 1.6% |
| Framingham | MetroWest | Regional Urban Center | 2.2% | 2.5% | 2.5% | $2,484,704 | 0.5% | $29,476,827 | 1.9% | $31,961,531 | 1.6% |
| Brookline | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.9% | 0.9% | 1.3% | $30,030,812 | 5.7% | $1,305,823 | 0.1% | $31,336,635 | 1.5% |
| Watertown | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.0% | 1.1% | 0.6% | $28,252,285 | 5.4% | $3,080,230 | 0.2% | $31,332,515 | 1.5% |
| Medford | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.8% | 1.0% | 1.5% | $72,911 | 0.0% | $30,420,970 | 2.0% | $30,493,880 | 1.5% |
| Revere | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.7% | 0.5% | 1.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $29,858,991 | 2.0% | $29,858,991 | 1.5% |
| Woburn | NSPC | Regional Urban Center | 1.2% | 2.2% | 1.5% | $22,326,115 | 4.3% | $6,474,344 | 0.4% | $28,800,459 | 1.4% |
| Everett | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.3% | 0.7% | 0.6% | $10,168,416 | 1.9% | $17,748,000 | 1.2% | $27,916,416 | 1.4% |
| Braintree | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 1.2% | 1.5% | 1.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $25,850,441 | 1.7% | $25,850,441 | 1.3% |
| Randolph | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 1.0% | 0.5% | 1.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $24,908,198 | 1.6% | $24,908,198 | 1.2% |
| Quincy | Inner Core | Regional Urban Center | 3.0% | 2.6% | 2.1% | $6,052,562 | 1.2% | $18,265,308 | 1.2% | $24,317,870 | 1.2% |
| Canton | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 1.2% | 1.1% | $325,719 | 0.1% | $23,937,776 | 1.6% | $24,263,495 | 1.2% |
| Newton | Inner Core | Inner Core | 2.8% | 3.0% | 2.6% | $1,042,574 | 0.2% | $22,595,183 | 1.5% | $23,637,757 | 1.2% |
| Belmont | Inner Core | Inner Core | 0.8% | 0.4% | 0.6% | $21,038,758 | 4.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $21,038,758 | 1.0% |
| Lexington | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 1.0% | 1.1% | 1.9% | $0 | 0.0% | $20,456,262 | 1.3% | $20,456,262 | 1.0% |
| Weston | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 1.3% | $18,393,832 | 3.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $18,393,832 | 0.9% |
| Reading | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.8% | 0.4% | 0.8% | $0 | 0.0% | $17,376,800 | 1.1% | $17,376,800 | 0.8% |
| Stoneham | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 0.4% | 0.8% | $796,817 | 0.2% | $15,414,505 | 1.0% | $16,211,322 | 0.8% |
| Waltham | Inner Core | Inner Core | 2.0% | 3.0% | 1.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $16,082,742 | 1.1% | $16,082,742 | 0.8% |
| Burlington | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.8% | 2.2% | 1.3% | $6,046,915 | 1.2% | $9,595,904 | 0.6% | $15,642,819 | 0.8% |
| Hingham | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 0.7% | 1.3% | $15,596,549 | 3.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $15,596,549 | 0.8% |
| Wrentham | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.3% | 1.0% | $15,587,884 | 3.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $15,587,884 | 0.8% |
| Boxborough | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $15,284,656 | 1.0% | $15,284,656 | 0.7% |
| Bellingham | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.9% | $0 | 0.0% | $14,249,535 | 0.9% | $14,249,535 | 0.7% |
| Cohasset | SSC | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.5% | $11,258,807 | 2.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $11,258,807 | 0.5% |
| Milford | SWAP | Regional Urban Center | 0.9% | 0.8% | 1.2% | $10,119,616 | 1.9% | $0 | 0.0% | $10,119,616 | 0.5% |
| Dedham | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.8% | 0.9% | 1.1% | $6,314,855 | 1.2% | $3,143,758 | 0.2% | $9,458,613 | 0.5% |
| Weymouth | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 1.7% | 1.0% | 1.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $9,018,690 | 0.6% | $9,018,690 | 0.4% |
| Swampscott | NSTF | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.3% | $8,932,000 | 1.7% | $0 | 0.0% | $8,932,000 | 0.4% |
| Middleton | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $8,508,556 | 0.6% | $8,508,556 | 0.4% |
| Danvers | NSTF | Maturing Suburb | 0.9% | 1.4% | 1.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $8,015,758 | 0.5% | $8,015,758 | 0.4% |
| Winchester | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 0.5% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $7,302,504 | 0.5% | $7,302,504 | 0.4% |
| Ipswich | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.7% | $5,490,888 | 1.0% | $1,567,895 | 0.1% | $7,058,783 | 0.3% |
| Foxborough | TRIC | Developing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.7% | 1.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $6,894,080 | 0.5% | $6,894,080 | 0.3% |
| Acton | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.7% | 0.5% | 1.1% | $8,017 | 0.0% | $6,752,478 | 0.4% | $6,760,495 | 0.3% |
| Winthrop | Inner Core | Inner Core | 0.6% | 0.1% | 0.3% | $6,617,959 | 1.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $6,617,959 | 0.3% |
| Littleton | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.3% | 1.0% | $3,992,645 | 0.8% | $2,521,264 | 0.2% | $6,513,909 | 0.3% |
| Lynnfield | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $6,180,338 | 0.4% | $6,180,338 | 0.3% |
| Wakefield | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.9% | $0 | 0.0% | $6,180,338 | 0.4% | $6,180,338 | 0.3% |
| Ashland | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.5% | $1,222,315 | 0.2% | $3,965,472 | 0.3% | $5,187,787 | 0.3% |
| Nahant | Inner Core | Maturing Suburb | 0.1% | 0.0% | 0.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $4,681,875 | 0.3% | $4,681,875 | 0.2% |
| Malden | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.9% | 0.8% | 1.0% | $72,911 | 0.0% | $4,181,800 | 0.3% | $4,254,711 | 0.2% |
| Stow | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $3,454,408 | 0.2% | $3,454,408 | 0.2% |
| Topsfield | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $3,258,119 | 0.2% | $3,258,119 | 0.2% |
| Hudson | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.7% | $0 | 0.0% | $2,970,998 | 0.2% | $2,970,998 | 0.1% |
| Marlborough | MetroWest | Regional Urban Center | 1.2% | 1.6% | 2.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $2,970,998 | 0.2% | $2,970,998 | 0.1% |
| Medway | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $2,807,468 | 0.2% | $2,807,468 | 0.1% |
| Sudbury | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.5% | 1.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $2,262,001 | 0.1% | $2,262,001 | 0.1% |
| Wayland | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.7% | $0 | 0.0% | $2,262,001 | 0.1% | $2,262,001 | 0.1% |
| Hamilton | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,567,895 | 0.1% | $1,567,895 | 0.1% |
| Maynard | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,520,953 | 0.1% | $1,520,953 | 0.1% |
| Sharon | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.2% | 1.1% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,436,915 | 0.1% | $1,436,915 | 0.1% |
| Arlington | Inner Core | Inner Core | 1.4% | 0.5% | 0.8% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,302,209 | 0.1% | $1,302,209 | 0.1% |
| Scituate | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.2% | 1.0% | $1,250,979 | 0.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,250,979 | 0.1% |
| Westwood | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.7% | $0 | 0.0% | $1,071,429 | 0.1% | $1,071,429 | 0.1% |
| Bedford | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 1.1% | 0.8% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Bolton | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.7% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Carlisle | MAGIC | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.0% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Concord | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.7% | 1.1% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Dover | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.0% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Essex | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Franklin | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 1.0% | 0.8% | 1.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Gloucester | NSTF | Regional Urban Center | 0.9% | 0.6% | 1.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Holbrook | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.3% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Holliston | MetroWest | Developing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Hull | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Lincoln | MAGIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Manchester | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Marblehead | NSTF | Maturing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.3% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Marshfield | SSC | Maturing Suburb | 0.8% | 0.3% | 1.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Medfield | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Melrose | Inner Core | Inner Core | 0.9% | 0.3% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Millis | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Needham | TRIC | Maturing Suburb | 0.9% | 1.0% | 1.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Norfolk | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.5% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| North Reading | NSPC | Maturing Suburb | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Norwell | SSC | Developing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.8% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Rockland | SSC | Developing Suburb | 0.6% | 0.4% | 0.6% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Rockport | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Saugus | Inner Core | Maturing Suburb | 0.9% | 0.6% | 0.8% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Sherborn | SWAP | Developing Suburb | 0.1% | 0.0% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Southborough | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 0.3% | 0.4% | 1.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Walpole | TRIC | Developing Suburb | 0.8% | 0.6% | 1.2% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Wellesley | MetroWest | Maturing Suburb | 0.9% | 0.9% | 0.9% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
| Wenham | NSTF | Developing Suburb | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.4% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% | $0 | 0.0% |
This appendix contains detailed background on the regulatory documents, legislation, and guidance that shape the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization’s (MPO) transportation planning process.
The Boston Region MPO is charged with executing its planning activities in line with federal and state regulatory guidance. Maintaining compliance with these regulations allows the MPO to directly support the work of these critical partners and ensures its continued role in helping the region move closer to achieving federal, state, and regional transportation goals. This appendix describes all of the regulations, policies, and guidance taken into consideration by the MPO during development of the certification documents and other core work the MPO will undertake during federal fiscal year (FFY) 2023.
The purpose of the national transportation goals, outlined in Title 23, section 150, of the United States Code (23 USC § 150), is to increase the accountability and transparency of the Federal-Aid Highway Program and to improve decision-making through performance-based planning and programming. The national transportation goals include the following:
The Boston Region MPO has incorporated these national goals, where practicable, into its vision, goals, and objectives, which provide a framework for the MPO’s planning processes. More information about the MPO’s vision, goals, and objectives is included in Chapter 1.
The MPO gives specific consideration to the federal planning factors, described in Title 23, section 134, of the US Code (23 USC § 134), when developing all documents that program federal transportation funds. In accordance with the legislation, studies and strategies undertaken by the MPO shall
The Boston Region MPO has also incorporated these federal planning factors into its vision, goals, and objectives.
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT), in consultation with states, MPOs, and other stakeholders, has established performance measures relevant to these national goals. These performance topic areas include roadway safety, transit system safety, National Highway System (NHS) bridge and pavement condition, transit asset condition, NHS reliability for both passenger and freight travel, traffic congestion, and on-road mobile source emissions. The FAST Act and related federal rulemakings require states, MPOs, and public transportation operators to follow performance-based planning and programming practices—such as setting targets—to ensure that transportation investments support progress towards these goals. See Chapter 3 for more information about how the MPO has and will continue to conduct performance-based planning and programming.
The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), signed into law on November 15, 2021, replaces the FAST Act as the nation’s five-year surface transportation bill, covering FFYs 2022–26. On December 30, 2021, the Federal Highway Administration and Federal Transit Administration jointly issued updated planning emphasis areas for use in MPOs’ transportation planning process. Those planning emphasis areas include the following:
While federal guidance is still being developing regarding the implementation of the BIL, the FAST Act’s national goals and planning factors remain in effect. For this reason, these components of both bills are listed here as governing regulations for the MPO’s transportation planning process.
The Clean Air Act, most recently amended in 1990, forms the basis of the United States’ air pollution control policy. The act identifies air quality standards, and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) designates geographic areas as attainment (in compliance) or nonattainment (not in compliance) areas with respect to these standards. If air quality in a nonattainment area improves such that it meets EPA standards, the EPA may redesignate that area as being a maintenance area for a 20-year period to ensure that the standard is maintained in that area.
The conformity provisions of the Clean Air Act “require that those areas that have poor air quality, or had it in the past, should examine the long-term air quality impacts of their transportation system and ensure its compatibility with the area’s clean air goals.” Agencies responsible for Clean Air Act requirements for nonattainment and maintenance areas must conduct air quality conformity determinations, which are demonstrations that transportation plans, programs, and projects addressing that area are consistent with a State Implementation Plan (SIP) for attaining air quality standards.
Air quality conformity determinations must be performed for capital improvement projects that receive federal funding and for those that are considered regionally significant, regardless of the funding source. These determinations must show that projects in the MPO’s Long-Range Transportation Plan (LRTP) and Transportation Improvement Program (TIP) will not cause or contribute to any new air quality violations; will not increase the frequency or severity of any existing air quality violations in any area; and will not delay the timely attainment of air quality standards in any area. The policy, criteria, and procedures for demonstrating air quality conformity in the Boston region were established in Title 40, parts 51 and 53, of the Code of Federal Regulations.
On April 1, 1996, the EPA classified the cities of Boston, Cambridge, Chelsea, Everett, Malden, Medford, Quincy, Revere, and Somerville as in attainment for carbon monoxide (CO) emissions. Subsequently, a CO maintenance plan was set up through the Massachusetts SIP to ensure that emission levels did not increase. While the maintenance plan was in effect, past TIPs and LRTPs included an air quality conformity analysis for these communities. As of April 1, 2016, however, the 20-year maintenance period for this CO maintenance area expired and transportation conformity is no longer required for this pollutant in these communities. This ruling is documented in a letter from the EPA dated May 12, 2016.
On April 22, 2002, the City of Waltham was redesignated as being in attainment for CO emissions with an EPA-approved limited-maintenance plan. In areas that have approved limited-maintenance plans, federal actions requiring conformity determinations under the EPA’s transportation conformity rule are considered to satisfy the conformity test.
On February 16, 2018, the US Court of Appeals for the DC Circuit issued a decision in South Coast Air Quality Management District v. EPA, which struck down portions of the 2008 Ozone National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) SIP Requirements Rule concerning the ozone NAAQS. Those portions of the SIP Requirements Rule included transportation conformity requirements associated with the EPA’s revocation of the 1997 ozone NAAQS. Massachusetts was designated as an attainment area in accord with the 2008 ozone NAAQS but as a nonattainment or maintenance area as relates to the 1997 ozone NAAQS. As a result of this court ruling, MPOs in Massachusetts must once again demonstrate conformity for ozone when developing LRTPs and TIPs.
MPOs must also perform conformity determinations if transportation control measures (TCM) are in effect in the region. TCMs are strategies that reduce transportation-related air pollution and fuel use by reducing vehicle-miles traveled and improving roadway operations. The Massachusetts SIP identifies TCMs in the Boston region. SIP-identified TCMs are federally enforceable and projects that address the identified air quality issues must be given first priority when federal transportation dollars are spent. Examples of TCMs that were programmed in previous TIPs include rapid-transit and commuter-rail extension programs (such as the Green Line Extension in Cambridge, Medford, and Somerville, and the Fairmount Line improvements in Boston), parking-freeze programs in Boston and Cambridge, statewide rideshare programs, park-and-ride facilities, residential parking-sticker programs, and the operation of high-occupancy-vehicle lanes.
In addition to reporting on the pollutants identified in the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments, the MPOs in Massachusetts are also required to perform air quality analyses for carbon dioxide as part of the state’s Global Warming Solutions Act (GWSA) (see below).
The Boston Region MPO complies with Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the American with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA), Executive Order 12898—Federal Actions to Address Environmental Justice in Minority Populations and Low-income Populations (EJ EO), and other federal and state nondiscrimination statutes and regulations in all programs and activities it conducts. Per federal and state law, the MPO does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin (including limited English proficiency), religion, creed, gender, ancestry, ethnicity, disability, age, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity or expression, veteran’s status, or background. The MPO strives to provide meaningful opportunities for participation of all persons in the region, including those protected by Title VI, the ADA, the EJ EO, and other nondiscrimination mandates.
The MPO also analyzes the likely benefits and adverse effects of transportation projects to equity populations (populations traditionally underserved by the transportation system, as identified in the MPO’s Transportation Equity program) when deciding which projects to fund. This analysis is conducted through the MPO’s project selection criteria, which were recently strengthened to prioritize projects that provide benefits to these populations. MPO staff also evaluate the projects that are selected for funding, in the aggregate, to determine their overall impacts and whether they improve transportation outcomes for equity populations. The major federal requirements pertaining to nondiscrimination are discussed below.
Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 requires that no person be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination on the basis of race, color, or national origin, under any program or activity provided by an agency receiving federal financial assistance. Executive Order 13166—Improving Access to Services for Persons with Limited English Proficiency, dated August 11, 2000, extends Title VI protections to people who, as a result of their nationality, have limited English proficiency. Specifically, it calls for improved access to federally assisted programs and activities, and it requires MPOs to develop and implement a system through which people with limited English proficiency can meaningfully participate in the transportation planning process. This requirement includes the development of a Language Assistance Plan that documents the organization’s process for providing meaningful language access to people with limited English proficiency who access their services and programs.
Executive Order 12898, dated February 11, 1994, requires each federal agency to advance environmental justice by identifying and addressing any disproportionately high and adverse human health or environmental effects, including interrelated social and economic effects, of its programs, policies, and activities on minority and low-income populations.
On April 15, 1997, the USDOT issued its Final Order to Address Environmental Justice in Minority Populations and Low-Income Populations. Among other provisions, this order requires programming and planning activities to
The 1997 Final Order was updated in 2012 with USDOT Order 5610.2(a), which provided clarification while maintaining the original framework and procedures.
Title III of the ADA “prohibits states, MPOs, and other public entities from discriminating on the basis of disability in the entities’ services, programs, or activities,” and requires all transportation projects, plans, and programs to be accessible to people with disabilities. Therefore, MPOs must consider the mobility needs of people with disabilities when programming federal funding for studies and capital projects. MPO-sponsored meetings must also be held in accessible venues and be conducted in a manner that provides for accessibility. Also, MPO materials must be made available in accessible formats.
The Age Discrimination Act of 1975 prohibits discrimination on the basis of age in programs or activities that receive federal financial assistance. Additionally, the Rehabilitation Act of 1975, and Title 23, section 324, of the US Code (23 USC § 324) prohibit discrimination based on sex.
Much of the MPO’s work focuses on encouraging mode shift and diminishing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through improving transit service, enhancing bicycle and pedestrian networks, and studying emerging transportation technologies. All of this work helps the Boston region contribute to statewide progress towards the priorities discussed in this section.
The Commission on the Future of Transportation in the Commonwealth—established by Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker’s Executive Order 579—published Choices for Stewardship in 2019. This report makes 18 recommendations across the following five thematic categories to adapt the transportation system in the Commonwealth to emerging needs:
The Boston Region MPO supports these statewide goals by conducting planning work and making investment decisions that complement MassDOT’s efforts and reflect the evolving needs of the transportation system in the region.
The Massachusetts 2018 Strategic Highway Safety Plan (SHSP) identifies the state’s key safety needs and guides investment decisions to achieve significant reductions in highway fatalities and serious injuries on all public roads. The SHSP establishes statewide safety goals and objectives and key safety emphasis areas, and it draws on the strengths of all highway safety partners in the Commonwealth to align and leverage resources to address the state’s safety challenges collectively. The Boston Region MPO considers SHSP goals, emphasis areas, and strategies when developing its plans, programs, and activities.
In 2017, MassDOT finalized the Massachusetts Freight Plan, which defines the short- and long-term vision for the Commonwealth’s freight transportation system. In 2018, MassDOT released the related Commonwealth of Massachusetts State Rail Plan, which outlines short- and long-term investment strategies for Massachusetts’ freight and passenger rail systems (excluding the commuter rail system). In 2019, MassDOT released the Massachusetts Bicycle Transportation Plan and the Massachusetts Pedestrian Transportation Plan, both of which define roadmaps, initiatives, and action plans to improve bicycle and pedestrian transportation in the Commonwealth. The MPO considers the findings and strategies of MassDOT’s modal plans when conducting its planning, including through its Freight Planning Support and Bicycle/Pedestrian Support Activities programs.
The GWSA makes Massachusetts a leader in setting aggressive and enforceable GHG reduction targets and implementing policies and initiatives to achieve these targets. In keeping with this law, the Massachusetts Executive Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs (EEA), in consultation with other state agencies and the public, developed the Massachusetts Clean Energy and Climate Plan for 2020. This implementation plan, released on December 29, 2010 (and updated in 2015), establishes the following targets for overall statewide GHG emission reductions:
In 2018, EEA published its GWSA 10-year Progress Report and the GHG Inventory estimated that 2018 GHG emissions were 22 percent below the 1990 baseline level.
MassDOT fulfills its responsibilities, defined in the Massachusetts Clean Energy and Climate Plan for 2020, through a policy directive that sets three principal objectives:
In January 2015, the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection amended Title 310, section 7.00, of the Code of Massachusetts Regulations (310 CMR 60.05), Global Warming Solutions Act Requirements for the Transportation Sector and the Massachusetts Department of Transportation, which was subsequently amended in August 2017. This regulation places a range of obligations on MassDOT and MPOs to support achievement of the Commonwealth’s climate change goals through the programming of transportation funds. For example, MPOs must use GHG impact as a selection criterion when they review projects to be programmed in their TIPs, and they must evaluate and report the GHG emissions impacts of transportation projects in LRTPs and TIPs.
The Commonwealth’s 10 MPOs (and three non-metropolitan planning regions) are integrally involved in supporting the GHG reductions mandated under the GWSA. The MPOs seek to realize these objectives by prioritizing projects in the LRTP and TIP that will help reduce emissions from the transportation sector. The Boston Region MPO uses its TIP project evaluation criteria to score projects based on their GHG emissions impacts, multimodal Complete Streets accommodations, and ability to support smart growth development. Tracking and evaluating GHG emissions by project will enable the MPOs to anticipate GHG impacts of planned and programmed projects. See Appendix A for more information about the MPO’s project selection criteria and Appendix B for more details about the MPO’s GHG monitoring and evaluation activities.
On September 9, 2013, MassDOT passed the Healthy Transportation Policy Directive to formalize its commitment to implementing and maintaining transportation networks that allow for various mode choices. This directive will ensure that all MassDOT projects are designed and implemented in ways that provide all customers with access to safe and comfortable walking, bicycling, and transit options.
In November 2015, MassDOT released the Separated Bike Lane Planning & Design Guide. This guide represents the next—but not the last—step in MassDOT’s continuing commitment to Complete Streets, sustainable transportation, and the creation of more safe and convenient transportation options for Massachusetts’ residents. This guide may be used by project planners and designers as a resource for considering, evaluating, and designing separated bike lanes as part of a Complete Streets approach.
In the LRTP, Destination 2040, the Boston Region MPO has continued to use investment programs—particularly its Complete Streets and Bicycle Network and Pedestrian Connections programs—that support the implementation of Complete Streets projects. In the Unified Planning Work Program, the MPO budgets to support these projects, such as the MPO’s Bicycle and Pedestrian Support Activities program, corridor studies undertaken by MPO staff to make conceptual recommendations for Complete Streets treatments, and various discrete studies aimed at improving pedestrian and bicycle accommodations.
MassDOT developed the Congestion in the Commonwealth 2019 report to identify specific causes of and impacts from traffic congestion on the NHS. The report also made recommendations for reducing congestion, including addressing local and regional bottlenecks, redesigning bus networks within the systems operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) and the other regional transit authorities, increasing MBTA capacity, and investigating congestion pricing mechanisms such as managed lanes. These recommendations guide multiple new efforts within MassDOT and the MBTA and are actively considered by the Boston Region MPO when making planning and investment decisions.
On March 18, 2019, MassDOT and the MBTA released Focus40, the MBTA’s Program for Mass Transportation, which is the 25-year investment plan that aims to position the MBTA to meet the transit needs of the Greater Boston region through 2040. Complemented by the MBTA’s Strategic Plan and other internal and external policy and planning initiatives, Focus40 serves as a comprehensive plan guiding all capital planning initiatives at the MBTA. These initiatives include the Rail Vision plan, which will inform the vision for the future of the MBTA’s commuter rail system; the Better Bus Project, the plan to redesign and improve the MBTA’s bus network; and other plans. The Boston Region MPO continues to monitor the status of Focus40 and related MBTA modal plans to inform its decision-making about transit capital investments, which are incorporated to the TIP and LRTP.
MetroCommon 2050, which was developed by the Metropolitan Area Planning Council (MAPC) and adopted in 2021, is Greater Boston’s regional land use and policy plan. MetroCommon 2050 builds off of MAPC’s previous plan, MetroFuture(adopted in 2008), and includes an updated set of strategies for achieving sustainable growth and equitable prosperity in the region. The MPO considers MetroCommon 2050’s goals, objectives, and strategies in its planning and activities.
MetroCommon 2050 will serve as the foundation for land use projections in the MPO’s next LRTP, Destination 2050. The MPO’s next LRTP is currently in the early stages of development and is anticipated to be adopted by the MPO board in the summer of 2023.
The purpose of the Congestion Management Process (CMP) is to monitor and analyze performance of facilities and services, develop strategies for managing congestion based on the results of traffic monitoring, and move those strategies into the implementation stage by providing decision-makers in the region with information and recommendations for improving the transportation system’s performance. The CMP monitors roadways and park-and-ride facilities in the Boston region for safety, congestion, and mobility, and identifies problem locations. The CMP is described in more detail in the Unified Planning Work Program (UPWP). Studies undertaken through the CMP are often the inspiration for discrete studies funded through the UPWP. Needs identified through the MPO’s CMP can also be addressed by projects funded in the TIP.
Every four years, the Boston Region MPO completes a Coordinated Public Transit-Human Services Transportation Plan (CPT-HST), in coordination with the development of the LRTP. The CPT-HST supports improved coordination of transportation for seniors and people with disabilities in the Boston region. This plan also guides transportation providers in the Boston region who are developing proposals to request funding from the Federal Transit Administration’s Section 5310 Program. To be eligible for funding, a proposal must meet a need identified in the CPT-HST. The CPT-HST contains information about
The COVID-19 pandemic has radically shifted the way many people in the Boston region interact with the regional transportation system. The pandemic’s effect on everyday life has had short-term impacts on the system and how people travel and it may have lasting impacts. State and regional partners have advanced immediate changes in the transportation network in response to the situation brought about by the pandemic. Some of the changes may become permanent, such as the expansion of bicycle, bus, sidewalk, and plaza networks, and a reduced emphasis on traditional work trips. As the region recovers from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic and the long-term effects become apparent, state and regional partners’ guidance and priorities are likely to be adjusted.
The Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) includes both permanent members and municipal members who are elected for three-year terms. Details about the MPO’s members are listed below.
The Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) was established under Chapter 25 (An Act Modernizing the Transportation Systems of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts) of the Acts of 2009. MassDOT has four divisions: Highway, Rail and Transit, Aeronautics, and the Registry of Motor Vehicles. The MassDOT Board of Directors, comprised of 11 members appointed by the governor, oversees all four divisions and MassDOT operations and works closely with the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Board of Directors. The MassDOT Board of Directors was expanded to 11 members by the legislature in 2015 based on a recommendation by Governor Baker’s Special Panel, a group of transportation leaders assembled to review structural problems with the MBTA and deliver recommendations for improvements. MassDOT has three seats on the MPO board, including seats for the Highway Division.
The MassDOT Highway Division has jurisdiction over the roadways, bridges, and tunnels that were overseen by the former Massachusetts Highway Department and Massachusetts Turnpike Authority. The Highway Division also has jurisdiction over many bridges and parkways that previously were under the authority of the Department of Conservation and Recreation. The Highway Division is responsible for the design, construction, and maintenance of the Commonwealth’s state highways and bridges. It is also responsible for overseeing traffic safety and engineering activities for the state highway system. These activities include operating the Highway Operations Control Center to ensure safe road and travel conditions.
The MBTA, created in 1964, is a body politic and corporate, and a political subdivision of the Commonwealth. Under the provisions of Chapter 161A of the Massachusetts General Laws, it has the statutory responsibility within its district of operating the public transportation system, preparing the engineering and architectural designs for transit development projects, and constructing and operating transit development projects. The MBTA district comprises 175 communities, including all of the 97 cities and towns of the Boston Region MPO area.
In April 2015, as a result of a plan of action to improve the MBTA, a five-member Fiscal and Management Control Board (FMCB) was created. The FMCB was created to oversee and improve the finances, management, and operations of the MBTA. The FMCB’s authorizing statute called for an initial three-year term, with the option for the board to request that the governor approve a single two-year extension. In 2017, the FMCB’s initial mandate, which would have expired in June 2018, was extended for two years, through June 30, 2020. In 2020, the FMCB’s mandate was extended a second time for an additional period of one year, through June 30, 2021.
Following the expiration of the FMCB’s extended mandate, the MBTA Board of Directors was formed as a permanent replacement to provide oversight for the agency. By statute, the board consists of seven members, including the Secretary of Transportation as an ex-officio member. The MBTA Advisory Board appoints one member who has municipal government experience in the MBTA’s service area and experience in transportation operations, transportation planning, housing policy, urban planning, or public or private finance. The Governor appoints the remaining five board members, which include an MBTA rider and member of an environmental justice population, and a person recommended by the President of the American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations.
The MBTA Advisory Board was created by the Massachusetts Legislature in 1964 through the same legislation that created the MBTA. The Advisory Board consists of representatives of the 175 cities and towns that compose the MBTA’s service area. Cities are represented by either the city manager or mayor, and towns are represented by the chairperson of the board of selectmen. Specific responsibilities of the Advisory Board include reviewing and commenting on the MBTA’s long-range plan, the Program for Mass Transportation; proposed fare increases; the annual MBTA Capital Investment Program; the MBTA’s documentation of net operating investment per passenger; and the MBTA’s operating budget. The MBTA Advisory Board advocates for the transit needs of its member communities and the riding public.
The Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport) has the statutory responsibility under Chapter 465 of the Acts of 1956, as amended, for planning, constructing, owning, and operating such transportation and related facilities as may be necessary for developing and improving commerce in Boston and the surrounding metropolitan area. Massport owns and operates Boston Logan International Airport, the Port of Boston’s Conley Terminal, Flynn Cruiseport Boston, Hanscom Field, Worcester Regional Airport, and various maritime and waterfront properties, including parks in the Boston neighborhoods of East Boston, South Boston, and Charlestown.
The Metropolitan Area Planning Council (MAPC) is the regional planning agency for the Boston region. It is composed of the chief executive officer (or a designee) of each of the cities and towns in the MAPC’s planning region, 21 gubernatorial appointees, and 12 ex-officio members. It has statutory responsibility for comprehensive regional planning in its region under Chapter 40B of the Massachusetts General Laws. It is the Boston Metropolitan Clearinghouse under Section 204 of the Demonstration Cities and Metropolitan Development Act of 1966 and Title VI of the Intergovernmental Cooperation Act of 1968. Also, its region has been designated an economic development district under Title IV of the Public Works and Economic Development Act of 1965, as amended. MAPC’s responsibilities for comprehensive planning encompass the areas of technical assistance to communities, transportation planning, and development of zoning, land use, demographic, and environmental studies. MAPC activities that are funded with federal metropolitan transportation planning dollars are documented in the Boston Region MPO’s Unified Planning Work Program.
The City of Boston, six elected cities (currently Beverly, Everett, Framingham, Newton, Somerville, and Burlington), and six elected towns (currently Acton, Arlington, Brookline, Medway, Norwood, and Rockland) represent the 97 municipalities in the Boston Region MPO area. The City of Boston is a permanent MPO member and has two seats. There is one elected municipal seat for each of the eight MAPC subregions and four seats for at-large elected municipalities (two cities and two towns). The elected at-large municipalities serve staggered three-year terms, as do the eight municipalities representing the MAPC subregions.
The Regional Transportation Advisory Council, the MPO’s citizen advisory group, provides the opportunity for transportation-related organizations, non-MPO member agencies, and municipal representatives to become actively involved in the decision-making processes of the MPO as it develops plans and prioritizes the implementation of transportation projects in the region. The Advisory Council reviews, comments on, and makes recommendations regarding certification documents. It also serves as a forum for providing information on transportation topics in the region, identifying issues, advocating for ways to address the region’s transportation needs, and generating interest among members of the general public in the work of the MPO.
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) and Federal Transit Administration (FTA) participate in the Boston Region MPO in an advisory (nonvoting) capacity, reviewing the Long-Range Transportation Plan, Transportation Improvement Program, and Unified Planning Work Program, and other facets of the MPO’s planning process to ensure compliance with federal planning and programming requirements. These two agencies oversee the highway and transit programs, respectively, of the United States Department of Transportation under pertinent legislation and the provisions of the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation (FAST) Act and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
In addition to the capital programs detailed throughout this document, highway and transit agencies in the Boston region are required to submit operations and maintenance (O&M) information for FFYs 2021–26 to the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) to satisfy federal requirements for the certification of the Transportation Improvement Program (TIP). These O&M tables outline the operating revenues for each agency, including farebox collections; federal, state, and local operating funds; interest income; and other auxiliary revenues from activities such as advertising and leasing. These tables also include a summary of the operating expenses for each agency with both revenues and expenses detailed for each fiscal year. This appendix documents the FFYs 2023–27 TIP O&M information for the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT), Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA), MetroWest Regional Transit Authority (MWRTA), and Cape Ann Transportation Authority (CATA).
Table G-1
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Operations and Maintenance Summary: MassDOT
| Operating and Maintenance Expenditures as of March 2022 | |||||
| Boston Region | |||||
| Program Group/Sub Group | Est SFY 2022 Spending | Est SFY 2023 Spending | Est SFY 2024 Spending | Est SFY 2025 Spending | Est SFY 2026 Spending |
| Part 2: Federal Aid | |||||
| Section I - Federal Aid Maintenance Projects | |||||
| 01 - ADA Retrofits | |||||
| Sidewalk Construction and Repairs | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 02 - Bicycles and pedestrians program | |||||
| Bikeway/Bike Path Construction | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 03 - Bridge | |||||
| Bridge Maintenance | $ 1,248,095 | $ - | $ 2,357,142 | $ - | $ - |
| Bridge Maintenance - Deck Repairs | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Bridge Maintenance - Joints | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Bridge Preservation | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Bridge Reconstruction/Rehab | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Drawbridge Maintenance | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Painting - Structural | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Structures Maintenance | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 04 - Capacity | |||||
| Hwy Reconstr - Added Capacity | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 05 - Facilities | |||||
| Vertical Construction (Ch 149) | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 07 - Intersection Improvements | |||||
| Traffic Signals | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 08 - Interstate Pavement | |||||
| Resurfacing Interstate | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 09 - Intelligent Transportation Systems Program | |||||
| Intelligent Transportation System | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 10 - Non-interstate DOT Pavement Program | |||||
| Milling and Cold Planing | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Resurfacing | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Resurfacing DOT Owned Non-Interstate | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 11 - Roadway Improvements | |||||
| Asbestos Removal | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Catch Basin Cleaning | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Contract Highway Maintenance | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Crack Sealing | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Culvert Maintenance | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Culvert Reconstruction/Rehab | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Drainage | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Guard Rail & Fencing | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Highway Sweeping | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Landscaping | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Mowing and Spraying | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Sewer and Water | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Tree Trimming | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 12 - Roadway Reconstruction | |||||
| Hwy Reconstr - Restr and Rehab | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| 13 - Safety Improvements | |||||
| Electrical | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Impact Attenuators | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Lighting | $ 5,557,056 | $ 9,931 | $ 978,483 | $ - | $ - |
| Pavement Marking | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Safety Improvements | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Sign Installation/Upgrading | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Structural Signing | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Section I Total: | $ 6,805,151 | $ 9,931 | $ 3,335,626 | $ - | $ - |
| Section II - Non Federal Aid Highway Operations - State Operating Budget Funding | |||||
| Snow and Ice Operations & Materials | |||||
| $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | |
| District Maintenance Payroll | |||||
| Mowing, Litter Mgmt, Sight Distance Clearing, Etc. | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Section II Total: | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Grand Total NFA: | $ 6,805,151 | $ 9,931 | $ 3,335,626 | $ - | $ - |
Table G-2
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Operations and Maintenance Summary: MBTA
| Category | FY23-FY27 | FY23 | FY24 | FY25 | FY26 | FY27 |
| Operations and Maintenance Revenues ($M) | ||||||
| Fare Revenue | 2,589 | 472 | 504 | 518 | 533 | 561 |
| Non-Fare Revenue | 521 | 98 | 103 | 105 | 107 | 109 |
| Sales Tax and Local Assessments | 7,754 | 1,459 | 1,504 | 1,549 | 1,596 | 1,645 |
| Additional State Assistance | 635 | 127 | 127 | 127 | 127 | 127 |
| Federal Relief & One-Time Revenue | 437 | 316 | 121 | |||
| Total Revenue | 11,936 | 2,473 | 2,359 | 2,300 | 2,363 | 2,442 |
| Operations and Maintenance Costs ($M) | ||||||
| Wages, Materials, and Services and Contracts | 10,611 | 1,939 | 2,035 | 2,134 | 2,218 | 2,286 |
| Debt Service | 2,904 | 533 | 560 | 571 | 613 | 627 |
| Total Costs | 13,515 | 2,472 | 2,595 | 2,705 | 2,831 | 2,913 |
| Difference Between Revenues and Costs | (1,579) | 0 | (236) | (406) | (467) | (471) |
| 1. FY 2023–FY27 spending and revenue estimates are based on Scenario 2 ridership projections as of the December Annual Pro Forma presentation to the MBTA Board of Directors on December 15, 2021. | ||||||
| 2. Additional state assistance is displayed as part of total revenue. | ||||||
| 3. Federal Relief & One-Time Revenue includes Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act funds, Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2021 (CRRSAA) funds, and American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) funds, along with a planned transfer of Operating Deficiency Reserve funds and Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) reimbursement revenues for COVID-19 expenses. | ||||||
| 4. Federal Relief & One-Time Revenue: The MBTA has an estimated allocation of one-time federal COVID-19 relief funding totaling $1,988 million with $827 million from the CARES Act from March 27, 2020, $301 million from the CRRSAA from December 27, 2020, and a projected $860 million from ARPA from March 11, 2021. | ||||||
| 5. Sales Tax: The dedicated revenues from the state sales tax are equal to whichever is greater, the amount of actual sales tax receipts generated from the statewide sales tax dedicated to the MBTA or a base revenue amount. The annual amount of dedicated sales tax revenues that the MBTA receives is subject to annual upward adjustment to a maximum three percent increase based on a comparison of the percentage increase of inflation to the increase in actual sales tax receipts. Legislation enacted in 2014 increased the base revenue amount in SFY 2015 to $970.6 million and increased the dedicated sales tax revenue amount for the MBTA by an additional $160 million annually. | ||||||
Table G-3
FFYs 2013–27 TIP Operations and Maintenance Summary: MWRTA
| Operating Revenue | actual | actual | actual | per approved budget | projected | projected | projected | projected | projected |
| FY19 | FY20 | FY21 | FY 22 | FY 23 | FY24 | FY25 | FY26 | FY27 | |
| Farebox | $ 607,985 | $ 479,129 | $ 20,701 | $ 442,513 | $ 455,989 | $ 467,389 | $ 479,074 | $ 491,051 | $ 503,327 |
| Section 5339 | |||||||||
| Section 5307 | $ 1,534,066 | $ 922,968 | $ 2,514,930 | $ 2,395,392 | $ 2,395,392 | ||||
| Section 5311 | |||||||||
| CMAQ/TDM | |||||||||
| Cares /Crrsaa/American Rescue Plan | $ 825,000 | $ 2,550,000 | $ 2,453,706 | $ 4,277,394 | $ 3,021,989 | ||||
| Advertising | $ 87,950 | $ 80,250 | $ 78,425 | $ 83,794 | $ 96,425 | $ 98,836 | $ 101,307 | $ 103,839 | $ 106,435 |
| Interest Income | $ 7,168 | $ 5,307 | $ 882 | $ 875 | $ 1,321 | $ 1,354 | |||
| Rental Income | $ 123,844 | $ 108,364 | $ 84,257 | $ 108,000 | $ 84,419 | $ 86,530 | $ 118,000 | $ 118,000 | $ 118,000 |
| Parking Revenue | $ 274,999 | $ 206,328 | $ 200,075 | $ 252,270 | $ 195,873 | $ 200,770 | $ 205,789 | $ 210,934 | $ 216,208 |
| State Operating Assistance | $ 3,542,451 | $ 3,474,631 | $ 3,514,840 | $ 3,939,264 | $ 3,192,206 | $ 3,672,011 | $ 3,763,811 | $ 3,857,907 | $ 3,954,354 |
| Local Assessment | $ 4,078,598 | $ 3,876,600 | $ 3,036,067 | $ 4,072,853 | $ 3,599,300 | $ 3,689,283 | $ 3,781,515 | $ 3,876,053 | $ 3,972,954 |
| Other: (Define) | $ 688,727 | $ 534,505 | $ 391,202 | $ 421,987 | $ 232,805 | $ 238,625 | $ 244,591 | $ 250,705 | $ 256,973 |
| TOTAL | $ 10,945,787 | $ 10,513,083 | $ 9,876,449 | $ 11,775,262 | $ 12,135,734 | $ 11,476,787 | $ 11,209,017 | $ 11,303,881 | $ 11,523,643 |
| Other - Operating (examples) | |||||||||
| Ins. Recoveries, misc. | $ 25,904 | $ 10,624 | $ 3,391 | $ 3,400 | $ 2,258 | $ 2,314 | $ 2,372 | $ 2,431 | $ 2,492 |
| Gain on Sale of Fixed Assets | |||||||||
| ID Income | |||||||||
| Miscellaneous | $ 13,142 | $ 4,283 | |||||||
| Vending | $ 5,254 | $ 4,687 | $ 3,333 | $ 5,254 | $ 2,078 | $ 2,130 | $ 2,183 | $ 2,237 | $ 2,293 |
| Fuel Tax Rebate | $ 53,733 | $ 31,334 | $ 19,937 | $ 20,000 | $ 18,848 | $ 19,319 | $ 19,802 | $ 20,297 | $ 20,805 |
| Vehicle Repair Reimbursement | $ 68,892 | $ 74,162 | $ 49,501 | $ 68,892 | $ 48,943 | $ 50,166 | $ 51,420 | $ 52,706 | $ 54,023 |
| MAPC Reimbursement | $ - | ||||||||
| HST Revenue | $ 1,251 | ||||||||
| CDL Workforce Development | $ 17,500 | ||||||||
| Hudson Shuttle | $ - | ||||||||
| Mass Bay Community College Shuttle | $ 212,789 | $ 176,674 | $ 212,789 | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | ||
| Travel Training Initiative | $ 84,262 | $ 76,048 | $ 78,594 | $ 48,867 | $ 100,000 | $ 102,500 | $ 105,063 | $ 107,689 | $ 110,381 |
| 5310 ADA Above and Beyond | $ 172,038 | ||||||||
| Solar Renew Energy Credit Rev | $ 260 | $ 52,770 | $ 50,762 | $ 52,284 | $ 49,361 | $ 50,595 | $ 51,860 | $ 53,156 | $ 54,485 |
| First Mile Last Mile Operating Grant | $ 11,653 | ||||||||
| Rte 20 Operating Grant | $ 3,603 | ||||||||
| Mass Dot Shuttle Reimbursement | $ 6,200 | $ 66,375 | |||||||
| COA Training Revenue | $ 7,377 | $ 11,548 | $ 8,843 | $ 10,500 | $ 11,318 | $ 11,601 | $ 11,891 | $ 12,188 | $ 12,493 |
| Rebate Income | $ 4,869 | ||||||||
| MW Health Foundation Training Grant | $ 26,000 | ||||||||
| MAPC Grant Revenue | $ 176,842 | ||||||||
| Other Operating Revenue | $ 688,727 | $ 534,505 | $ 391,202 | $ 421,987 | $ 232,805 | $ 238,625 | $ 244,591 | $ 250,705 | $ 256,973 |
| Operating Expenses | $ 10,945,787 | $ 10,513,083 | $ 9,876,449 | $ 11,818,383 | $ 12,135,734 | $ 11,476,787 | $ 11,209,017 | $ 11,303,881 | $ 11,523,643 |
Table G-4
FFYs 2023–27 TIP Operations and Maintenance Summary: CATA
| Previous (Actual) |
Current (Budgeted) | Year Two (Projected) | Year Three (Projected) | Year Four (Projected) | Year Five (Projected) | |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | |
| Farebox | $ 66,825 | $ 120,000 | $ 190,000 | $ 190,000 | $ 190,000 | $ 190,000 |
| Section 5307 | $ 144,821 | $ 250,992 | $ 501,984 | $ 514,534 | $ 527,397 | $ 540,582 |
| Section 5311 | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| CMAQ/TDM | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Fully Funded | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| MassDOT Discretionary Grant | $ - | $ 96,680 | $ - | $ - | $ - | $ - |
| Community Transit Grant | $ 46,874 | $ 97,024 | $ 50,000 | $ 50,000 | $ 50,000 | $ 50,000 |
| Auxiliary Revenues * | $ 2,822,586 | $ 762,156 | $ 500,000 | $ 500,000 | $ 500,000 | $ 500,000 |
| Interest Income | $ 10,641 | $ 2,000 | $ 2,000 | $ 2,000 | $ 2,000 | $ 2,000 |
| State Contract Assistance ** | $ 1,465,569 | $ 1,506,637 | $ 1,544,303 | $ 1,582,910 | $ 1,622,483 | $ 1,663,045 |
| Local Assessment | $ 775,531 | $ 795,480 | $ 815,367 | $ 835,751 | $ 856,645 | $ 878,061 |
| Total | $ 5,332,847 | $ 3,630,969 | $ 3,603,654 | $ 3,675,195 | $ 3,748,525 | $ 3,823,688 |
| Operating Expenses *** | Previous | Current | Year Two | Year Three | Year Four | Year Five |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | |
| $ 5,332,847 | $ 3,630,969 | $ 3,603,654 | $ 3,675,195 | $ 3,748,525 | $ 3,823,688 | |
| * Auxiliary Revenues include contract transportation (HST, Beverly Shuttle, adult day care, etc), rental income, advertising | ||||||
| ** Operating Assistance provided by the state | ||||||
| *** Description of Operating Expenses: Salaries and wages; fringe benefit; legal, accounting, and professional services; promotional/marketing; insurance; equipment; non-capitalized maintenace/repair; fuel costs; tire costs; office supplies and equipment; interest expense; management fees; travel and training; an dother miscellaneous expense items | ||||||